Switch to an ewma fork that allows setting the warmup samples #
This commit is contained in:
parent
9ec8a35468
commit
7956ba5b10
|
|
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ package main
|
|||
import (
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/VividCortex/ewma"
|
||||
"github.com/jedisct1/ewma"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,8 +15,8 @@ import (
|
|||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/VividCortex/ewma"
|
||||
"github.com/jedisct1/dlog"
|
||||
"github.com/jedisct1/ewma"
|
||||
clocksmith "github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith"
|
||||
stamps "github.com/jedisct1/go-dnsstamps"
|
||||
"github.com/miekg/dns"
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
2
go.mod
2
go.mod
|
|
@ -4,13 +4,13 @@ go 1.17
|
|||
|
||||
require (
|
||||
github.com/BurntSushi/toml v1.0.0
|
||||
github.com/VividCortex/ewma v1.2.0
|
||||
github.com/coreos/go-systemd v0.0.0-20191104093116-d3cd4ed1dbcf
|
||||
github.com/dchest/safefile v0.0.0-20151022103144-855e8d98f185
|
||||
github.com/hashicorp/go-immutable-radix v1.3.1
|
||||
github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru v0.5.4
|
||||
github.com/hectane/go-acl v0.0.0-20190604041725-da78bae5fc95
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-dnsstamps v0.0.0-20210810213811-61cc83d2a354
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-hpke-compact v0.0.0-20210930135406-0763750339f0
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
4
go.sum
4
go.sum
|
|
@ -52,8 +52,6 @@ github.com/OneOfOne/xxhash v1.2.2/go.mod h1:HSdplMjZKSmBqAxg5vPj2TmRDmfkzw+cTzAE
|
|||
github.com/OpenPeeDeeP/depguard v1.0.1 h1:VlW4R6jmBIv3/u1JNlawEvJMM4J+dPORPaZasQee8Us=
|
||||
github.com/OpenPeeDeeP/depguard v1.0.1/go.mod h1:xsIw86fROiiwelg+jB2uM9PiKihMMmUx/1V+TNhjQvM=
|
||||
github.com/StackExchange/wmi v0.0.0-20190523213315-cbe66965904d/go.mod h1:3eOhrUMpNV+6aFIbp5/iudMxNCF27Vw2OZgy4xEx0Fg=
|
||||
github.com/VividCortex/ewma v1.2.0 h1:f58SaIzcDXrSy3kWaHNvuJgJ3Nmz59Zji6XoJR/q1ow=
|
||||
github.com/VividCortex/ewma v1.2.0/go.mod h1:nz4BbCtbLyFDeC9SUHbtcT5644juEuWfUAUnGx7j5l4=
|
||||
github.com/alecthomas/template v0.0.0-20160405071501-a0175ee3bccc/go.mod h1:LOuyumcjzFXgccqObfd/Ljyb9UuFJ6TxHnclSeseNhc=
|
||||
github.com/alecthomas/template v0.0.0-20190718012654-fb15b899a751/go.mod h1:LOuyumcjzFXgccqObfd/Ljyb9UuFJ6TxHnclSeseNhc=
|
||||
github.com/alecthomas/units v0.0.0-20151022065526-2efee857e7cf/go.mod h1:ybxpYRFXyAe+OPACYpWeL0wqObRcbAqCMya13uyzqw0=
|
||||
|
|
@ -353,6 +351,8 @@ github.com/inconshreveable/mousetrap v1.0.0 h1:Z8tu5sraLXCXIcARxBp/8cbvlwVa7Z1NH
|
|||
github.com/inconshreveable/mousetrap v1.0.0/go.mod h1:PxqpIevigyE2G7u3NXJIT2ANytuPF1OarO4DADm73n8=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f h1:XICcphytniQKdtd4FGrK0b1ERzS7FBvFtVUCReSppmU=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f/go.mod h1:35aII3PkLMvmc8daWy0vcZXDU+a40lJczHHTFRJmnvw=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9 h1:U5QPCoM1KkMJ9RfEfP0joKNwwwIHG1oP9RzjvQTuh98=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9/go.mod h1:qCWdft6DX9wxyNsUS+sxS44UkxE7eQnNtBttTWoW0cU=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868 h1:QZ79mRbNwYYYmiVjyv+X0NKgYE6nyN1yo3gtEFdzpiE=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868/go.mod h1:SAINchklztk2jcLWJ4bpNF4KnwDUSUTX+cJbspWC2Rw=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-dnsstamps v0.0.0-20210810213811-61cc83d2a354 h1:sIB9mDh2spQdh95jeXF2h9uSNtObbehD0YbDCzmqbM8=
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.*.sw?
|
||||
/coverage.txt
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"settingsInheritedFrom": "VividCortex/whitesource-config@master"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|||
The MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
|
||||
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,145 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# EWMA
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/VividCortex/ewma)
|
||||

|
||||
[](https://codecov.io/gh/VividCortex/ewma)
|
||||
|
||||
This repo provides Exponentially Weighted Moving Average algorithms, or EWMAs for short, [based on our
|
||||
Quantifying Abnormal Behavior talk](https://vividcortex.com/blog/2013/07/23/a-fast-go-library-for-exponential-moving-averages/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Exponentially Weighted Moving Average
|
||||
|
||||
An exponentially weighted moving average is a way to continuously compute a type of
|
||||
average for a series of numbers, as the numbers arrive. After a value in the series is
|
||||
added to the average, its weight in the average decreases exponentially over time. This
|
||||
biases the average towards more recent data. EWMAs are useful for several reasons, chiefly
|
||||
their inexpensive computational and memory cost, as well as the fact that they represent
|
||||
the recent central tendency of the series of values.
|
||||
|
||||
The EWMA algorithm requires a decay factor, alpha. The larger the alpha, the more the average
|
||||
is biased towards recent history. The alpha must be between 0 and 1, and is typically
|
||||
a fairly small number, such as 0.04. We will discuss the choice of alpha later.
|
||||
|
||||
The algorithm works thus, in pseudocode:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Multiply the next number in the series by alpha.
|
||||
2. Multiply the current value of the average by 1 minus alpha.
|
||||
3. Add the result of steps 1 and 2, and store it as the new current value of the average.
|
||||
4. Repeat for each number in the series.
|
||||
|
||||
There are special-case behaviors for how to initialize the current value, and these vary
|
||||
between implementations. One approach is to start with the first value in the series;
|
||||
another is to average the first 10 or so values in the series using an arithmetic average,
|
||||
and then begin the incremental updating of the average. Each method has pros and cons.
|
||||
|
||||
It may help to look at it pictorially. Suppose the series has five numbers, and we choose
|
||||
alpha to be 0.50 for simplicity. Here's the series, with numbers in the neighborhood of 300.
|
||||
|
||||
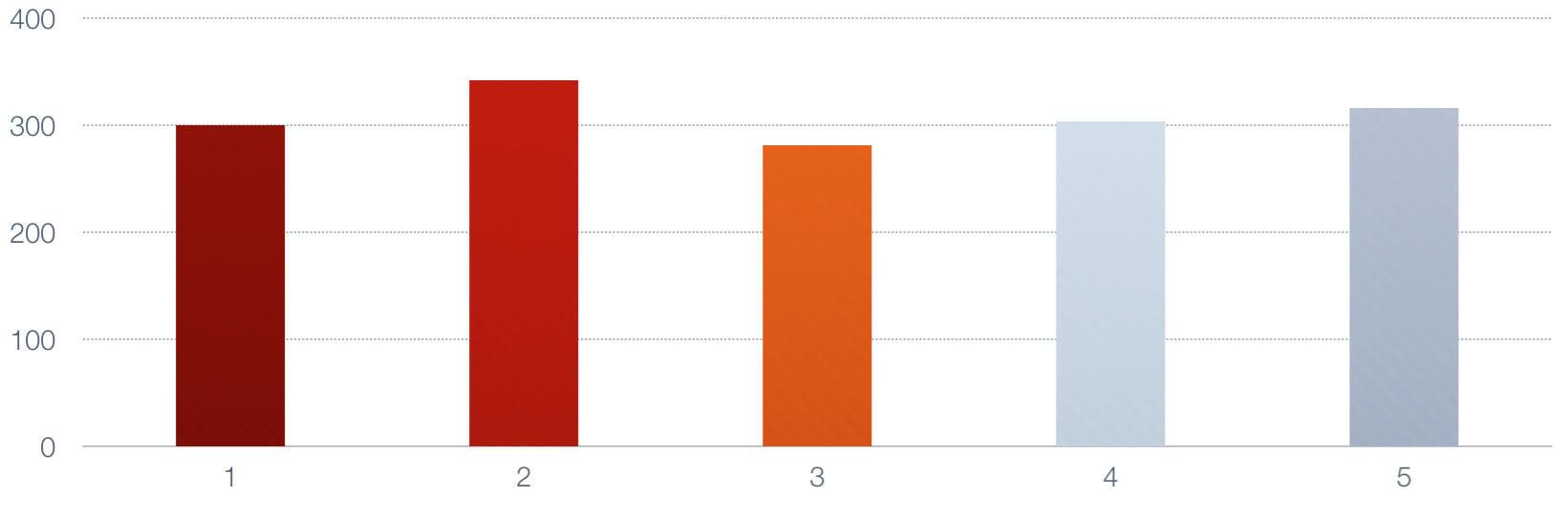
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's take the moving average of those numbers. First we set the average to the value
|
||||
of the first number.
|
||||
|
||||
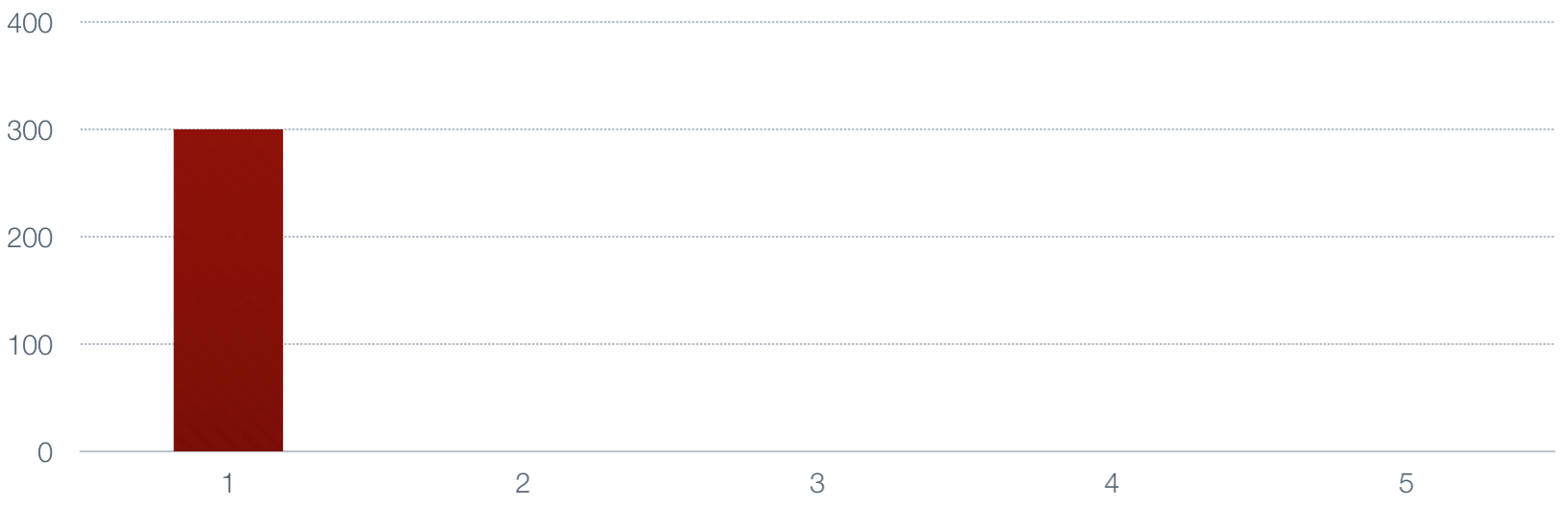
|
||||
|
||||
Next we multiply the next number by alpha, multiply the current value by 1-alpha, and add
|
||||
them to generate a new value.
|
||||
|
||||
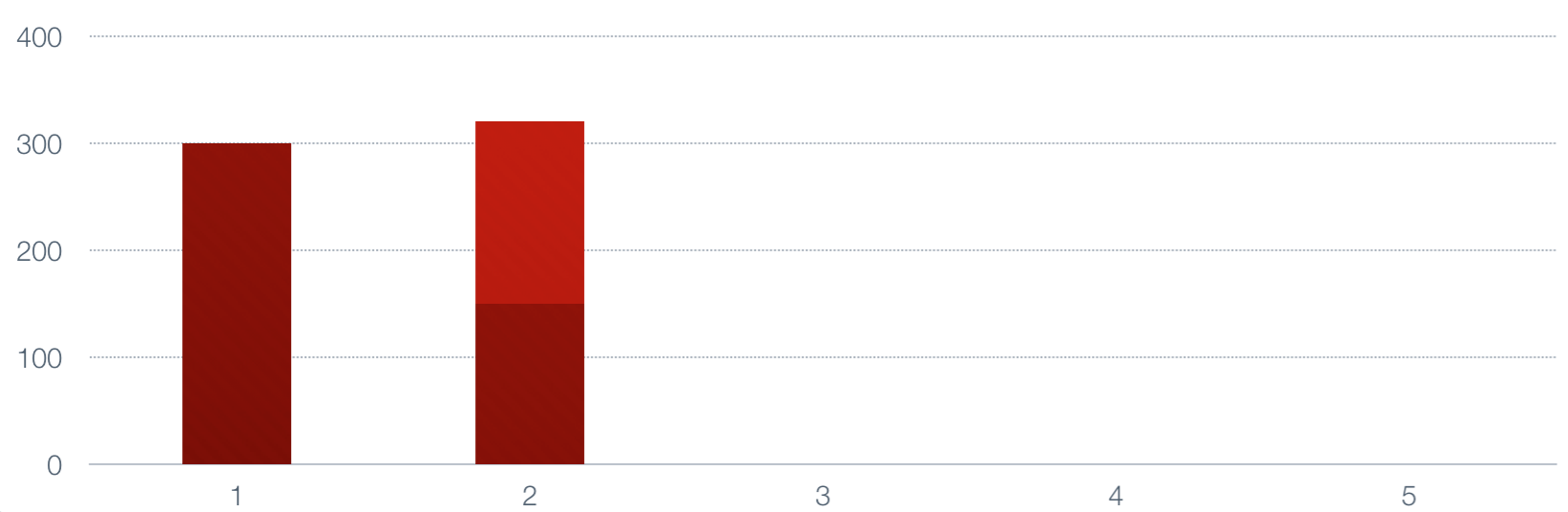
|
||||
|
||||
This continues until we are done.
|
||||
|
||||
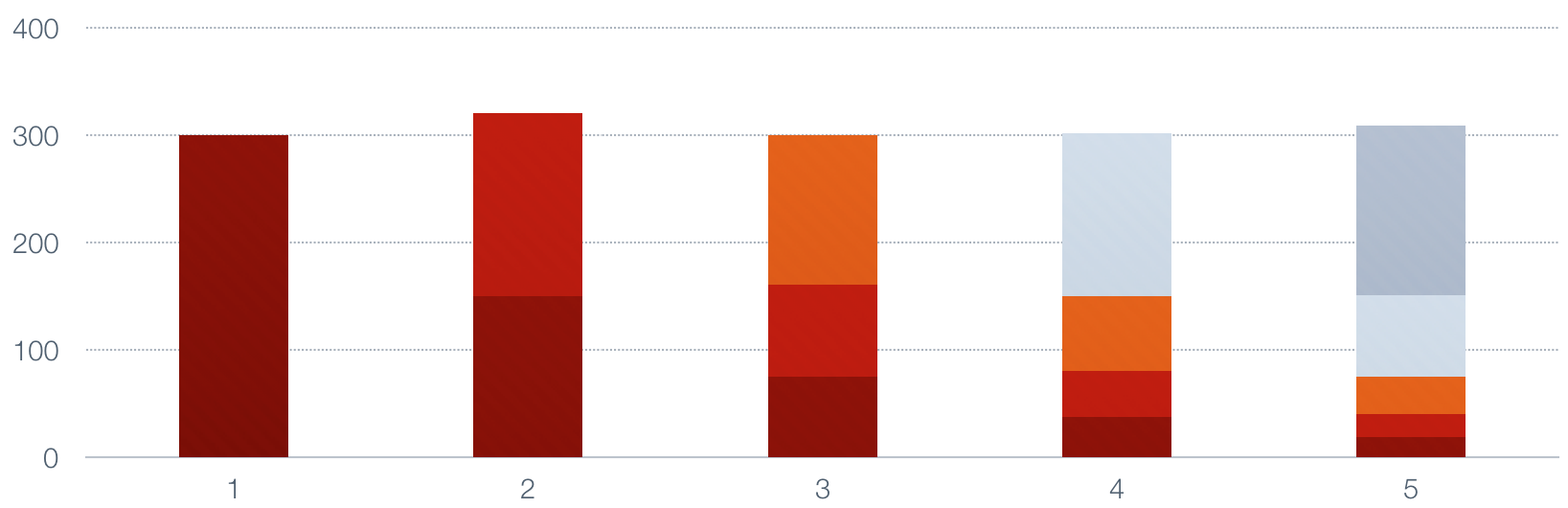
|
||||
|
||||
Notice how each of the values in the series decays by half each time a new value
|
||||
is added, and the top of the bars in the lower portion of the image represents the
|
||||
size of the moving average. It is a smoothed, or low-pass, average of the original
|
||||
series.
|
||||
|
||||
For further reading, see [Exponentially weighted moving average](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moving_average#Exponential_moving_average) on wikipedia.
|
||||
|
||||
### Choosing Alpha
|
||||
|
||||
Consider a fixed-size sliding-window moving average (not an exponentially weighted moving average)
|
||||
that averages over the previous N samples. What is the average age of each sample? It is N/2.
|
||||
|
||||
Now suppose that you wish to construct a EWMA whose samples have the same average age. The formula
|
||||
to compute the alpha required for this is: alpha = 2/(N+1). Proof is in the book
|
||||
"Production and Operations Analysis" by Steven Nahmias.
|
||||
|
||||
So, for example, if you have a time-series with samples once per second, and you want to get the
|
||||
moving average over the previous minute, you should use an alpha of .032786885. This, by the way,
|
||||
is the constant alpha used for this repository's SimpleEWMA.
|
||||
|
||||
### Implementations
|
||||
|
||||
This repository contains two implementations of the EWMA algorithm, with different properties.
|
||||
|
||||
The implementations all conform to the MovingAverage interface, and the constructor returns
|
||||
that type.
|
||||
|
||||
Current implementations assume an implicit time interval of 1.0 between every sample added.
|
||||
That is, the passage of time is treated as though it's the same as the arrival of samples.
|
||||
If you need time-based decay when samples are not arriving precisely at set intervals, then
|
||||
this package will not support your needs at present.
|
||||
|
||||
#### SimpleEWMA
|
||||
|
||||
A SimpleEWMA is designed for low CPU and memory consumption. It **will** have different behavior than the VariableEWMA
|
||||
for multiple reasons. It has no warm-up period and it uses a constant
|
||||
decay. These properties let it use less memory. It will also behave
|
||||
differently when it's equal to zero, which is assumed to mean
|
||||
uninitialized, so if a value is likely to actually become zero over time,
|
||||
then any non-zero value will cause a sharp jump instead of a small change.
|
||||
|
||||
#### VariableEWMA
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike SimpleEWMA, this supports a custom age which must be stored, and thus uses more memory.
|
||||
It also has a "warmup" time when you start adding values to it. It will report a value of 0.0
|
||||
until you have added the required number of samples to it. It uses some memory to store the
|
||||
number of samples added to it. As a result it uses a little over twice the memory of SimpleEWMA.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### API Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
View the GoDoc generated documentation [here](http://godoc.org/github.com/VividCortex/ewma).
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/VividCortex/ewma"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
samples := [100]float64{
|
||||
4599, 5711, 4746, 4621, 5037, 4218, 4925, 4281, 5207, 5203, 5594, 5149,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
e := ewma.NewMovingAverage() //=> Returns a SimpleEWMA if called without params
|
||||
a := ewma.NewMovingAverage(5) //=> returns a VariableEWMA with a decay of 2 / (5 + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
for _, f := range samples {
|
||||
e.Add(f)
|
||||
a.Add(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
e.Value() //=> 13.577404704631077
|
||||
a.Value() //=> 1.5806140565521463e-12
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
We only accept pull requests for minor fixes or improvements. This includes:
|
||||
|
||||
* Small bug fixes
|
||||
* Typos
|
||||
* Documentation or comments
|
||||
|
||||
Please open issues to discuss new features. Pull requests for new features will be rejected,
|
||||
so we recommend forking the repository and making changes in your fork for your use case.
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
This repository is Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
It is licensed under the MIT license. Please see the LICENSE file for applicable license terms.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
|
|||
coverage:
|
||||
status:
|
||||
project:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
threshold: 15%
|
||||
patch: off
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package ewma implements exponentially weighted moving averages.
|
||||
package ewma
|
||||
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Please see the LICENSE file for applicable license terms.
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// By default, we average over a one-minute period, which means the average
|
||||
// age of the metrics in the period is 30 seconds.
|
||||
AVG_METRIC_AGE float64 = 30.0
|
||||
|
||||
// The formula for computing the decay factor from the average age comes
|
||||
// from "Production and Operations Analysis" by Steven Nahmias.
|
||||
DECAY float64 = 2 / (float64(AVG_METRIC_AGE) + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
// For best results, the moving average should not be initialized to the
|
||||
// samples it sees immediately. The book "Production and Operations
|
||||
// Analysis" by Steven Nahmias suggests initializing the moving average to
|
||||
// the mean of the first 10 samples. Until the VariableEwma has seen this
|
||||
// many samples, it is not "ready" to be queried for the value of the
|
||||
// moving average. This adds some memory cost.
|
||||
WARMUP_SAMPLES uint8 = 10
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// MovingAverage is the interface that computes a moving average over a time-
|
||||
// series stream of numbers. The average may be over a window or exponentially
|
||||
// decaying.
|
||||
type MovingAverage interface {
|
||||
Add(float64)
|
||||
Value() float64
|
||||
Set(float64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMovingAverage constructs a MovingAverage that computes an average with the
|
||||
// desired characteristics in the moving window or exponential decay. If no
|
||||
// age is given, it constructs a default exponentially weighted implementation
|
||||
// that consumes minimal memory. The age is related to the decay factor alpha
|
||||
// by the formula given for the DECAY constant. It signifies the average age
|
||||
// of the samples as time goes to infinity.
|
||||
func NewMovingAverage(age ...float64) MovingAverage {
|
||||
if len(age) == 0 || age[0] == AVG_METRIC_AGE {
|
||||
return new(SimpleEWMA)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &VariableEWMA{
|
||||
decay: 2 / (age[0] + 1),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A SimpleEWMA represents the exponentially weighted moving average of a
|
||||
// series of numbers. It WILL have different behavior than the VariableEWMA
|
||||
// for multiple reasons. It has no warm-up period and it uses a constant
|
||||
// decay. These properties let it use less memory. It will also behave
|
||||
// differently when it's equal to zero, which is assumed to mean
|
||||
// uninitialized, so if a value is likely to actually become zero over time,
|
||||
// then any non-zero value will cause a sharp jump instead of a small change.
|
||||
// However, note that this takes a long time, and the value may just
|
||||
// decays to a stable value that's close to zero, but which won't be mistaken
|
||||
// for uninitialized. See http://play.golang.org/p/litxBDr_RC for example.
|
||||
type SimpleEWMA struct {
|
||||
// The current value of the average. After adding with Add(), this is
|
||||
// updated to reflect the average of all values seen thus far.
|
||||
value float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add adds a value to the series and updates the moving average.
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Add(value float64) {
|
||||
if e.value == 0 { // this is a proxy for "uninitialized"
|
||||
e.value = value
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
e.value = (value * DECAY) + (e.value * (1 - DECAY))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the current value of the moving average.
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Value() float64 {
|
||||
return e.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set sets the EWMA's value.
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Set(value float64) {
|
||||
e.value = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VariableEWMA represents the exponentially weighted moving average of a series of
|
||||
// numbers. Unlike SimpleEWMA, it supports a custom age, and thus uses more memory.
|
||||
type VariableEWMA struct {
|
||||
// The multiplier factor by which the previous samples decay.
|
||||
decay float64
|
||||
// The current value of the average.
|
||||
value float64
|
||||
// The number of samples added to this instance.
|
||||
count uint8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add adds a value to the series and updates the moving average.
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Add(value float64) {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case e.count < WARMUP_SAMPLES:
|
||||
e.count++
|
||||
e.value += value
|
||||
case e.count == WARMUP_SAMPLES:
|
||||
e.count++
|
||||
e.value = e.value / float64(WARMUP_SAMPLES)
|
||||
e.value = (value * e.decay) + (e.value * (1 - e.decay))
|
||||
default:
|
||||
e.value = (value * e.decay) + (e.value * (1 - e.decay))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the current value of the average, or 0.0 if the series hasn't
|
||||
// warmed up yet.
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Value() float64 {
|
||||
if e.count <= WARMUP_SAMPLES {
|
||||
return 0.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return e.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set sets the EWMA's value.
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Set(value float64) {
|
||||
e.value = value
|
||||
if e.count <= WARMUP_SAMPLES {
|
||||
e.count = WARMUP_SAMPLES + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,9 +14,6 @@ github.com/Masterminds/semver
|
|||
# github.com/OpenPeeDeeP/depguard v1.0.1
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.13
|
||||
github.com/OpenPeeDeeP/depguard
|
||||
# github.com/VividCortex/ewma v1.2.0
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.12
|
||||
github.com/VividCortex/ewma
|
||||
# github.com/alexkohler/prealloc v1.0.0
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.15
|
||||
github.com/alexkohler/prealloc/pkg
|
||||
|
|
@ -251,6 +248,9 @@ github.com/inconshreveable/mousetrap
|
|||
# github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.17
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog
|
||||
# github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.12
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma
|
||||
# github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868
|
||||
## explicit
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue