Switch to lifenjoiner's ewma variant
This commit is contained in:
parent
c08852feb1
commit
034d3bd424
|
|
@ -3,17 +3,17 @@ package main
|
|||
import (
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/jedisct1/ewma"
|
||||
"github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type QuestionSizeEstimator struct {
|
||||
sync.RWMutex
|
||||
minQuestionSize int
|
||||
ewma ewma.MovingAverage
|
||||
ewma *ewma.EWMA
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewQuestionSizeEstimator() QuestionSizeEstimator {
|
||||
return QuestionSizeEstimator{minQuestionSize: InitialMinQuestionSize, ewma: &ewma.SimpleEWMA{}}
|
||||
return QuestionSizeEstimator{minQuestionSize: InitialMinQuestionSize, ewma: &ewma.EWMA{}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (questionSizeEstimator *QuestionSizeEstimator) MinQuestionSize() int {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,9 +16,9 @@ import (
|
|||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/jedisct1/dlog"
|
||||
"github.com/jedisct1/ewma"
|
||||
clocksmith "github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith"
|
||||
stamps "github.com/jedisct1/go-dnsstamps"
|
||||
"github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma"
|
||||
"github.com/miekg/dns"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/crypto/ed25519"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ type DOHClientCreds struct {
|
|||
type ServerInfo struct {
|
||||
DOHClientCreds DOHClientCreds
|
||||
lastActionTS time.Time
|
||||
rtt ewma.MovingAverage
|
||||
rtt *ewma.EWMA
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
HostName string
|
||||
UDPAddr *net.UDPAddr
|
||||
|
|
@ -194,7 +194,6 @@ func (serversInfo *ServersInfo) refreshServer(proxy *Proxy, name string, stamp s
|
|||
dlog.Fatalf("[%s] != [%s]", name, newServer.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
newServer.rtt = ewma.NewMovingAverage(RTTEwmaDecay)
|
||||
newServer.rtt.SetWarmupSamples(1)
|
||||
newServer.rtt.Set(float64(newServer.initialRtt))
|
||||
isNew = true
|
||||
serversInfo.Lock()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
6
go.mod
6
go.mod
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,6 @@ require (
|
|||
github.com/hashicorp/golang-lru v0.5.4
|
||||
github.com/hectane/go-acl v0.0.0-20190604041725-da78bae5fc95
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-dnsstamps v0.0.0-20210810213811-61cc83d2a354
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-hpke-compact v0.0.0-20210930135406-0763750339f0
|
||||
|
|
@ -18,6 +17,7 @@ require (
|
|||
github.com/jedisct1/xsecretbox v0.0.0-20210927135450-ebe41aef7bef
|
||||
github.com/k-sone/critbitgo v1.4.0
|
||||
github.com/kardianos/service v1.2.1
|
||||
github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma v0.0.0-20210320054258-4f227d7eb8a2
|
||||
github.com/miekg/dns v1.1.46
|
||||
github.com/powerman/check v1.6.0
|
||||
golang.org/x/crypto v0.0.0-20220214200702-86341886e292
|
||||
|
|
@ -152,9 +152,9 @@ require (
|
|||
github.com/ultraware/whitespace v0.0.4 // indirect
|
||||
github.com/uudashr/gocognit v1.0.1 // indirect
|
||||
github.com/yeya24/promlinter v0.1.0 // indirect
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.5.1 // indirect
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.4.2 // indirect
|
||||
golang.org/x/text v0.3.7 // indirect
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.9 // indirect
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.6-0.20210726203631-07bc1bf47fb2 // indirect
|
||||
golang.org/x/xerrors v0.0.0-20200804184101-5ec99f83aff1 // indirect
|
||||
google.golang.org/genproto v0.0.0-20200707001353-8e8330bf89df // indirect
|
||||
google.golang.org/grpc v1.38.0 // indirect
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
13
go.sum
13
go.sum
|
|
@ -351,8 +351,6 @@ github.com/inconshreveable/mousetrap v1.0.0 h1:Z8tu5sraLXCXIcARxBp/8cbvlwVa7Z1NH
|
|||
github.com/inconshreveable/mousetrap v1.0.0/go.mod h1:PxqpIevigyE2G7u3NXJIT2ANytuPF1OarO4DADm73n8=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f h1:XICcphytniQKdtd4FGrK0b1ERzS7FBvFtVUCReSppmU=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f/go.mod h1:35aII3PkLMvmc8daWy0vcZXDU+a40lJczHHTFRJmnvw=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9 h1:U5QPCoM1KkMJ9RfEfP0joKNwwwIHG1oP9RzjvQTuh98=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9/go.mod h1:qCWdft6DX9wxyNsUS+sxS44UkxE7eQnNtBttTWoW0cU=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868 h1:QZ79mRbNwYYYmiVjyv+X0NKgYE6nyN1yo3gtEFdzpiE=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868/go.mod h1:SAINchklztk2jcLWJ4bpNF4KnwDUSUTX+cJbspWC2Rw=
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-dnsstamps v0.0.0-20210810213811-61cc83d2a354 h1:sIB9mDh2spQdh95jeXF2h9uSNtObbehD0YbDCzmqbM8=
|
||||
|
|
@ -424,6 +422,8 @@ github.com/letsencrypt/pkcs11key/v4 v4.0.0/go.mod h1:EFUvBDay26dErnNb70Nd0/VW3tJ
|
|||
github.com/lib/pq v1.0.0/go.mod h1:5WUZQaWbwv1U+lTReE5YruASi9Al49XbQIvNi/34Woo=
|
||||
github.com/lib/pq v1.8.0/go.mod h1:AlVN5x4E4T544tWzH6hKfbfQvm3HdbOxrmggDNAPY9o=
|
||||
github.com/lib/pq v1.9.0/go.mod h1:AlVN5x4E4T544tWzH6hKfbfQvm3HdbOxrmggDNAPY9o=
|
||||
github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma v0.0.0-20210320054258-4f227d7eb8a2 h1:eD3+F7WMC7wryFGBrLSyzoRqK+kR7nCT/9VT2E3XJzc=
|
||||
github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma v0.0.0-20210320054258-4f227d7eb8a2/go.mod h1:SJvYtJnDKXqTrIvyRocCJmuNuM3bUb4krn9UbZXj+tw=
|
||||
github.com/logrusorgru/aurora v0.0.0-20181002194514-a7b3b318ed4e/go.mod h1:7rIyQOR62GCctdiQpZ/zOJlFyk6y+94wXzv6RNZgaR4=
|
||||
github.com/magiconair/properties v1.8.0/go.mod h1:PppfXfuXeibc/6YijjN8zIbojt8czPbwD3XqdrwzmxQ=
|
||||
github.com/magiconair/properties v1.8.1 h1:ZC2Vc7/ZFkGmsVC9KvOjumD+G5lXy2RtTKyzRKO2BQ4=
|
||||
|
|
@ -693,7 +693,6 @@ github.com/yuin/goldmark v1.1.27/go.mod h1:3hX8gzYuyVAZsxl0MRgGTJEmQBFcNTphYh9de
|
|||
github.com/yuin/goldmark v1.1.32/go.mod h1:3hX8gzYuyVAZsxl0MRgGTJEmQBFcNTphYh9decYSb74=
|
||||
github.com/yuin/goldmark v1.2.1/go.mod h1:3hX8gzYuyVAZsxl0MRgGTJEmQBFcNTphYh9decYSb74=
|
||||
github.com/yuin/goldmark v1.3.5/go.mod h1:mwnBkeHKe2W/ZEtQ+71ViKU8L12m81fl3OWwC1Zlc8k=
|
||||
github.com/yuin/goldmark v1.4.1/go.mod h1:mwnBkeHKe2W/ZEtQ+71ViKU8L12m81fl3OWwC1Zlc8k=
|
||||
go.etcd.io/bbolt v1.3.2/go.mod h1:IbVyRI1SCnLcuJnV2u8VeU0CEYM7e686BmAb1XKL+uU=
|
||||
go.etcd.io/bbolt v1.3.3/go.mod h1:IbVyRI1SCnLcuJnV2u8VeU0CEYM7e686BmAb1XKL+uU=
|
||||
go.etcd.io/bbolt v1.3.4/go.mod h1:G5EMThwa9y8QZGBClrRx5EY+Yw9kAhnjy3bSjsnlVTQ=
|
||||
|
|
@ -759,9 +758,8 @@ golang.org/x/mod v0.2.0/go.mod h1:s0Qsj1ACt9ePp/hMypM3fl4fZqREWJwdYDEqhRiZZUA=
|
|||
golang.org/x/mod v0.3.0/go.mod h1:s0Qsj1ACt9ePp/hMypM3fl4fZqREWJwdYDEqhRiZZUA=
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.4.0/go.mod h1:s0Qsj1ACt9ePp/hMypM3fl4fZqREWJwdYDEqhRiZZUA=
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.4.1/go.mod h1:s0Qsj1ACt9ePp/hMypM3fl4fZqREWJwdYDEqhRiZZUA=
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.4.2 h1:Gz96sIWK3OalVv/I/qNygP42zyoKp3xptRVCWRFEBvo=
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.4.2/go.mod h1:s0Qsj1ACt9ePp/hMypM3fl4fZqREWJwdYDEqhRiZZUA=
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.5.1 h1:OJxoQ/rynoF0dcCdI7cLPktw/hR2cueqYfjm43oqK38=
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod v0.5.1/go.mod h1:5OXOZSfqPIIbmVBIIKWRFfZjPR0E5r58TLhUjH0a2Ro=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20180724234803-3673e40ba225/go.mod h1:mL1N/T3taQHkDXs73rZJwtUhF3w3ftmwwsq0BUmARs4=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20180826012351-8a410e7b638d/go.mod h1:mL1N/T3taQHkDXs73rZJwtUhF3w3ftmwwsq0BUmARs4=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20180906233101-161cd47e91fd/go.mod h1:mL1N/T3taQHkDXs73rZJwtUhF3w3ftmwwsq0BUmARs4=
|
||||
|
|
@ -804,7 +802,6 @@ golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20201202161906-c7110b5ffcbb/go.mod h1:sp8m0HH+o8qH0wwXwY
|
|||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20210226172049-e18ecbb05110/go.mod h1:m0MpNAwzfU5UDzcl9v0D8zg8gWTRqZa9RBIspLL5mdg=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20210405180319-a5a99cb37ef4/go.mod h1:p54w0d4576C0XHj96bSt6lcn1PtDYWL6XObtHCRCNQM=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20210726213435-c6fcb2dbf985/go.mod h1:9nx3DQGgdP8bBQD5qxJ1jj9UTztislL4KSBs9R2vV5Y=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20211015210444-4f30a5c0130f/go.mod h1:9nx3DQGgdP8bBQD5qxJ1jj9UTztislL4KSBs9R2vV5Y=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20211112202133-69e39bad7dc2/go.mod h1:9nx3DQGgdP8bBQD5qxJ1jj9UTztislL4KSBs9R2vV5Y=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20220127200216-cd36cc0744dd h1:O7DYs+zxREGLKzKoMQrtrEacpb0ZVXA5rIwylE2Xchk=
|
||||
golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20220127200216-cd36cc0744dd/go.mod h1:CfG3xpIq0wQ8r1q4Su4UZFWDARRcnwPjda9FqA0JpMk=
|
||||
|
|
@ -884,7 +881,6 @@ golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20210615035016-665e8c7367d1/go.mod h1:oPkhp1MJrh7nUepCBc
|
|||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20210616094352-59db8d763f22/go.mod h1:oPkhp1MJrh7nUepCBck5+mAzfO9JrbApNNgaTdGDITg=
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20210630005230-0f9fa26af87c/go.mod h1:oPkhp1MJrh7nUepCBck5+mAzfO9JrbApNNgaTdGDITg=
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20210927094055-39ccf1dd6fa6/go.mod h1:oPkhp1MJrh7nUepCBck5+mAzfO9JrbApNNgaTdGDITg=
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20211019181941-9d821ace8654/go.mod h1:oPkhp1MJrh7nUepCBck5+mAzfO9JrbApNNgaTdGDITg=
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20211216021012-1d35b9e2eb4e/go.mod h1:oPkhp1MJrh7nUepCBck5+mAzfO9JrbApNNgaTdGDITg=
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20220209214540-3681064d5158 h1:rm+CHSpPEEW2IsXUib1ThaHIjuBVZjxNgSKmBLFfD4c=
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20220209214540-3681064d5158/go.mod h1:oPkhp1MJrh7nUepCBck5+mAzfO9JrbApNNgaTdGDITg=
|
||||
|
|
@ -991,9 +987,8 @@ golang.org/x/tools v0.1.0/go.mod h1:xkSsbof2nBLbhDlRMhhhyNLN/zl3eTqcnHD5viDpcZ0=
|
|||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.1/go.mod h1:o0xws9oXOQQZyjljx8fwUC0k7L1pTE6eaCbjGeHmOkk=
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.2/go.mod h1:o0xws9oXOQQZyjljx8fwUC0k7L1pTE6eaCbjGeHmOkk=
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.3/go.mod h1:o0xws9oXOQQZyjljx8fwUC0k7L1pTE6eaCbjGeHmOkk=
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.6-0.20210726203631-07bc1bf47fb2 h1:BonxutuHCTL0rBDnZlKjpGIQFTjyUVTexFOdWkB6Fg0=
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.6-0.20210726203631-07bc1bf47fb2/go.mod h1:o0xws9oXOQQZyjljx8fwUC0k7L1pTE6eaCbjGeHmOkk=
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.9 h1:j9KsMiaP1c3B0OTQGth0/k+miLGTgLsAFUCrF2vLcF8=
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools v0.1.9/go.mod h1:nABZi5QlRsZVlzPpHl034qft6wpY4eDcsTt5AaioBiU=
|
||||
golang.org/x/xerrors v0.0.0-20190717185122-a985d3407aa7/go.mod h1:I/5z698sn9Ka8TeJc9MKroUUfqBBauWjQqLJ2OPfmY0=
|
||||
golang.org/x/xerrors v0.0.0-20191011141410-1b5146add898/go.mod h1:I/5z698sn9Ka8TeJc9MKroUUfqBBauWjQqLJ2OPfmY0=
|
||||
golang.org/x/xerrors v0.0.0-20191204190536-9bdfabe68543/go.mod h1:I/5z698sn9Ka8TeJc9MKroUUfqBBauWjQqLJ2OPfmY0=
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.*.sw?
|
||||
/coverage.txt
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"settingsInheritedFrom": "VividCortex/whitesource-config@master"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,145 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# EWMA
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/VividCortex/ewma)
|
||||

|
||||
[](https://codecov.io/gh/VividCortex/ewma)
|
||||
|
||||
This repo provides Exponentially Weighted Moving Average algorithms, or EWMAs for short, [based on our
|
||||
Quantifying Abnormal Behavior talk](https://vividcortex.com/blog/2013/07/23/a-fast-go-library-for-exponential-moving-averages/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Exponentially Weighted Moving Average
|
||||
|
||||
An exponentially weighted moving average is a way to continuously compute a type of
|
||||
average for a series of numbers, as the numbers arrive. After a value in the series is
|
||||
added to the average, its weight in the average decreases exponentially over time. This
|
||||
biases the average towards more recent data. EWMAs are useful for several reasons, chiefly
|
||||
their inexpensive computational and memory cost, as well as the fact that they represent
|
||||
the recent central tendency of the series of values.
|
||||
|
||||
The EWMA algorithm requires a decay factor, alpha. The larger the alpha, the more the average
|
||||
is biased towards recent history. The alpha must be between 0 and 1, and is typically
|
||||
a fairly small number, such as 0.04. We will discuss the choice of alpha later.
|
||||
|
||||
The algorithm works thus, in pseudocode:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Multiply the next number in the series by alpha.
|
||||
2. Multiply the current value of the average by 1 minus alpha.
|
||||
3. Add the result of steps 1 and 2, and store it as the new current value of the average.
|
||||
4. Repeat for each number in the series.
|
||||
|
||||
There are special-case behaviors for how to initialize the current value, and these vary
|
||||
between implementations. One approach is to start with the first value in the series;
|
||||
another is to average the first 10 or so values in the series using an arithmetic average,
|
||||
and then begin the incremental updating of the average. Each method has pros and cons.
|
||||
|
||||
It may help to look at it pictorially. Suppose the series has five numbers, and we choose
|
||||
alpha to be 0.50 for simplicity. Here's the series, with numbers in the neighborhood of 300.
|
||||
|
||||
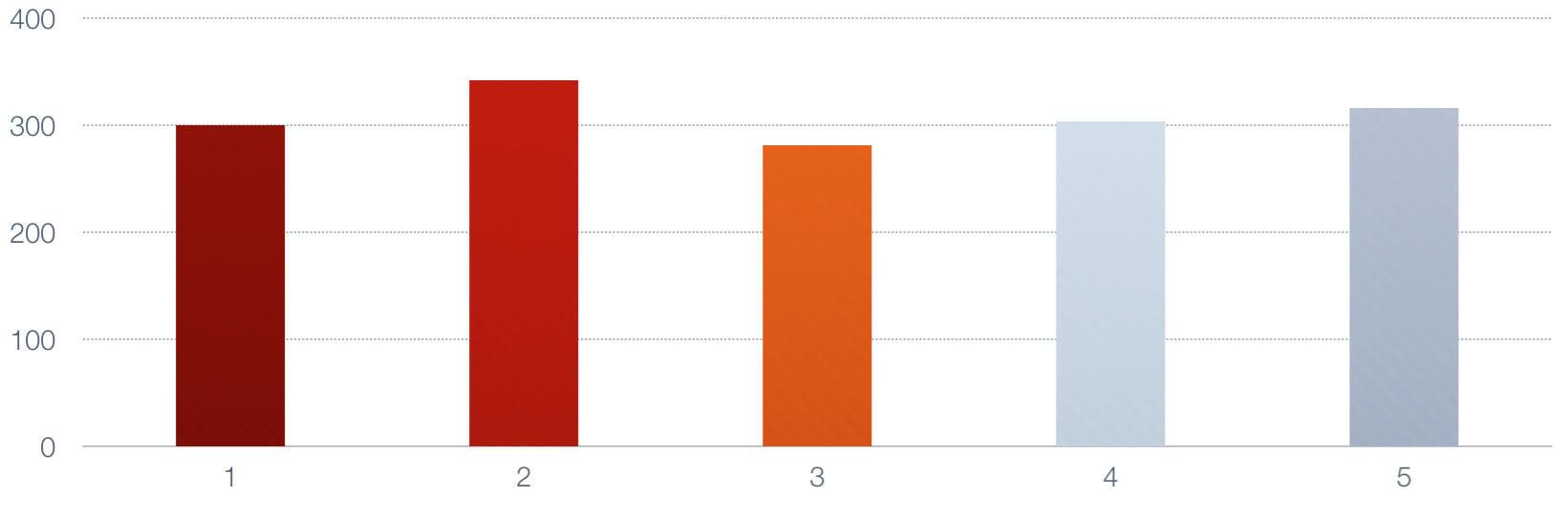
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's take the moving average of those numbers. First we set the average to the value
|
||||
of the first number.
|
||||
|
||||
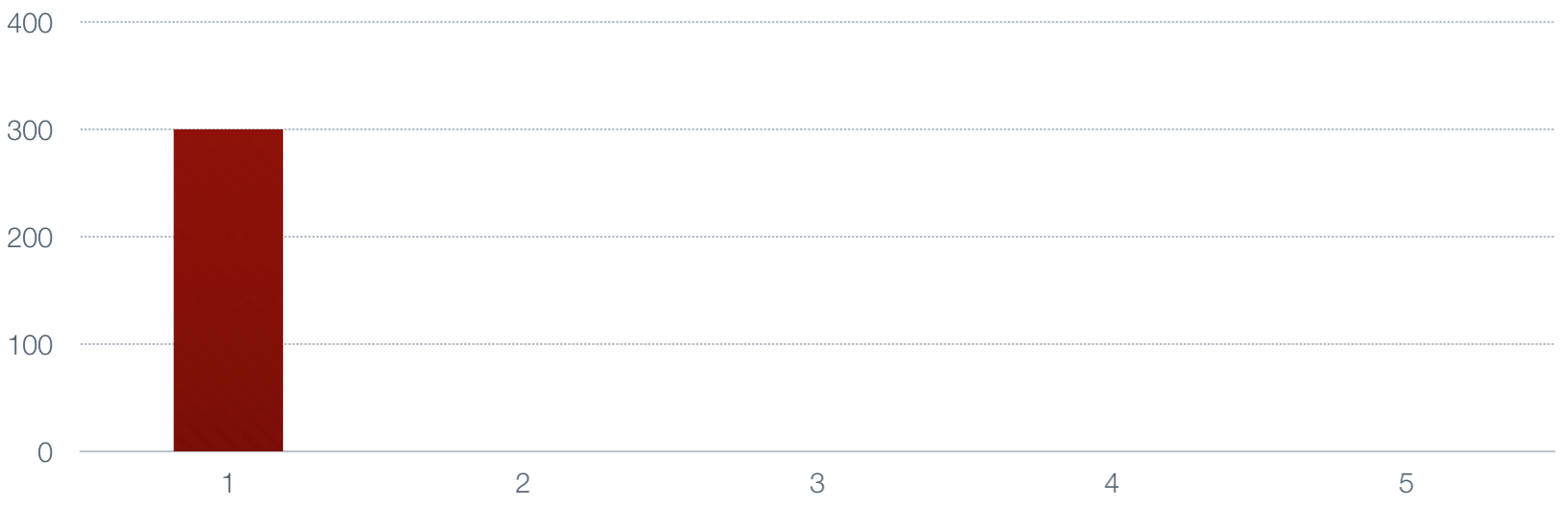
|
||||
|
||||
Next we multiply the next number by alpha, multiply the current value by 1-alpha, and add
|
||||
them to generate a new value.
|
||||
|
||||
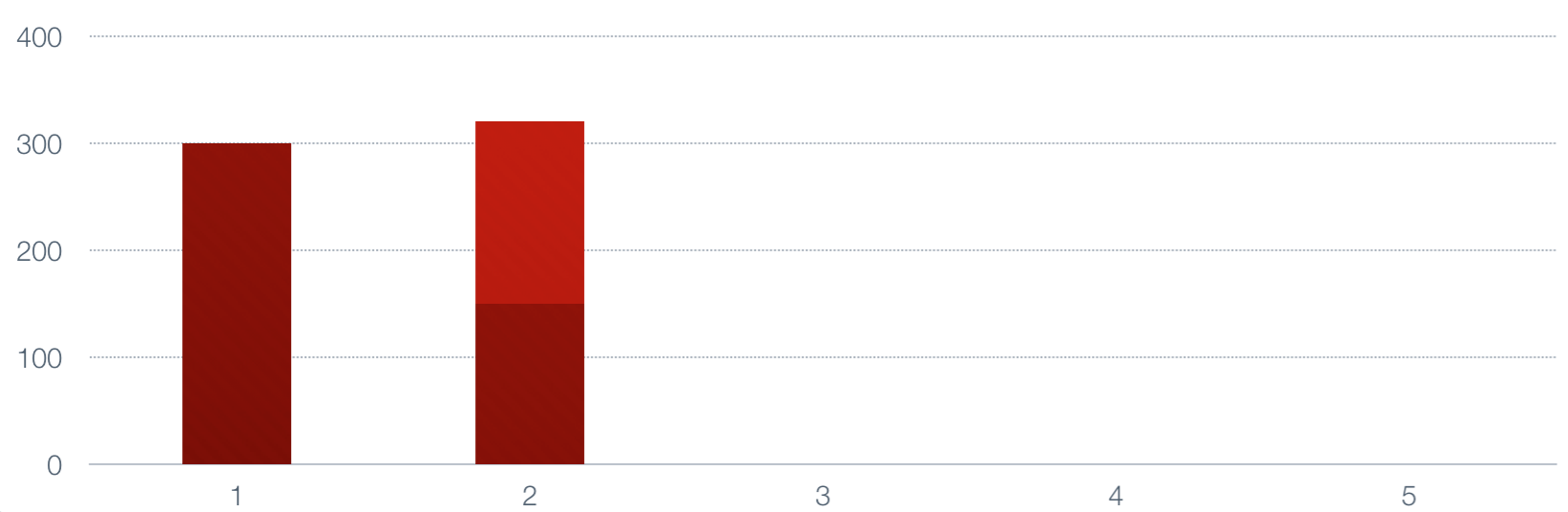
|
||||
|
||||
This continues until we are done.
|
||||
|
||||
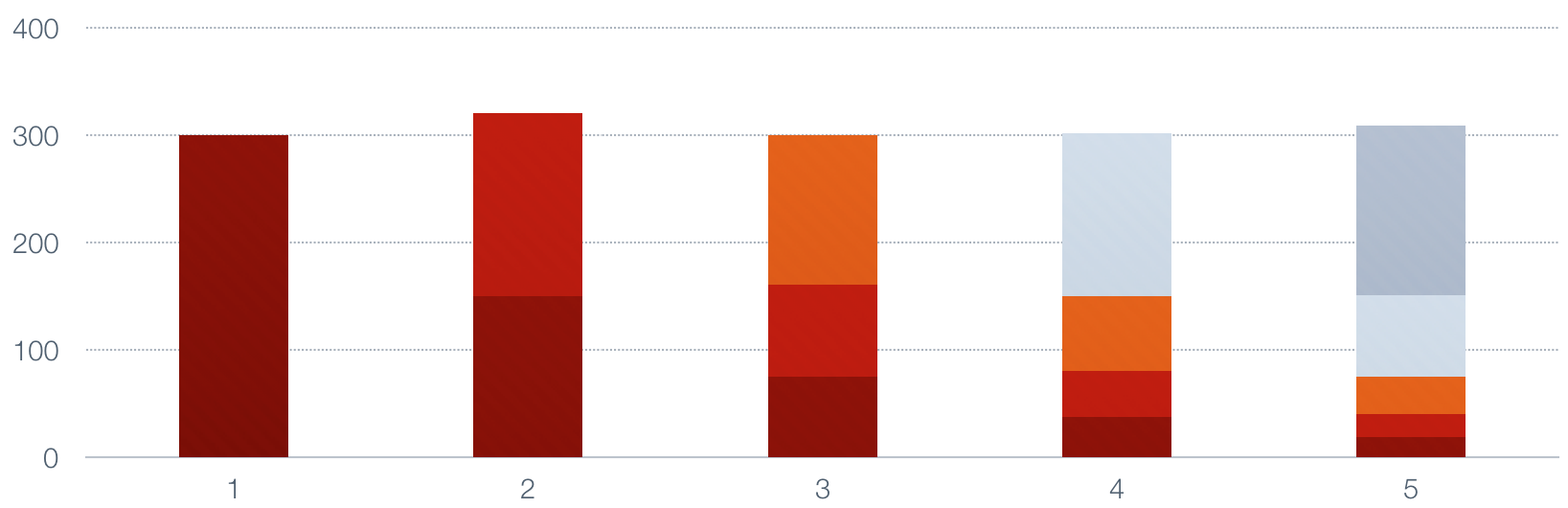
|
||||
|
||||
Notice how each of the values in the series decays by half each time a new value
|
||||
is added, and the top of the bars in the lower portion of the image represents the
|
||||
size of the moving average. It is a smoothed, or low-pass, average of the original
|
||||
series.
|
||||
|
||||
For further reading, see [Exponentially weighted moving average](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moving_average#Exponential_moving_average) on wikipedia.
|
||||
|
||||
### Choosing Alpha
|
||||
|
||||
Consider a fixed-size sliding-window moving average (not an exponentially weighted moving average)
|
||||
that averages over the previous N samples. What is the average age of each sample? It is N/2.
|
||||
|
||||
Now suppose that you wish to construct a EWMA whose samples have the same average age. The formula
|
||||
to compute the alpha required for this is: alpha = 2/(N+1). Proof is in the book
|
||||
"Production and Operations Analysis" by Steven Nahmias.
|
||||
|
||||
So, for example, if you have a time-series with samples once per second, and you want to get the
|
||||
moving average over the previous minute, you should use an alpha of .032786885. This, by the way,
|
||||
is the constant alpha used for this repository's SimpleEWMA.
|
||||
|
||||
### Implementations
|
||||
|
||||
This repository contains two implementations of the EWMA algorithm, with different properties.
|
||||
|
||||
The implementations all conform to the MovingAverage interface, and the constructor returns
|
||||
that type.
|
||||
|
||||
Current implementations assume an implicit time interval of 1.0 between every sample added.
|
||||
That is, the passage of time is treated as though it's the same as the arrival of samples.
|
||||
If you need time-based decay when samples are not arriving precisely at set intervals, then
|
||||
this package will not support your needs at present.
|
||||
|
||||
#### SimpleEWMA
|
||||
|
||||
A SimpleEWMA is designed for low CPU and memory consumption. It **will** have different behavior than the VariableEWMA
|
||||
for multiple reasons. It has no warm-up period and it uses a constant
|
||||
decay. These properties let it use less memory. It will also behave
|
||||
differently when it's equal to zero, which is assumed to mean
|
||||
uninitialized, so if a value is likely to actually become zero over time,
|
||||
then any non-zero value will cause a sharp jump instead of a small change.
|
||||
|
||||
#### VariableEWMA
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike SimpleEWMA, this supports a custom age which must be stored, and thus uses more memory.
|
||||
It also has a "warmup" time when you start adding values to it. It will report a value of 0.0
|
||||
until you have added the required number of samples to it. It uses some memory to store the
|
||||
number of samples added to it. As a result it uses a little over twice the memory of SimpleEWMA.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### API Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
View the GoDoc generated documentation [here](http://godoc.org/github.com/VividCortex/ewma).
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/VividCortex/ewma"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
samples := [100]float64{
|
||||
4599, 5711, 4746, 4621, 5037, 4218, 4925, 4281, 5207, 5203, 5594, 5149,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
e := ewma.NewMovingAverage() //=> Returns a SimpleEWMA if called without params
|
||||
a := ewma.NewMovingAverage(5) //=> returns a VariableEWMA with a decay of 2 / (5 + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
for _, f := range samples {
|
||||
e.Add(f)
|
||||
a.Add(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
e.Value() //=> 13.577404704631077
|
||||
a.Value() //=> 1.5806140565521463e-12
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
We only accept pull requests for minor fixes or improvements. This includes:
|
||||
|
||||
* Small bug fixes
|
||||
* Typos
|
||||
* Documentation or comments
|
||||
|
||||
Please open issues to discuss new features. Pull requests for new features will be rejected,
|
||||
so we recommend forking the repository and making changes in your fork for your use case.
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
This repository is Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
It is licensed under the MIT license. Please see the LICENSE file for applicable license terms.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
|
|||
coverage:
|
||||
status:
|
||||
project:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
threshold: 15%
|
||||
patch: off
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,160 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package ewma implements exponentially weighted moving averages.
|
||||
package ewma
|
||||
|
||||
import "fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex, Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Please see the LICENSE file for applicable license terms.
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// By default, we average over a one-minute period, which means the average
|
||||
// age of the metrics in the period is 30 seconds.
|
||||
AVG_METRIC_AGE float64 = 30.0
|
||||
|
||||
// The formula for computing the decay factor from the average age comes
|
||||
// from "Production and Operations Analysis" by Steven Nahmias.
|
||||
DECAY float64 = 2 / (float64(AVG_METRIC_AGE) + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
// For best results, the moving average should not be initialized to the
|
||||
// samples it sees immediately. The book "Production and Operations
|
||||
// Analysis" by Steven Nahmias suggests initializing the moving average to
|
||||
// the mean of the first 10 samples. Until the VariableEwma has seen this
|
||||
// many samples, it is not "ready" to be queried for the value of the
|
||||
// moving average. This adds some memory cost.
|
||||
DEFAULT_WARMUP_SAMPLES uint8 = 10
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// MovingAverage is the interface that computes a moving average over a time-
|
||||
// series stream of numbers. The average may be over a window or exponentially
|
||||
// decaying.
|
||||
type MovingAverage interface {
|
||||
Add(float64)
|
||||
Value() float64
|
||||
Set(float64)
|
||||
SetWarmupSamples(uint8) error
|
||||
WarmupSamples() uint8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMovingAverage constructs a MovingAverage that computes an average with the
|
||||
// desired characteristics in the moving window or exponential decay. If no
|
||||
// age is given, it constructs a default exponentially weighted implementation
|
||||
// that consumes minimal memory. The age is related to the decay factor alpha
|
||||
// by the formula given for the DECAY constant. It signifies the average age
|
||||
// of the samples as time goes to infinity.
|
||||
func NewMovingAverage(age ...float64) MovingAverage {
|
||||
if len(age) == 0 || age[0] == AVG_METRIC_AGE {
|
||||
return new(SimpleEWMA)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &VariableEWMA{
|
||||
decay: 2 / (age[0] + 1),
|
||||
warmup_samples: DEFAULT_WARMUP_SAMPLES,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A SimpleEWMA represents the exponentially weighted moving average of a
|
||||
// series of numbers. It WILL have different behavior than the VariableEWMA
|
||||
// for multiple reasons. It has no warm-up period and it uses a constant
|
||||
// decay. These properties let it use less memory. It will also behave
|
||||
// differently when it's equal to zero, which is assumed to mean
|
||||
// uninitialized, so if a value is likely to actually become zero over time,
|
||||
// then any non-zero value will cause a sharp jump instead of a small change.
|
||||
// However, note that this takes a long time, and the value may just
|
||||
// decays to a stable value that's close to zero, but which won't be mistaken
|
||||
// for uninitialized. See http://play.golang.org/p/litxBDr_RC for example.
|
||||
type SimpleEWMA struct {
|
||||
// The current value of the average. After adding with Add(), this is
|
||||
// updated to reflect the average of all values seen thus far.
|
||||
value *float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add adds a value to the series and updates the moving average.
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Add(value float64) {
|
||||
if e.value == nil { // this is a proxy for "uninitialized"
|
||||
e.value = &value
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
*e.value = (value * DECAY) + (e.Value() * (1 - DECAY))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the current value of the moving average.
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Value() float64 {
|
||||
if e.value == nil { // this is a proxy for "uninitialized"
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return *e.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set sets the EWMA's value.
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) Set(value float64) {
|
||||
e.value = &value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) WarmupSamples() uint8 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *SimpleEWMA) SetWarmupSamples(warmup_samples uint8) error {
|
||||
if warmup_samples > 0 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("warmup samples must be 0")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VariableEWMA represents the exponentially weighted moving average of a series of
|
||||
// numbers. Unlike SimpleEWMA, it supports a custom age, and thus uses more memory.
|
||||
type VariableEWMA struct {
|
||||
// The multiplier factor by which the previous samples decay.
|
||||
decay float64
|
||||
// The current value of the average.
|
||||
value float64
|
||||
// The number of samples added to this instance.
|
||||
count uint8
|
||||
// The number of warmup samples
|
||||
warmup_samples uint8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add adds a value to the series and updates the moving average.
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Add(value float64) {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case e.count < e.warmup_samples:
|
||||
e.count++
|
||||
e.value += value
|
||||
case e.count == e.warmup_samples:
|
||||
e.count++
|
||||
e.value = e.value / float64(e.warmup_samples)
|
||||
e.value = (value * e.decay) + (e.value * (1 - e.decay))
|
||||
default:
|
||||
e.value = (value * e.decay) + (e.value * (1 - e.decay))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the current value of the average, or 0.0 if the series hasn't
|
||||
// warmed up yet.
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Value() float64 {
|
||||
if e.count <= e.warmup_samples {
|
||||
return 0.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return e.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set sets the EWMA's value.
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) Set(value float64) {
|
||||
e.value = value
|
||||
if e.count <= e.warmup_samples {
|
||||
e.count = e.warmup_samples + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) SetWarmupSamples(warmup_samples uint8) error {
|
||||
if warmup_samples < 1 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("warmup samples must be between 1 and 255")
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.warmup_samples = warmup_samples
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *VariableEWMA) WarmupSamples() uint8 {
|
||||
return e.warmup_samples
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
|||
# Binaries for programs and plugins
|
||||
*.exe
|
||||
*.exe~
|
||||
*.dll
|
||||
*.so
|
||||
*.dylib
|
||||
|
||||
# Test binary, built with `go test -c`
|
||||
*.test
|
||||
|
||||
# Output of the go coverage tool, specifically when used with LiteIDE
|
||||
*.out
|
||||
|
||||
# Dependency directories (remove the comment below to include it)
|
||||
# vendor/
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/jedisct1/ewma/LICENSE → vendor/github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma/LICENSE
generated
vendored
12
vendor/github.com/jedisct1/ewma/LICENSE → vendor/github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|||
The MIT License
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2013 VividCortex
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2021 lifenjoiner
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
|
|
@ -9,13 +9,13 @@ to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
|||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
|
||||
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||
# EWMA
|
||||
|
||||
EWMA: Exponentially Weighted Moving Average algorithms
|
||||
|
||||
This is a variant of [EWMA](https://github.com/VividCortex/ewma).
|
||||
|
||||
### Variant
|
||||
|
||||
During the "warmup" stage, it uses a just-in-time `alpha` to get a more reasonable average.
|
||||
|
||||
Just one form.
|
||||
|
||||
[EWMA Comparisons](https://github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma/issues/1)
|
||||
|
||||
### Implementation
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
|||
// Package ewma: exponentially weighted moving averages
|
||||
package ewma
|
||||
|
||||
// New EWMA by moving window size.
|
||||
func NewMovingAverage(slide int) *EWMA {
|
||||
return &EWMA{
|
||||
slide: slide,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type EWMA struct {
|
||||
// Too big slide is meaningless.
|
||||
slide int
|
||||
// Count before warmed up.
|
||||
count int
|
||||
// Decay by slide size.
|
||||
decay float64
|
||||
// The average.
|
||||
value float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add a value to the series and update the moving average.
|
||||
func (a *EWMA) Add(value float64) {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case a.count <= a.slide:
|
||||
a.count++
|
||||
a.decay = 2 / float64(a.count + 1)
|
||||
a.value = a.value * (1 - a.decay) + value * a.decay
|
||||
default:
|
||||
a.value = a.value * (1 - a.decay) + value * a.decay
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the current EWMA value.
|
||||
func (a *EWMA) Value() float64 {
|
||||
return a.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set the EWMA value for continuing.
|
||||
func (a *EWMA) Set(value float64) {
|
||||
a.value = value
|
||||
a.decay = 2 / float64(a.slide + 1)
|
||||
a.count = a.slide + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -194,15 +194,12 @@ func (x *FileSyntax) updateLine(line *Line, tokens ...string) {
|
|||
line.Token = tokens
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// markRemoved modifies line so that it (and its end-of-line comment, if any)
|
||||
// will be dropped by (*FileSyntax).Cleanup.
|
||||
func (line *Line) markRemoved() {
|
||||
func (x *FileSyntax) removeLine(line *Line) {
|
||||
line.Token = nil
|
||||
line.Comments.Suffix = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cleanup cleans up the file syntax x after any edit operations.
|
||||
// To avoid quadratic behavior, (*Line).markRemoved marks the line as dead
|
||||
// To avoid quadratic behavior, removeLine marks the line as dead
|
||||
// by setting line.Token = nil but does not remove it from the slice
|
||||
// in which it appears. After edits have all been indicated,
|
||||
// calling Cleanup cleans out the dead lines.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -47,9 +47,8 @@ type File struct {
|
|||
|
||||
// A Module is the module statement.
|
||||
type Module struct {
|
||||
Mod module.Version
|
||||
Deprecated string
|
||||
Syntax *Line
|
||||
Mod module.Version
|
||||
Syntax *Line
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Go is the go statement.
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,6 +57,13 @@ type Go struct {
|
|||
Syntax *Line
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Require is a single require statement.
|
||||
type Require struct {
|
||||
Mod module.Version
|
||||
Indirect bool // has "// indirect" comment
|
||||
Syntax *Line
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An Exclude is a single exclude statement.
|
||||
type Exclude struct {
|
||||
Mod module.Version
|
||||
|
|
@ -86,93 +92,6 @@ type VersionInterval struct {
|
|||
Low, High string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Require is a single require statement.
|
||||
type Require struct {
|
||||
Mod module.Version
|
||||
Indirect bool // has "// indirect" comment
|
||||
Syntax *Line
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *Require) markRemoved() {
|
||||
r.Syntax.markRemoved()
|
||||
*r = Require{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *Require) setVersion(v string) {
|
||||
r.Mod.Version = v
|
||||
|
||||
if line := r.Syntax; len(line.Token) > 0 {
|
||||
if line.InBlock {
|
||||
// If the line is preceded by an empty line, remove it; see
|
||||
// https://golang.org/issue/33779.
|
||||
if len(line.Comments.Before) == 1 && len(line.Comments.Before[0].Token) == 0 {
|
||||
line.Comments.Before = line.Comments.Before[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(line.Token) >= 2 { // example.com v1.2.3
|
||||
line.Token[1] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if len(line.Token) >= 3 { // require example.com v1.2.3
|
||||
line.Token[2] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setIndirect sets line to have (or not have) a "// indirect" comment.
|
||||
func (r *Require) setIndirect(indirect bool) {
|
||||
r.Indirect = indirect
|
||||
line := r.Syntax
|
||||
if isIndirect(line) == indirect {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if indirect {
|
||||
// Adding comment.
|
||||
if len(line.Suffix) == 0 {
|
||||
// New comment.
|
||||
line.Suffix = []Comment{{Token: "// indirect", Suffix: true}}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
com := &line.Suffix[0]
|
||||
text := strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimPrefix(com.Token, string(slashSlash)))
|
||||
if text == "" {
|
||||
// Empty comment.
|
||||
com.Token = "// indirect"
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Insert at beginning of existing comment.
|
||||
com.Token = "// indirect; " + text
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Removing comment.
|
||||
f := strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimPrefix(line.Suffix[0].Token, string(slashSlash)))
|
||||
if f == "indirect" {
|
||||
// Remove whole comment.
|
||||
line.Suffix = nil
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Remove comment prefix.
|
||||
com := &line.Suffix[0]
|
||||
i := strings.Index(com.Token, "indirect;")
|
||||
com.Token = "//" + com.Token[i+len("indirect;"):]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isIndirect reports whether line has a "// indirect" comment,
|
||||
// meaning it is in go.mod only for its effect on indirect dependencies,
|
||||
// so that it can be dropped entirely once the effective version of the
|
||||
// indirect dependency reaches the given minimum version.
|
||||
func isIndirect(line *Line) bool {
|
||||
if len(line.Suffix) == 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
f := strings.Fields(strings.TrimPrefix(line.Suffix[0].Token, string(slashSlash)))
|
||||
return (len(f) == 1 && f[0] == "indirect" || len(f) > 1 && f[0] == "indirect;")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *File) AddModuleStmt(path string) error {
|
||||
if f.Syntax == nil {
|
||||
f.Syntax = new(FileSyntax)
|
||||
|
|
@ -212,15 +131,8 @@ var dontFixRetract VersionFixer = func(_, vers string) (string, error) {
|
|||
return vers, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses and returns a go.mod file.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// file is the name of the file, used in positions and errors.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// data is the content of the file.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// fix is an optional function that canonicalizes module versions.
|
||||
// If fix is nil, all module versions must be canonical (module.CanonicalVersion
|
||||
// must return the same string).
|
||||
// Parse parses the data, reported in errors as being from file,
|
||||
// into a File struct. It applies fix, if non-nil, to canonicalize all module versions found.
|
||||
func Parse(file string, data []byte, fix VersionFixer) (*File, error) {
|
||||
return parseToFile(file, data, fix, true)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -297,7 +209,6 @@ func parseToFile(file string, data []byte, fix VersionFixer, strict bool) (parse
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var GoVersionRE = lazyregexp.New(`^([1-9][0-9]*)\.(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$`)
|
||||
var laxGoVersionRE = lazyregexp.New(`^v?(([1-9][0-9]*)\.(0|[1-9][0-9]*))([^0-9].*)$`)
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *File) add(errs *ErrorList, block *LineBlock, line *Line, verb string, args []string, fix VersionFixer, strict bool) {
|
||||
// If strict is false, this module is a dependency.
|
||||
|
|
@ -348,17 +259,8 @@ func (f *File) add(errs *ErrorList, block *LineBlock, line *Line, verb string, a
|
|||
errorf("go directive expects exactly one argument")
|
||||
return
|
||||
} else if !GoVersionRE.MatchString(args[0]) {
|
||||
fixed := false
|
||||
if !strict {
|
||||
if m := laxGoVersionRE.FindStringSubmatch(args[0]); m != nil {
|
||||
args[0] = m[1]
|
||||
fixed = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !fixed {
|
||||
errorf("invalid go version '%s': must match format 1.23", args[0])
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
errorf("invalid go version '%s': must match format 1.23", args[0])
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.Go = &Go{Syntax: line}
|
||||
|
|
@ -369,11 +271,7 @@ func (f *File) add(errs *ErrorList, block *LineBlock, line *Line, verb string, a
|
|||
errorf("repeated module statement")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
deprecated := parseDeprecation(block, line)
|
||||
f.Module = &Module{
|
||||
Syntax: line,
|
||||
Deprecated: deprecated,
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Module = &Module{Syntax: line}
|
||||
if len(args) != 1 {
|
||||
errorf("usage: module module/path")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
|
@ -487,7 +385,7 @@ func (f *File) add(errs *ErrorList, block *LineBlock, line *Line, verb string, a
|
|||
})
|
||||
|
||||
case "retract":
|
||||
rationale := parseDirectiveComment(block, line)
|
||||
rationale := parseRetractRationale(block, line)
|
||||
vi, err := parseVersionInterval(verb, "", &args, dontFixRetract)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if strict {
|
||||
|
|
@ -556,6 +454,58 @@ func (f *File) fixRetract(fix VersionFixer, errs *ErrorList) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isIndirect reports whether line has a "// indirect" comment,
|
||||
// meaning it is in go.mod only for its effect on indirect dependencies,
|
||||
// so that it can be dropped entirely once the effective version of the
|
||||
// indirect dependency reaches the given minimum version.
|
||||
func isIndirect(line *Line) bool {
|
||||
if len(line.Suffix) == 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
f := strings.Fields(strings.TrimPrefix(line.Suffix[0].Token, string(slashSlash)))
|
||||
return (len(f) == 1 && f[0] == "indirect" || len(f) > 1 && f[0] == "indirect;")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setIndirect sets line to have (or not have) a "// indirect" comment.
|
||||
func setIndirect(line *Line, indirect bool) {
|
||||
if isIndirect(line) == indirect {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if indirect {
|
||||
// Adding comment.
|
||||
if len(line.Suffix) == 0 {
|
||||
// New comment.
|
||||
line.Suffix = []Comment{{Token: "// indirect", Suffix: true}}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
com := &line.Suffix[0]
|
||||
text := strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimPrefix(com.Token, string(slashSlash)))
|
||||
if text == "" {
|
||||
// Empty comment.
|
||||
com.Token = "// indirect"
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Insert at beginning of existing comment.
|
||||
com.Token = "// indirect; " + text
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Removing comment.
|
||||
f := strings.Fields(line.Suffix[0].Token)
|
||||
if len(f) == 2 {
|
||||
// Remove whole comment.
|
||||
line.Suffix = nil
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Remove comment prefix.
|
||||
com := &line.Suffix[0]
|
||||
i := strings.Index(com.Token, "indirect;")
|
||||
com.Token = "//" + com.Token[i+len("indirect;"):]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsDirectoryPath reports whether the given path should be interpreted
|
||||
// as a directory path. Just like on the go command line, relative paths
|
||||
// and rooted paths are directory paths; the rest are module paths.
|
||||
|
|
@ -662,29 +612,10 @@ func parseString(s *string) (string, error) {
|
|||
return t, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var deprecatedRE = lazyregexp.New(`(?s)(?:^|\n\n)Deprecated: *(.*?)(?:$|\n\n)`)
|
||||
|
||||
// parseDeprecation extracts the text of comments on a "module" directive and
|
||||
// extracts a deprecation message from that.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A deprecation message is contained in a paragraph within a block of comments
|
||||
// that starts with "Deprecated:" (case sensitive). The message runs until the
|
||||
// end of the paragraph and does not include the "Deprecated:" prefix. If the
|
||||
// comment block has multiple paragraphs that start with "Deprecated:",
|
||||
// parseDeprecation returns the message from the first.
|
||||
func parseDeprecation(block *LineBlock, line *Line) string {
|
||||
text := parseDirectiveComment(block, line)
|
||||
m := deprecatedRE.FindStringSubmatch(text)
|
||||
if m == nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m[1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseDirectiveComment extracts the text of comments on a directive.
|
||||
// If the directive's line does not have comments and is part of a block that
|
||||
// does have comments, the block's comments are used.
|
||||
func parseDirectiveComment(block *LineBlock, line *Line) string {
|
||||
// parseRetractRationale extracts the rationale for a retract directive from the
|
||||
// surrounding comments. If the line does not have comments and is part of a
|
||||
// block that does have comments, the block's comments are used.
|
||||
func parseRetractRationale(block *LineBlock, line *Line) string {
|
||||
comments := line.Comment()
|
||||
if block != nil && len(comments.Before) == 0 && len(comments.Suffix) == 0 {
|
||||
comments = block.Comment()
|
||||
|
|
@ -863,12 +794,6 @@ func (f *File) AddGoStmt(version string) error {
|
|||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddRequire sets the first require line for path to version vers,
|
||||
// preserving any existing comments for that line and removing all
|
||||
// other lines for path.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If no line currently exists for path, AddRequire adds a new line
|
||||
// at the end of the last require block.
|
||||
func (f *File) AddRequire(path, vers string) error {
|
||||
need := true
|
||||
for _, r := range f.Require {
|
||||
|
|
@ -878,7 +803,7 @@ func (f *File) AddRequire(path, vers string) error {
|
|||
f.Syntax.updateLine(r.Syntax, "require", AutoQuote(path), vers)
|
||||
need = false
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.Syntax.markRemoved()
|
||||
f.Syntax.removeLine(r.Syntax)
|
||||
*r = Require{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -890,290 +815,77 @@ func (f *File) AddRequire(path, vers string) error {
|
|||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddNewRequire adds a new require line for path at version vers at the end of
|
||||
// the last require block, regardless of any existing require lines for path.
|
||||
func (f *File) AddNewRequire(path, vers string, indirect bool) {
|
||||
line := f.Syntax.addLine(nil, "require", AutoQuote(path), vers)
|
||||
r := &Require{
|
||||
Mod: module.Version{Path: path, Version: vers},
|
||||
Syntax: line,
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.setIndirect(indirect)
|
||||
f.Require = append(f.Require, r)
|
||||
setIndirect(line, indirect)
|
||||
f.Require = append(f.Require, &Require{module.Version{Path: path, Version: vers}, indirect, line})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetRequire updates the requirements of f to contain exactly req, preserving
|
||||
// the existing block structure and line comment contents (except for 'indirect'
|
||||
// markings) for the first requirement on each named module path.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Syntax field is ignored for the requirements in req.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Any requirements not already present in the file are added to the block
|
||||
// containing the last require line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The requirements in req must specify at most one distinct version for each
|
||||
// module path.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If any existing requirements may be removed, the caller should call Cleanup
|
||||
// after all edits are complete.
|
||||
func (f *File) SetRequire(req []*Require) {
|
||||
type elem struct {
|
||||
version string
|
||||
indirect bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
need := make(map[string]elem)
|
||||
need := make(map[string]string)
|
||||
indirect := make(map[string]bool)
|
||||
for _, r := range req {
|
||||
if prev, dup := need[r.Mod.Path]; dup && prev.version != r.Mod.Version {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("SetRequire called with conflicting versions for path %s (%s and %s)", r.Mod.Path, prev.version, r.Mod.Version))
|
||||
}
|
||||
need[r.Mod.Path] = elem{r.Mod.Version, r.Indirect}
|
||||
need[r.Mod.Path] = r.Mod.Version
|
||||
indirect[r.Mod.Path] = r.Indirect
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Update or delete the existing Require entries to preserve
|
||||
// only the first for each module path in req.
|
||||
for _, r := range f.Require {
|
||||
e, ok := need[r.Mod.Path]
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
r.setVersion(e.version)
|
||||
r.setIndirect(e.indirect)
|
||||
if v, ok := need[r.Mod.Path]; ok {
|
||||
r.Mod.Version = v
|
||||
r.Indirect = indirect[r.Mod.Path]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.markRemoved()
|
||||
*r = Require{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
delete(need, r.Mod.Path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add new entries in the last block of the file for any paths that weren't
|
||||
// already present.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This step is nondeterministic, but the final result will be deterministic
|
||||
// because we will sort the block.
|
||||
for path, e := range need {
|
||||
f.AddNewRequire(path, e.version, e.indirect)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.SortBlocks()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetRequireSeparateIndirect updates the requirements of f to contain the given
|
||||
// requirements. Comment contents (except for 'indirect' markings) are retained
|
||||
// from the first existing requirement for each module path. Like SetRequire,
|
||||
// SetRequireSeparateIndirect adds requirements for new paths in req,
|
||||
// updates the version and "// indirect" comment on existing requirements,
|
||||
// and deletes requirements on paths not in req. Existing duplicate requirements
|
||||
// are deleted.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// As its name suggests, SetRequireSeparateIndirect puts direct and indirect
|
||||
// requirements into two separate blocks, one containing only direct
|
||||
// requirements, and the other containing only indirect requirements.
|
||||
// SetRequireSeparateIndirect may move requirements between these two blocks
|
||||
// when their indirect markings change. However, SetRequireSeparateIndirect
|
||||
// won't move requirements from other blocks, especially blocks with comments.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the file initially has one uncommented block of requirements,
|
||||
// SetRequireSeparateIndirect will split it into a direct-only and indirect-only
|
||||
// block. This aids in the transition to separate blocks.
|
||||
func (f *File) SetRequireSeparateIndirect(req []*Require) {
|
||||
// hasComments returns whether a line or block has comments
|
||||
// other than "indirect".
|
||||
hasComments := func(c Comments) bool {
|
||||
return len(c.Before) > 0 || len(c.After) > 0 || len(c.Suffix) > 1 ||
|
||||
(len(c.Suffix) == 1 &&
|
||||
strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimPrefix(c.Suffix[0].Token, string(slashSlash))) != "indirect")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// moveReq adds r to block. If r was in another block, moveReq deletes
|
||||
// it from that block and transfers its comments.
|
||||
moveReq := func(r *Require, block *LineBlock) {
|
||||
var line *Line
|
||||
if r.Syntax == nil {
|
||||
line = &Line{Token: []string{AutoQuote(r.Mod.Path), r.Mod.Version}}
|
||||
r.Syntax = line
|
||||
if r.Indirect {
|
||||
r.setIndirect(true)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
line = new(Line)
|
||||
*line = *r.Syntax
|
||||
if !line.InBlock && len(line.Token) > 0 && line.Token[0] == "require" {
|
||||
line.Token = line.Token[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.Syntax.Token = nil // Cleanup will delete the old line.
|
||||
r.Syntax = line
|
||||
}
|
||||
line.InBlock = true
|
||||
block.Line = append(block.Line, line)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Examine existing require lines and blocks.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// We may insert new requirements into the last uncommented
|
||||
// direct-only and indirect-only blocks. We may also move requirements
|
||||
// to the opposite block if their indirect markings change.
|
||||
lastDirectIndex = -1
|
||||
lastIndirectIndex = -1
|
||||
|
||||
// If there are no direct-only or indirect-only blocks, a new block may
|
||||
// be inserted after the last require line or block.
|
||||
lastRequireIndex = -1
|
||||
|
||||
// If there's only one require line or block, and it's uncommented,
|
||||
// we'll move its requirements to the direct-only or indirect-only blocks.
|
||||
requireLineOrBlockCount = 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Track the block each requirement belongs to (if any) so we can
|
||||
// move them later.
|
||||
lineToBlock = make(map[*Line]*LineBlock)
|
||||
)
|
||||
for i, stmt := range f.Syntax.Stmt {
|
||||
var newStmts []Expr
|
||||
for _, stmt := range f.Syntax.Stmt {
|
||||
switch stmt := stmt.(type) {
|
||||
case *Line:
|
||||
if len(stmt.Token) == 0 || stmt.Token[0] != "require" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case *LineBlock:
|
||||
if len(stmt.Token) > 0 && stmt.Token[0] == "require" {
|
||||
var newLines []*Line
|
||||
for _, line := range stmt.Line {
|
||||
if p, err := parseString(&line.Token[0]); err == nil && need[p] != "" {
|
||||
if len(line.Comments.Before) == 1 && len(line.Comments.Before[0].Token) == 0 {
|
||||
line.Comments.Before = line.Comments.Before[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
line.Token[1] = need[p]
|
||||
delete(need, p)
|
||||
setIndirect(line, indirect[p])
|
||||
newLines = append(newLines, line)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(newLines) == 0 {
|
||||
continue // drop stmt
|
||||
}
|
||||
stmt.Line = newLines
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastRequireIndex = i
|
||||
requireLineOrBlockCount++
|
||||
if !hasComments(stmt.Comments) {
|
||||
if isIndirect(stmt) {
|
||||
lastIndirectIndex = i
|
||||
|
||||
case *Line:
|
||||
if len(stmt.Token) > 0 && stmt.Token[0] == "require" {
|
||||
if p, err := parseString(&stmt.Token[1]); err == nil && need[p] != "" {
|
||||
stmt.Token[2] = need[p]
|
||||
delete(need, p)
|
||||
setIndirect(stmt, indirect[p])
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lastDirectIndex = i
|
||||
continue // drop stmt
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case *LineBlock:
|
||||
if len(stmt.Token) == 0 || stmt.Token[0] != "require" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastRequireIndex = i
|
||||
requireLineOrBlockCount++
|
||||
allDirect := len(stmt.Line) > 0 && !hasComments(stmt.Comments)
|
||||
allIndirect := len(stmt.Line) > 0 && !hasComments(stmt.Comments)
|
||||
for _, line := range stmt.Line {
|
||||
lineToBlock[line] = stmt
|
||||
if hasComments(line.Comments) {
|
||||
allDirect = false
|
||||
allIndirect = false
|
||||
} else if isIndirect(line) {
|
||||
allDirect = false
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
allIndirect = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if allDirect {
|
||||
lastDirectIndex = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
if allIndirect {
|
||||
lastIndirectIndex = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
newStmts = append(newStmts, stmt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Syntax.Stmt = newStmts
|
||||
|
||||
oneFlatUncommentedBlock := requireLineOrBlockCount == 1 &&
|
||||
!hasComments(*f.Syntax.Stmt[lastRequireIndex].Comment())
|
||||
|
||||
// Create direct and indirect blocks if needed. Convert lines into blocks
|
||||
// if needed. If we end up with an empty block or a one-line block,
|
||||
// Cleanup will delete it or convert it to a line later.
|
||||
insertBlock := func(i int) *LineBlock {
|
||||
block := &LineBlock{Token: []string{"require"}}
|
||||
f.Syntax.Stmt = append(f.Syntax.Stmt, nil)
|
||||
copy(f.Syntax.Stmt[i+1:], f.Syntax.Stmt[i:])
|
||||
f.Syntax.Stmt[i] = block
|
||||
return block
|
||||
for path, vers := range need {
|
||||
f.AddNewRequire(path, vers, indirect[path])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ensureBlock := func(i int) *LineBlock {
|
||||
switch stmt := f.Syntax.Stmt[i].(type) {
|
||||
case *LineBlock:
|
||||
return stmt
|
||||
case *Line:
|
||||
block := &LineBlock{
|
||||
Token: []string{"require"},
|
||||
Line: []*Line{stmt},
|
||||
}
|
||||
stmt.Token = stmt.Token[1:] // remove "require"
|
||||
stmt.InBlock = true
|
||||
f.Syntax.Stmt[i] = block
|
||||
return block
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(fmt.Sprintf("unexpected statement: %v", stmt))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var lastDirectBlock *LineBlock
|
||||
if lastDirectIndex < 0 {
|
||||
if lastIndirectIndex >= 0 {
|
||||
lastDirectIndex = lastIndirectIndex
|
||||
lastIndirectIndex++
|
||||
} else if lastRequireIndex >= 0 {
|
||||
lastDirectIndex = lastRequireIndex + 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lastDirectIndex = len(f.Syntax.Stmt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lastDirectBlock = insertBlock(lastDirectIndex)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lastDirectBlock = ensureBlock(lastDirectIndex)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var lastIndirectBlock *LineBlock
|
||||
if lastIndirectIndex < 0 {
|
||||
lastIndirectIndex = lastDirectIndex + 1
|
||||
lastIndirectBlock = insertBlock(lastIndirectIndex)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lastIndirectBlock = ensureBlock(lastIndirectIndex)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Delete requirements we don't want anymore.
|
||||
// Update versions and indirect comments on requirements we want to keep.
|
||||
// If a requirement is in last{Direct,Indirect}Block with the wrong
|
||||
// indirect marking after this, or if the requirement is in an single
|
||||
// uncommented mixed block (oneFlatUncommentedBlock), move it to the
|
||||
// correct block.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Some blocks may be empty after this. Cleanup will remove them.
|
||||
need := make(map[string]*Require)
|
||||
for _, r := range req {
|
||||
need[r.Mod.Path] = r
|
||||
}
|
||||
have := make(map[string]*Require)
|
||||
for _, r := range f.Require {
|
||||
path := r.Mod.Path
|
||||
if need[path] == nil || have[path] != nil {
|
||||
// Requirement not needed, or duplicate requirement. Delete.
|
||||
r.markRemoved()
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
have[r.Mod.Path] = r
|
||||
r.setVersion(need[path].Mod.Version)
|
||||
r.setIndirect(need[path].Indirect)
|
||||
if need[path].Indirect &&
|
||||
(oneFlatUncommentedBlock || lineToBlock[r.Syntax] == lastDirectBlock) {
|
||||
moveReq(r, lastIndirectBlock)
|
||||
} else if !need[path].Indirect &&
|
||||
(oneFlatUncommentedBlock || lineToBlock[r.Syntax] == lastIndirectBlock) {
|
||||
moveReq(r, lastDirectBlock)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add new requirements.
|
||||
for path, r := range need {
|
||||
if have[path] == nil {
|
||||
if r.Indirect {
|
||||
moveReq(r, lastIndirectBlock)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
moveReq(r, lastDirectBlock)
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Require = append(f.Require, r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.SortBlocks()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *File) DropRequire(path string) error {
|
||||
for _, r := range f.Require {
|
||||
if r.Mod.Path == path {
|
||||
r.Syntax.markRemoved()
|
||||
f.Syntax.removeLine(r.Syntax)
|
||||
*r = Require{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1204,7 +916,7 @@ func (f *File) AddExclude(path, vers string) error {
|
|||
func (f *File) DropExclude(path, vers string) error {
|
||||
for _, x := range f.Exclude {
|
||||
if x.Mod.Path == path && x.Mod.Version == vers {
|
||||
x.Syntax.markRemoved()
|
||||
f.Syntax.removeLine(x.Syntax)
|
||||
*x = Exclude{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1235,7 +947,7 @@ func (f *File) AddReplace(oldPath, oldVers, newPath, newVers string) error {
|
|||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Already added; delete other replacements for same.
|
||||
r.Syntax.markRemoved()
|
||||
f.Syntax.removeLine(r.Syntax)
|
||||
*r = Replace{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r.Old.Path == oldPath {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1251,7 +963,7 @@ func (f *File) AddReplace(oldPath, oldVers, newPath, newVers string) error {
|
|||
func (f *File) DropReplace(oldPath, oldVers string) error {
|
||||
for _, r := range f.Replace {
|
||||
if r.Old.Path == oldPath && r.Old.Version == oldVers {
|
||||
r.Syntax.markRemoved()
|
||||
f.Syntax.removeLine(r.Syntax)
|
||||
*r = Replace{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1292,7 +1004,7 @@ func (f *File) AddRetract(vi VersionInterval, rationale string) error {
|
|||
func (f *File) DropRetract(vi VersionInterval) error {
|
||||
for _, r := range f.Retract {
|
||||
if r.VersionInterval == vi {
|
||||
r.Syntax.markRemoved()
|
||||
f.Syntax.removeLine(r.Syntax)
|
||||
*r = Retract{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -192,21 +192,6 @@ func (e *InvalidVersionError) Error() string {
|
|||
|
||||
func (e *InvalidVersionError) Unwrap() error { return e.Err }
|
||||
|
||||
// An InvalidPathError indicates a module, import, or file path doesn't
|
||||
// satisfy all naming constraints. See CheckPath, CheckImportPath,
|
||||
// and CheckFilePath for specific restrictions.
|
||||
type InvalidPathError struct {
|
||||
Kind string // "module", "import", or "file"
|
||||
Path string
|
||||
Err error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *InvalidPathError) Error() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("malformed %s path %q: %v", e.Kind, e.Path, e.Err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *InvalidPathError) Unwrap() error { return e.Err }
|
||||
|
||||
// Check checks that a given module path, version pair is valid.
|
||||
// In addition to the path being a valid module path
|
||||
// and the version being a valid semantic version,
|
||||
|
|
@ -311,36 +296,30 @@ func fileNameOK(r rune) bool {
|
|||
// this second requirement is replaced by a requirement that the path
|
||||
// follow the gopkg.in server's conventions.
|
||||
// Third, no path element may begin with a dot.
|
||||
func CheckPath(path string) (err error) {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
err = &InvalidPathError{Kind: "module", Path: path, Err: err}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
func CheckPath(path string) error {
|
||||
if err := checkPath(path, modulePath); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed module path %q: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
i := strings.Index(path, "/")
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
i = len(path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i == 0 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("leading slash")
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed module path %q: leading slash", path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !strings.Contains(path[:i], ".") {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("missing dot in first path element")
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed module path %q: missing dot in first path element", path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if path[0] == '-' {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("leading dash in first path element")
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed module path %q: leading dash in first path element", path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, r := range path[:i] {
|
||||
if !firstPathOK(r) {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("invalid char %q in first path element", r)
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed module path %q: invalid char %q in first path element", path, r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, _, ok := SplitPathVersion(path); !ok {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("invalid version")
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed module path %q: invalid version", path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -364,7 +343,7 @@ func CheckPath(path string) (err error) {
|
|||
// subtleties of Unicode.
|
||||
func CheckImportPath(path string) error {
|
||||
if err := checkPath(path, importPath); err != nil {
|
||||
return &InvalidPathError{Kind: "import", Path: path, Err: err}
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed import path %q: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -379,13 +358,12 @@ const (
|
|||
filePath
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// checkPath checks that a general path is valid. kind indicates what
|
||||
// specific constraints should be applied.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// checkPath returns an error describing why the path is not valid.
|
||||
// Because these checks apply to module, import, and file paths,
|
||||
// and because other checks may be applied, the caller is expected to wrap
|
||||
// this error with InvalidPathError.
|
||||
// checkPath checks that a general path is valid.
|
||||
// It returns an error describing why but not mentioning path.
|
||||
// Because these checks apply to both module paths and import paths,
|
||||
// the caller is expected to add the "malformed ___ path %q: " prefix.
|
||||
// fileName indicates whether the final element of the path is a file name
|
||||
// (as opposed to a directory name).
|
||||
func checkPath(path string, kind pathKind) error {
|
||||
if !utf8.ValidString(path) {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("invalid UTF-8")
|
||||
|
|
@ -393,7 +371,7 @@ func checkPath(path string, kind pathKind) error {
|
|||
if path == "" {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("empty string")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if path[0] == '-' && kind != filePath {
|
||||
if path[0] == '-' {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("leading dash")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if strings.Contains(path, "//") {
|
||||
|
|
@ -499,7 +477,7 @@ func checkElem(elem string, kind pathKind) error {
|
|||
// subtleties of Unicode.
|
||||
func CheckFilePath(path string) error {
|
||||
if err := checkPath(path, filePath); err != nil {
|
||||
return &InvalidPathError{Kind: "file", Path: path, Err: err}
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("malformed file path %q: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,250 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2018 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Pseudo-versions
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Code authors are expected to tag the revisions they want users to use,
|
||||
// including prereleases. However, not all authors tag versions at all,
|
||||
// and not all commits a user might want to try will have tags.
|
||||
// A pseudo-version is a version with a special form that allows us to
|
||||
// address an untagged commit and order that version with respect to
|
||||
// other versions we might encounter.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A pseudo-version takes one of the general forms:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (1) vX.0.0-yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456
|
||||
// (2) vX.Y.(Z+1)-0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456
|
||||
// (3) vX.Y.(Z+1)-0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456+incompatible
|
||||
// (4) vX.Y.Z-pre.0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456
|
||||
// (5) vX.Y.Z-pre.0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456+incompatible
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If there is no recently tagged version with the right major version vX,
|
||||
// then form (1) is used, creating a space of pseudo-versions at the bottom
|
||||
// of the vX version range, less than any tagged version, including the unlikely v0.0.0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the most recent tagged version before the target commit is vX.Y.Z or vX.Y.Z+incompatible,
|
||||
// then the pseudo-version uses form (2) or (3), making it a prerelease for the next
|
||||
// possible semantic version after vX.Y.Z. The leading 0 segment in the prerelease string
|
||||
// ensures that the pseudo-version compares less than possible future explicit prereleases
|
||||
// like vX.Y.(Z+1)-rc1 or vX.Y.(Z+1)-1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the most recent tagged version before the target commit is vX.Y.Z-pre or vX.Y.Z-pre+incompatible,
|
||||
// then the pseudo-version uses form (4) or (5), making it a slightly later prerelease.
|
||||
|
||||
package module
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/mod/internal/lazyregexp"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/mod/semver"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var pseudoVersionRE = lazyregexp.New(`^v[0-9]+\.(0\.0-|\d+\.\d+-([^+]*\.)?0\.)\d{14}-[A-Za-z0-9]+(\+[0-9A-Za-z-]+(\.[0-9A-Za-z-]+)*)?$`)
|
||||
|
||||
const PseudoVersionTimestampFormat = "20060102150405"
|
||||
|
||||
// PseudoVersion returns a pseudo-version for the given major version ("v1")
|
||||
// preexisting older tagged version ("" or "v1.2.3" or "v1.2.3-pre"), revision time,
|
||||
// and revision identifier (usually a 12-byte commit hash prefix).
|
||||
func PseudoVersion(major, older string, t time.Time, rev string) string {
|
||||
if major == "" {
|
||||
major = "v0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
segment := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%s", t.UTC().Format(PseudoVersionTimestampFormat), rev)
|
||||
build := semver.Build(older)
|
||||
older = semver.Canonical(older)
|
||||
if older == "" {
|
||||
return major + ".0.0-" + segment // form (1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if semver.Prerelease(older) != "" {
|
||||
return older + ".0." + segment + build // form (4), (5)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Form (2), (3).
|
||||
// Extract patch from vMAJOR.MINOR.PATCH
|
||||
i := strings.LastIndex(older, ".") + 1
|
||||
v, patch := older[:i], older[i:]
|
||||
|
||||
// Reassemble.
|
||||
return v + incDecimal(patch) + "-0." + segment + build
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ZeroPseudoVersion returns a pseudo-version with a zero timestamp and
|
||||
// revision, which may be used as a placeholder.
|
||||
func ZeroPseudoVersion(major string) string {
|
||||
return PseudoVersion(major, "", time.Time{}, "000000000000")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// incDecimal returns the decimal string incremented by 1.
|
||||
func incDecimal(decimal string) string {
|
||||
// Scan right to left turning 9s to 0s until you find a digit to increment.
|
||||
digits := []byte(decimal)
|
||||
i := len(digits) - 1
|
||||
for ; i >= 0 && digits[i] == '9'; i-- {
|
||||
digits[i] = '0'
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
digits[i]++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// digits is all zeros
|
||||
digits[0] = '1'
|
||||
digits = append(digits, '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
return string(digits)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// decDecimal returns the decimal string decremented by 1, or the empty string
|
||||
// if the decimal is all zeroes.
|
||||
func decDecimal(decimal string) string {
|
||||
// Scan right to left turning 0s to 9s until you find a digit to decrement.
|
||||
digits := []byte(decimal)
|
||||
i := len(digits) - 1
|
||||
for ; i >= 0 && digits[i] == '0'; i-- {
|
||||
digits[i] = '9'
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
// decimal is all zeros
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i == 0 && digits[i] == '1' && len(digits) > 1 {
|
||||
digits = digits[1:]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
digits[i]--
|
||||
}
|
||||
return string(digits)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsPseudoVersion reports whether v is a pseudo-version.
|
||||
func IsPseudoVersion(v string) bool {
|
||||
return strings.Count(v, "-") >= 2 && semver.IsValid(v) && pseudoVersionRE.MatchString(v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsZeroPseudoVersion returns whether v is a pseudo-version with a zero base,
|
||||
// timestamp, and revision, as returned by ZeroPseudoVersion.
|
||||
func IsZeroPseudoVersion(v string) bool {
|
||||
return v == ZeroPseudoVersion(semver.Major(v))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PseudoVersionTime returns the time stamp of the pseudo-version v.
|
||||
// It returns an error if v is not a pseudo-version or if the time stamp
|
||||
// embedded in the pseudo-version is not a valid time.
|
||||
func PseudoVersionTime(v string) (time.Time, error) {
|
||||
_, timestamp, _, _, err := parsePseudoVersion(v)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return time.Time{}, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
t, err := time.Parse("20060102150405", timestamp)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return time.Time{}, &InvalidVersionError{
|
||||
Version: v,
|
||||
Pseudo: true,
|
||||
Err: fmt.Errorf("malformed time %q", timestamp),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PseudoVersionRev returns the revision identifier of the pseudo-version v.
|
||||
// It returns an error if v is not a pseudo-version.
|
||||
func PseudoVersionRev(v string) (rev string, err error) {
|
||||
_, _, rev, _, err = parsePseudoVersion(v)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PseudoVersionBase returns the canonical parent version, if any, upon which
|
||||
// the pseudo-version v is based.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If v has no parent version (that is, if it is "vX.0.0-[…]"),
|
||||
// PseudoVersionBase returns the empty string and a nil error.
|
||||
func PseudoVersionBase(v string) (string, error) {
|
||||
base, _, _, build, err := parsePseudoVersion(v)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch pre := semver.Prerelease(base); pre {
|
||||
case "":
|
||||
// vX.0.0-yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456 → ""
|
||||
if build != "" {
|
||||
// Pseudo-versions of the form vX.0.0-yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456+incompatible
|
||||
// are nonsensical: the "vX.0.0-" prefix implies that there is no parent tag,
|
||||
// but the "+incompatible" suffix implies that the major version of
|
||||
// the parent tag is not compatible with the module's import path.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// There are a few such entries in the index generated by proxy.golang.org,
|
||||
// but we believe those entries were generated by the proxy itself.
|
||||
return "", &InvalidVersionError{
|
||||
Version: v,
|
||||
Pseudo: true,
|
||||
Err: fmt.Errorf("lacks base version, but has build metadata %q", build),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "", nil
|
||||
|
||||
case "-0":
|
||||
// vX.Y.(Z+1)-0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456 → vX.Y.Z
|
||||
// vX.Y.(Z+1)-0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456+incompatible → vX.Y.Z+incompatible
|
||||
base = strings.TrimSuffix(base, pre)
|
||||
i := strings.LastIndexByte(base, '.')
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
panic("base from parsePseudoVersion missing patch number: " + base)
|
||||
}
|
||||
patch := decDecimal(base[i+1:])
|
||||
if patch == "" {
|
||||
// vX.0.0-0 is invalid, but has been observed in the wild in the index
|
||||
// generated by requests to proxy.golang.org.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// NOTE(bcmills): I cannot find a historical bug that accounts for
|
||||
// pseudo-versions of this form, nor have I seen such versions in any
|
||||
// actual go.mod files. If we find actual examples of this form and a
|
||||
// reasonable theory of how they came into existence, it seems fine to
|
||||
// treat them as equivalent to vX.0.0 (especially since the invalid
|
||||
// pseudo-versions have lower precedence than the real ones). For now, we
|
||||
// reject them.
|
||||
return "", &InvalidVersionError{
|
||||
Version: v,
|
||||
Pseudo: true,
|
||||
Err: fmt.Errorf("version before %s would have negative patch number", base),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return base[:i+1] + patch + build, nil
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// vX.Y.Z-pre.0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456 → vX.Y.Z-pre
|
||||
// vX.Y.Z-pre.0.yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdef123456+incompatible → vX.Y.Z-pre+incompatible
|
||||
if !strings.HasSuffix(base, ".0") {
|
||||
panic(`base from parsePseudoVersion missing ".0" before date: ` + base)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strings.TrimSuffix(base, ".0") + build, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var errPseudoSyntax = errors.New("syntax error")
|
||||
|
||||
func parsePseudoVersion(v string) (base, timestamp, rev, build string, err error) {
|
||||
if !IsPseudoVersion(v) {
|
||||
return "", "", "", "", &InvalidVersionError{
|
||||
Version: v,
|
||||
Pseudo: true,
|
||||
Err: errPseudoSyntax,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
build = semver.Build(v)
|
||||
v = strings.TrimSuffix(v, build)
|
||||
j := strings.LastIndex(v, "-")
|
||||
v, rev = v[:j], v[j+1:]
|
||||
i := strings.LastIndex(v, "-")
|
||||
if j := strings.LastIndex(v, "."); j > i {
|
||||
base = v[:j] // "vX.Y.Z-pre.0" or "vX.Y.(Z+1)-0"
|
||||
timestamp = v[j+1:]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
base = v[:i] // "vX.0.0"
|
||||
timestamp = v[i+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return base, timestamp, rev, build, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,8 +22,6 @@
|
|||
// as shorthands for vMAJOR.0.0 and vMAJOR.MINOR.0.
|
||||
package semver
|
||||
|
||||
import "sort"
|
||||
|
||||
// parsed returns the parsed form of a semantic version string.
|
||||
type parsed struct {
|
||||
major string
|
||||
|
|
@ -152,24 +150,6 @@ func Max(v, w string) string {
|
|||
return w
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ByVersion implements sort.Interface for sorting semantic version strings.
|
||||
type ByVersion []string
|
||||
|
||||
func (vs ByVersion) Len() int { return len(vs) }
|
||||
func (vs ByVersion) Swap(i, j int) { vs[i], vs[j] = vs[j], vs[i] }
|
||||
func (vs ByVersion) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
cmp := Compare(vs[i], vs[j])
|
||||
if cmp != 0 {
|
||||
return cmp < 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return vs[i] < vs[j]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sort sorts a list of semantic version strings using ByVersion.
|
||||
func Sort(list []string) {
|
||||
sort.Sort(ByVersion(list))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parse(v string) (p parsed, ok bool) {
|
||||
if v == "" || v[0] != 'v' {
|
||||
p.err = "missing v prefix"
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"bufio"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
|
|
@ -46,18 +45,14 @@ func ParseProfiles(fileName string) ([]*Profile, error) {
|
|||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer pf.Close()
|
||||
return ParseProfilesFromReader(pf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseProfilesFromReader parses profile data from the Reader and
|
||||
// returns a Profile for each source file described therein.
|
||||
func ParseProfilesFromReader(rd io.Reader) ([]*Profile, error) {
|
||||
files := make(map[string]*Profile)
|
||||
buf := bufio.NewReader(pf)
|
||||
// First line is "mode: foo", where foo is "set", "count", or "atomic".
|
||||
// Rest of file is in the format
|
||||
// encoding/base64/base64.go:34.44,37.40 3 1
|
||||
// where the fields are: name.go:line.column,line.column numberOfStatements count
|
||||
files := make(map[string]*Profile)
|
||||
s := bufio.NewScanner(rd)
|
||||
s := bufio.NewScanner(buf)
|
||||
mode := ""
|
||||
for s.Scan() {
|
||||
line := s.Text()
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -51,11 +51,6 @@ type asmArch struct {
|
|||
bigEndian bool
|
||||
stack string
|
||||
lr bool
|
||||
// retRegs is a list of registers for return value in register ABI (ABIInternal).
|
||||
// For now, as we only check whether we write to any result, here we only need to
|
||||
// include the first integer register and first floating-point register. Accessing
|
||||
// any of them counts as writing to result.
|
||||
retRegs []string
|
||||
// calculated during initialization
|
||||
sizes types.Sizes
|
||||
intSize int
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,8 +79,8 @@ type asmVar struct {
|
|||
var (
|
||||
asmArch386 = asmArch{name: "386", bigEndian: false, stack: "SP", lr: false}
|
||||
asmArchArm = asmArch{name: "arm", bigEndian: false, stack: "R13", lr: true}
|
||||
asmArchArm64 = asmArch{name: "arm64", bigEndian: false, stack: "RSP", lr: true, retRegs: []string{"R0", "F0"}}
|
||||
asmArchAmd64 = asmArch{name: "amd64", bigEndian: false, stack: "SP", lr: false, retRegs: []string{"AX", "X0"}}
|
||||
asmArchArm64 = asmArch{name: "arm64", bigEndian: false, stack: "RSP", lr: true}
|
||||
asmArchAmd64 = asmArch{name: "amd64", bigEndian: false, stack: "SP", lr: false}
|
||||
asmArchMips = asmArch{name: "mips", bigEndian: true, stack: "R29", lr: true}
|
||||
asmArchMipsLE = asmArch{name: "mipsle", bigEndian: false, stack: "R29", lr: true}
|
||||
asmArchMips64 = asmArch{name: "mips64", bigEndian: true, stack: "R29", lr: true}
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,7 +137,7 @@ var (
|
|||
asmSP = re(`[^+\-0-9](([0-9]+)\(([A-Z0-9]+)\))`)
|
||||
asmOpcode = re(`^\s*(?:[A-Z0-9a-z_]+:)?\s*([A-Z]+)\s*([^,]*)(?:,\s*(.*))?`)
|
||||
ppc64Suff = re(`([BHWD])(ZU|Z|U|BR)?$`)
|
||||
abiSuff = re(`^(.+)<(ABI.+)>$`)
|
||||
abiSuff = re(`^(.+)<ABI.+>$`)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -190,7 +185,6 @@ Files:
|
|||
var (
|
||||
fn *asmFunc
|
||||
fnName string
|
||||
abi string
|
||||
localSize, argSize int
|
||||
wroteSP bool
|
||||
noframe bool
|
||||
|
|
@ -201,22 +195,18 @@ Files:
|
|||
flushRet := func() {
|
||||
if fn != nil && fn.vars["ret"] != nil && !haveRetArg && len(retLine) > 0 {
|
||||
v := fn.vars["ret"]
|
||||
resultStr := fmt.Sprintf("%d-byte ret+%d(FP)", v.size, v.off)
|
||||
if abi == "ABIInternal" {
|
||||
resultStr = "result register"
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, line := range retLine {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(analysisutil.LineStart(tf, line), "[%s] %s: RET without writing to %s", arch, fnName, resultStr)
|
||||
pass.Reportf(analysisutil.LineStart(tf, line), "[%s] %s: RET without writing to %d-byte ret+%d(FP)", arch, fnName, v.size, v.off)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
retLine = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
trimABI := func(fnName string) (string, string) {
|
||||
trimABI := func(fnName string) string {
|
||||
m := abiSuff.FindStringSubmatch(fnName)
|
||||
if m != nil {
|
||||
return m[1], m[2]
|
||||
return m[1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fnName, ""
|
||||
return fnName
|
||||
}
|
||||
for lineno, line := range lines {
|
||||
lineno++
|
||||
|
|
@ -283,12 +273,11 @@ Files:
|
|||
// log.Printf("%s:%d: [%s] cannot check cross-package assembly function: %s is in package %s", fname, lineno, arch, fnName, pkgPath)
|
||||
fn = nil
|
||||
fnName = ""
|
||||
abi = ""
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Trim off optional ABI selector.
|
||||
fnName, abi = trimABI(fnName)
|
||||
fnName := trimABI(fnName)
|
||||
flag := m[3]
|
||||
fn = knownFunc[fnName][arch]
|
||||
if fn != nil {
|
||||
|
|
@ -316,7 +305,6 @@ Files:
|
|||
flushRet()
|
||||
fn = nil
|
||||
fnName = ""
|
||||
abi = ""
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -347,15 +335,6 @@ Files:
|
|||
haveRetArg = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if abi == "ABIInternal" && !haveRetArg {
|
||||
for _, reg := range archDef.retRegs {
|
||||
if strings.Contains(line, reg) {
|
||||
haveRetArg = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, m := range asmSP.FindAllStringSubmatch(line, -1) {
|
||||
if m[3] != archDef.stack || wroteSP || noframe {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = `check for unkeyed composite literals
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,61 +67,41 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
// skip whitelisted types
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var structuralTypes []types.Type
|
||||
switch typ := typ.(type) {
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.StructuralTerms(typ)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return // invalid type
|
||||
under := typ.Underlying()
|
||||
for {
|
||||
ptr, ok := under.(*types.Pointer)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, term := range terms {
|
||||
structuralTypes = append(structuralTypes, term.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
structuralTypes = append(structuralTypes, typ)
|
||||
under = ptr.Elem().Underlying()
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, typ := range structuralTypes {
|
||||
under := deref(typ.Underlying())
|
||||
if _, ok := under.(*types.Struct); !ok {
|
||||
// skip non-struct composite literals
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if isLocalType(pass, typ) {
|
||||
// allow unkeyed locally defined composite literal
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// check if the CompositeLit contains an unkeyed field
|
||||
allKeyValue := true
|
||||
for _, e := range cl.Elts {
|
||||
if _, ok := e.(*ast.KeyValueExpr); !ok {
|
||||
allKeyValue = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if allKeyValue {
|
||||
// all the composite literal fields are keyed
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(cl, "%s composite literal uses unkeyed fields", typeName)
|
||||
if _, ok := under.(*types.Struct); !ok {
|
||||
// skip non-struct composite literals
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if isLocalType(pass, typ) {
|
||||
// allow unkeyed locally defined composite literal
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// check if the CompositeLit contains an unkeyed field
|
||||
allKeyValue := true
|
||||
for _, e := range cl.Elts {
|
||||
if _, ok := e.(*ast.KeyValueExpr); !ok {
|
||||
allKeyValue = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if allKeyValue {
|
||||
// all the composite literal fields are keyed
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(cl, "%s composite literal uses unkeyed fields", typeName)
|
||||
})
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func deref(typ types.Type) types.Type {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
ptr, ok := typ.(*types.Pointer)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
typ = ptr.Elem().Underlying()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return typ
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func isLocalType(pass *analysis.Pass, typ types.Type) bool {
|
||||
switch x := typ.(type) {
|
||||
case *types.Struct:
|
||||
|
|
@ -133,8 +112,6 @@ func isLocalType(pass *analysis.Pass, typ types.Type) bool {
|
|||
case *types.Named:
|
||||
// names in package foo are local to foo_test too
|
||||
return strings.TrimSuffix(x.Obj().Pkg().Path(), "_test") == strings.TrimSuffix(pass.Pkg.Path(), "_test")
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
return strings.TrimSuffix(x.Obj().Pkg().Path(), "_test") == strings.TrimSuffix(pass.Pkg.Path(), "_test")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/internal/analysisutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = `check for locks erroneously passed by value
|
||||
|
|
@ -146,7 +145,7 @@ func checkCopyLocksCallExpr(pass *analysis.Pass, ce *ast.CallExpr) {
|
|||
func checkCopyLocksFunc(pass *analysis.Pass, name string, recv *ast.FieldList, typ *ast.FuncType) {
|
||||
if recv != nil && len(recv.List) > 0 {
|
||||
expr := recv.List[0].Type
|
||||
if path := lockPath(pass.Pkg, pass.TypesInfo.Types[expr].Type, nil); path != nil {
|
||||
if path := lockPath(pass.Pkg, pass.TypesInfo.Types[expr].Type); path != nil {
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(expr, "%s passes lock by value: %v", name, path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -154,7 +153,7 @@ func checkCopyLocksFunc(pass *analysis.Pass, name string, recv *ast.FieldList, t
|
|||
if typ.Params != nil {
|
||||
for _, field := range typ.Params.List {
|
||||
expr := field.Type
|
||||
if path := lockPath(pass.Pkg, pass.TypesInfo.Types[expr].Type, nil); path != nil {
|
||||
if path := lockPath(pass.Pkg, pass.TypesInfo.Types[expr].Type); path != nil {
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(expr, "%s passes lock by value: %v", name, path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -200,12 +199,12 @@ func checkCopyLocksRangeVar(pass *analysis.Pass, rtok token.Token, e ast.Expr) {
|
|||
if typ == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if path := lockPath(pass.Pkg, typ, nil); path != nil {
|
||||
if path := lockPath(pass.Pkg, typ); path != nil {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(e.Pos(), "range var %s copies lock: %v", analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, e), path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type typePath []string
|
||||
type typePath []types.Type
|
||||
|
||||
// String pretty-prints a typePath.
|
||||
func (path typePath) String() string {
|
||||
|
|
@ -216,7 +215,7 @@ func (path typePath) String() string {
|
|||
fmt.Fprint(&buf, " contains ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The human-readable path is in reverse order, outermost to innermost.
|
||||
fmt.Fprint(&buf, path[n-i-1])
|
||||
fmt.Fprint(&buf, path[n-i-1].String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -235,57 +234,16 @@ func lockPathRhs(pass *analysis.Pass, x ast.Expr) typePath {
|
|||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lockPath(pass.Pkg, pass.TypesInfo.Types[x].Type, nil)
|
||||
return lockPath(pass.Pkg, pass.TypesInfo.Types[x].Type)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lockPath returns a typePath describing the location of a lock value
|
||||
// contained in typ. If there is no contained lock, it returns nil.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The seenTParams map is used to short-circuit infinite recursion via type
|
||||
// parameters.
|
||||
func lockPath(tpkg *types.Package, typ types.Type, seenTParams map[*typeparams.TypeParam]bool) typePath {
|
||||
func lockPath(tpkg *types.Package, typ types.Type) typePath {
|
||||
if typ == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if tpar, ok := typ.(*typeparams.TypeParam); ok {
|
||||
if seenTParams == nil {
|
||||
// Lazily allocate seenTParams, since the common case will not involve
|
||||
// any type parameters.
|
||||
seenTParams = make(map[*typeparams.TypeParam]bool)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if seenTParams[tpar] {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
seenTParams[tpar] = true
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.StructuralTerms(tpar)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil // invalid type
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, term := range terms {
|
||||
subpath := lockPath(tpkg, term.Type(), seenTParams)
|
||||
if len(subpath) > 0 {
|
||||
if term.Tilde() {
|
||||
// Prepend a tilde to our lock path entry to clarify the resulting
|
||||
// diagnostic message. Consider the following example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func _[Mutex interface{ ~sync.Mutex; M() }](m Mutex) {}
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Here the naive error message will be something like "passes lock
|
||||
// by value: Mutex contains sync.Mutex". This is misleading because
|
||||
// the local type parameter doesn't actually contain sync.Mutex,
|
||||
// which lacks the M method.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With tilde, it is clearer that the containment is via an
|
||||
// approximation element.
|
||||
subpath[len(subpath)-1] = "~" + subpath[len(subpath)-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return append(subpath, typ.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
atyp, ok := typ.Underlying().(*types.Array)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
|
|
@ -294,17 +252,6 @@ func lockPath(tpkg *types.Package, typ types.Type, seenTParams map[*typeparams.T
|
|||
typ = atyp.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ttyp, ok := typ.Underlying().(*types.Tuple)
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < ttyp.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
subpath := lockPath(tpkg, ttyp.At(i).Type(), seenTParams)
|
||||
if subpath != nil {
|
||||
return append(subpath, typ.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We're only interested in the case in which the underlying
|
||||
// type is a struct. (Interfaces and pointers are safe to copy.)
|
||||
styp, ok := typ.Underlying().(*types.Struct)
|
||||
|
|
@ -316,7 +263,7 @@ func lockPath(tpkg *types.Package, typ types.Type, seenTParams map[*typeparams.T
|
|||
// is a sync.Locker, but a value is not. This differentiates
|
||||
// embedded interfaces from embedded values.
|
||||
if types.Implements(types.NewPointer(typ), lockerType) && !types.Implements(typ, lockerType) {
|
||||
return []string{typ.String()}
|
||||
return []types.Type{typ}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// In go1.10, sync.noCopy did not implement Locker.
|
||||
|
|
@ -325,15 +272,15 @@ func lockPath(tpkg *types.Package, typ types.Type, seenTParams map[*typeparams.T
|
|||
if named, ok := typ.(*types.Named); ok &&
|
||||
named.Obj().Name() == "noCopy" &&
|
||||
named.Obj().Pkg().Path() == "sync" {
|
||||
return []string{typ.String()}
|
||||
return []types.Type{typ}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
nfields := styp.NumFields()
|
||||
for i := 0; i < nfields; i++ {
|
||||
ftyp := styp.Field(i).Type()
|
||||
subpath := lockPath(tpkg, ftyp, seenTParams)
|
||||
subpath := lockPath(tpkg, ftyp)
|
||||
if subpath != nil {
|
||||
return append(subpath, typ.String())
|
||||
return append(subpath, typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -187,11 +187,7 @@ func (c *CFGs) callMayReturn(call *ast.CallExpr) (r bool) {
|
|||
return false // panic never returns
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this a static call? Also includes static functions
|
||||
// parameterized by a type. Such functions may or may not
|
||||
// return depending on the parameter type, but in some
|
||||
// cases the answer is definite. We let ctrlflow figure
|
||||
// that out.
|
||||
// Is this a static call?
|
||||
fn := typeutil.StaticCallee(c.pass.TypesInfo, call)
|
||||
if fn == nil {
|
||||
return true // callee not statically known; be conservative
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -51,12 +51,6 @@ func assertableTo(v, t types.Type) *types.Func {
|
|||
if V == nil || T == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Mitigations for interface comparisons and generics.
|
||||
// TODO(https://github.com/golang/go/issues/50658): Support more precise conclusion.
|
||||
if isParameterized(V) || isParameterized(T) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f, wrongType := types.MissingMethod(V, T, false); wrongType {
|
||||
return f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2022 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
package ifaceassert
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// isParameterized reports whether typ contains any of the type parameters of tparams.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// NOTE: Adapted from go/types/infer.go. If that is exported in a future release remove this copy.
|
||||
func isParameterized(typ types.Type) bool {
|
||||
w := tpWalker{
|
||||
seen: make(map[types.Type]bool),
|
||||
}
|
||||
return w.isParameterized(typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type tpWalker struct {
|
||||
seen map[types.Type]bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *tpWalker) isParameterized(typ types.Type) (res bool) {
|
||||
// detect cycles
|
||||
if x, ok := w.seen[typ]; ok {
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.seen[typ] = false
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
w.seen[typ] = res
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
switch t := typ.(type) {
|
||||
case nil, *types.Basic: // TODO(gri) should nil be handled here?
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Array:
|
||||
return w.isParameterized(t.Elem())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Slice:
|
||||
return w.isParameterized(t.Elem())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Struct:
|
||||
for i, n := 0, t.NumFields(); i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if w.isParameterized(t.Field(i).Type()) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Pointer:
|
||||
return w.isParameterized(t.Elem())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Tuple:
|
||||
n := t.Len()
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if w.isParameterized(t.At(i).Type()) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Signature:
|
||||
// t.tparams may not be nil if we are looking at a signature
|
||||
// of a generic function type (or an interface method) that is
|
||||
// part of the type we're testing. We don't care about these type
|
||||
// parameters.
|
||||
// Similarly, the receiver of a method may declare (rather then
|
||||
// use) type parameters, we don't care about those either.
|
||||
// Thus, we only need to look at the input and result parameters.
|
||||
return w.isParameterized(t.Params()) || w.isParameterized(t.Results())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Interface:
|
||||
for i, n := 0, t.NumMethods(); i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if w.isParameterized(t.Method(i).Type()) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.InterfaceTermSet(t)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, term := range terms {
|
||||
if w.isParameterized(term.Type()) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Map:
|
||||
return w.isParameterized(t.Key()) || w.isParameterized(t.Elem())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Chan:
|
||||
return w.isParameterized(t.Elem())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Named:
|
||||
list := typeparams.NamedTypeArgs(t)
|
||||
for i, n := 0, list.Len(); i < n; i++ {
|
||||
if w.isParameterized(list.At(i)) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(t) // unreachable
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = `check for useless comparisons between functions and nil
|
||||
|
|
@ -60,12 +59,6 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
obj = pass.TypesInfo.Uses[v]
|
||||
case *ast.SelectorExpr:
|
||||
obj = pass.TypesInfo.Uses[v.Sel]
|
||||
case *ast.IndexExpr, *typeparams.IndexListExpr:
|
||||
// Check generic functions such as "f[T1,T2]".
|
||||
x, _, _, _ := typeparams.UnpackIndexExpr(v)
|
||||
if id, ok := x.(*ast.Ident); ok {
|
||||
obj = pass.TypesInfo.Uses[id]
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -135,11 +135,6 @@ func runFunc(pass *analysis.Pass, fn *ssa.Function) {
|
|||
if nilnessOf(stack, instr.X) == isnil {
|
||||
reportf("nilpanic", instr.Pos(), "panic with nil value")
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *ssa.SliceToArrayPointer:
|
||||
nn := nilnessOf(stack, instr.X)
|
||||
if nn == isnil && slice2ArrayPtrLen(instr) > 0 {
|
||||
reportf("conversionpanic", instr.Pos(), "nil slice being cast to an array of len > 0 will always panic")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -264,26 +259,6 @@ func nilnessOf(stack []fact, v ssa.Value) nilness {
|
|||
if underlying := nilnessOf(stack, v.X); underlying != unknown {
|
||||
return underlying
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *ssa.SliceToArrayPointer:
|
||||
nn := nilnessOf(stack, v.X)
|
||||
if slice2ArrayPtrLen(v) > 0 {
|
||||
if nn == isnil {
|
||||
// We know that *(*[1]byte)(nil) is going to panic because of the
|
||||
// conversion. So return unknown to the caller, prevent useless
|
||||
// nil deference reporting due to * operator.
|
||||
return unknown
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Otherwise, the conversion will yield a non-nil pointer to array.
|
||||
// Note that the instruction can still panic if array length greater
|
||||
// than slice length. If the value is used by another instruction,
|
||||
// that instruction can assume the panic did not happen when that
|
||||
// instruction is reached.
|
||||
return isnonnil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// In case array length is zero, the conversion result depends on nilness of the slice.
|
||||
if nn != unknown {
|
||||
return nn
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is value intrinsically nil or non-nil?
|
||||
|
|
@ -317,10 +292,6 @@ func nilnessOf(stack []fact, v ssa.Value) nilness {
|
|||
return unknown
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func slice2ArrayPtrLen(v *ssa.SliceToArrayPointer) int64 {
|
||||
return v.Type().(*types.Pointer).Elem().Underlying().(*types.Array).Len()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If b ends with an equality comparison, eq returns the operation and
|
||||
// its true (equal) and false (not equal) successors.
|
||||
func eq(b *ssa.BasicBlock) (op *ssa.BinOp, tsucc, fsucc *ssa.BasicBlock) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/internal/analysisutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/types/typeutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
|
|
@ -453,15 +452,8 @@ func stringConstantArg(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr, idx int) (string
|
|||
if idx >= len(call.Args) {
|
||||
return "", false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return stringConstantExpr(pass, call.Args[idx])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// stringConstantExpr returns expression's string constant value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ("", false) is returned if expression isn't a string
|
||||
// constant.
|
||||
func stringConstantExpr(pass *analysis.Pass, expr ast.Expr) (string, bool) {
|
||||
lit := pass.TypesInfo.Types[expr].Value
|
||||
arg := call.Args[idx]
|
||||
lit := pass.TypesInfo.Types[arg].Value
|
||||
if lit != nil && lit.Kind() == constant.String {
|
||||
return constant.StringVal(lit), true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -498,7 +490,7 @@ func printfNameAndKind(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr) (fn *types.Func,
|
|||
_, ok = isPrint[strings.ToLower(fn.Name())]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
if fn.FullName() == "fmt.Errorf" {
|
||||
if fn.Name() == "Errorf" {
|
||||
kind = KindErrorf
|
||||
} else if strings.HasSuffix(fn.Name(), "f") {
|
||||
kind = KindPrintf
|
||||
|
|
@ -521,12 +513,7 @@ func printfNameAndKind(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr) (fn *types.Func,
|
|||
func isFormatter(typ types.Type) bool {
|
||||
// If the type is an interface, the value it holds might satisfy fmt.Formatter.
|
||||
if _, ok := typ.Underlying().(*types.Interface); ok {
|
||||
// Don't assume type parameters could be formatters. With the greater
|
||||
// expressiveness of constraint interface syntax we expect more type safety
|
||||
// when using type parameters.
|
||||
if !typeparams.IsTypeParam(typ) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
obj, _, _ := types.LookupFieldOrMethod(typ, false, nil, "Format")
|
||||
fn, ok := obj.(*types.Func)
|
||||
|
|
@ -603,9 +590,12 @@ func checkPrintf(pass *analysis.Pass, kind Kind, call *ast.CallExpr, fn *types.F
|
|||
}
|
||||
if state.verb == 'w' {
|
||||
switch kind {
|
||||
case KindNone, KindPrint, KindPrintf:
|
||||
case KindNone, KindPrint:
|
||||
pass.Reportf(call.Pos(), "%s does not support error-wrapping directive %%w", state.name)
|
||||
return
|
||||
case KindPrintf:
|
||||
pass.Reportf(call.Pos(), "%s call has error-wrapping directive %%w, which is only supported for functions backed by fmt.Errorf", state.name)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if anyW {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(call.Pos(), "%s call has more than one error-wrapping directive %%w", state.name)
|
||||
|
|
@ -847,9 +837,8 @@ func okPrintfArg(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr, state *formatState) (o
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Could current arg implement fmt.Formatter?
|
||||
// Skip check for the %w verb, which requires an error.
|
||||
formatter := false
|
||||
if v.typ != argError && state.argNum < len(call.Args) {
|
||||
if state.argNum < len(call.Args) {
|
||||
if tv, ok := pass.TypesInfo.Types[call.Args[state.argNum]]; ok {
|
||||
formatter = isFormatter(tv.Type)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -885,12 +874,8 @@ func okPrintfArg(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr, state *formatState) (o
|
|||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
arg := call.Args[argNum]
|
||||
if reason, ok := matchArgType(pass, argInt, arg); !ok {
|
||||
details := ""
|
||||
if reason != "" {
|
||||
details = " (" + reason + ")"
|
||||
}
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(call, "%s format %s uses non-int %s%s as argument of *", state.name, state.format, analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, arg), details)
|
||||
if !matchArgType(pass, argInt, nil, arg) {
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(call, "%s format %s uses non-int %s as argument of *", state.name, state.format, analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, arg))
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -907,16 +892,12 @@ func okPrintfArg(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr, state *formatState) (o
|
|||
pass.ReportRangef(call, "%s format %s arg %s is a func value, not called", state.name, state.format, analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, arg))
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if reason, ok := matchArgType(pass, v.typ, arg); !ok {
|
||||
if !matchArgType(pass, v.typ, nil, arg) {
|
||||
typeString := ""
|
||||
if typ := pass.TypesInfo.Types[arg].Type; typ != nil {
|
||||
typeString = typ.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
details := ""
|
||||
if reason != "" {
|
||||
details = " (" + reason + ")"
|
||||
}
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(call, "%s format %s has arg %s of wrong type %s%s", state.name, state.format, analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, arg), typeString, details)
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(call, "%s format %s has arg %s of wrong type %s", state.name, state.format, analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, arg), typeString)
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.typ&argString != 0 && v.verb != 'T' && !bytes.Contains(state.flags, []byte{'#'}) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1074,10 +1055,10 @@ func checkPrint(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr, fn *types.Func) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
arg := args[0]
|
||||
if s, ok := stringConstantExpr(pass, arg); ok {
|
||||
// Ignore trailing % character
|
||||
if lit, ok := arg.(*ast.BasicLit); ok && lit.Kind == token.STRING {
|
||||
// Ignore trailing % character in lit.Value.
|
||||
// The % in "abc 0.0%" couldn't be a formatting directive.
|
||||
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, "%")
|
||||
s := strings.TrimSuffix(lit.Value, `%"`)
|
||||
if strings.Contains(s, "%") {
|
||||
m := printFormatRE.FindStringSubmatch(s)
|
||||
if m != nil {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1088,8 +1069,9 @@ func checkPrint(pass *analysis.Pass, call *ast.CallExpr, fn *types.Func) {
|
|||
if strings.HasSuffix(fn.Name(), "ln") {
|
||||
// The last item, if a string, should not have a newline.
|
||||
arg = args[len(args)-1]
|
||||
if s, ok := stringConstantExpr(pass, arg); ok {
|
||||
if strings.HasSuffix(s, "\n") {
|
||||
if lit, ok := arg.(*ast.BasicLit); ok && lit.Kind == token.STRING {
|
||||
str, _ := strconv.Unquote(lit.Value)
|
||||
if strings.HasSuffix(str, "\n") {
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(call, "%s arg list ends with redundant newline", fn.FullName())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,60 +5,45 @@
|
|||
package printf
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/internal/analysisutil"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var errorType = types.Universe.Lookup("error").Type().Underlying().(*types.Interface)
|
||||
|
||||
// matchArgType reports an error if printf verb t is not appropriate for
|
||||
// operand arg.
|
||||
// matchArgType reports an error if printf verb t is not appropriate
|
||||
// for operand arg.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If arg is a type parameter, the verb t must be appropriate for every type in
|
||||
// the type parameter type set.
|
||||
func matchArgType(pass *analysis.Pass, t printfArgType, arg ast.Expr) (reason string, ok bool) {
|
||||
// typ is used only for recursive calls; external callers must supply nil.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (Recursion arises from the compound types {map,chan,slice} which
|
||||
// may be printed with %d etc. if that is appropriate for their element
|
||||
// types.)
|
||||
func matchArgType(pass *analysis.Pass, t printfArgType, typ types.Type, arg ast.Expr) bool {
|
||||
return matchArgTypeInternal(pass, t, typ, arg, make(map[types.Type]bool))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// matchArgTypeInternal is the internal version of matchArgType. It carries a map
|
||||
// remembering what types are in progress so we don't recur when faced with recursive
|
||||
// types or mutually recursive types.
|
||||
func matchArgTypeInternal(pass *analysis.Pass, t printfArgType, typ types.Type, arg ast.Expr, inProgress map[types.Type]bool) bool {
|
||||
// %v, %T accept any argument type.
|
||||
if t == anyType {
|
||||
return "", true
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
typ := pass.TypesInfo.Types[arg].Type
|
||||
if typ == nil {
|
||||
return "", true // probably a type check problem
|
||||
// external call
|
||||
typ = pass.TypesInfo.Types[arg].Type
|
||||
if typ == nil {
|
||||
return true // probably a type check problem
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m := &argMatcher{t: t, seen: make(map[types.Type]bool)}
|
||||
ok = m.match(typ, true)
|
||||
return m.reason, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// argMatcher recursively matches types against the printfArgType t.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To short-circuit recursion, it keeps track of types that have already been
|
||||
// matched (or are in the process of being matched) via the seen map. Recursion
|
||||
// arises from the compound types {map,chan,slice} which may be printed with %d
|
||||
// etc. if that is appropriate for their element types, as well as from type
|
||||
// parameters, which are expanded to the constituents of their type set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The reason field may be set to report the cause of the mismatch.
|
||||
type argMatcher struct {
|
||||
t printfArgType
|
||||
seen map[types.Type]bool
|
||||
reason string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// match checks if typ matches m's printf arg type. If topLevel is true, typ is
|
||||
// the actual type of the printf arg, for which special rules apply. As a
|
||||
// special case, top level type parameters pass topLevel=true when checking for
|
||||
// matches among the constituents of their type set, as type arguments will
|
||||
// replace the type parameter at compile time.
|
||||
func (m *argMatcher) match(typ types.Type, topLevel bool) bool {
|
||||
// %w accepts only errors.
|
||||
if m.t == argError {
|
||||
if t == argError {
|
||||
return types.ConvertibleTo(typ, errorType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,122 +51,65 @@ func (m *argMatcher) match(typ types.Type, topLevel bool) bool {
|
|||
if isFormatter(typ) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If we can use a string, might arg (dynamically) implement the Stringer or Error interface?
|
||||
if m.t&argString != 0 && isConvertibleToString(typ) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typ, _ := typ.(*typeparams.TypeParam); typ != nil {
|
||||
// Avoid infinite recursion through type parameters.
|
||||
if m.seen[typ] {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.seen[typ] = true
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.StructuralTerms(typ)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return true // invalid type (possibly an empty type set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(terms) == 0 {
|
||||
// No restrictions on the underlying of typ. Type parameters implementing
|
||||
// error, fmt.Formatter, or fmt.Stringer were handled above, and %v and
|
||||
// %T was handled in matchType. We're about to check restrictions the
|
||||
// underlying; if the underlying type is unrestricted there must be an
|
||||
// element of the type set that violates one of the arg type checks
|
||||
// below, so we can safely return false here.
|
||||
|
||||
if m.t == anyType { // anyType must have already been handled.
|
||||
panic("unexpected printfArgType")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Only report a reason if typ is the argument type, otherwise it won't
|
||||
// make sense. Note that it is not sufficient to check if topLevel == here,
|
||||
// as type parameters can have a type set consisting of other type
|
||||
// parameters.
|
||||
reportReason := len(m.seen) == 1
|
||||
|
||||
for _, term := range terms {
|
||||
if !m.match(term.Type(), topLevel) {
|
||||
if reportReason {
|
||||
if term.Tilde() {
|
||||
m.reason = fmt.Sprintf("contains ~%s", term.Type())
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
m.reason = fmt.Sprintf("contains %s", term.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t&argString != 0 && isConvertibleToString(pass, typ) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
typ = typ.Underlying()
|
||||
if m.seen[typ] {
|
||||
// We've already considered typ, or are in the process of considering it.
|
||||
// In case we've already considered typ, it must have been valid (else we
|
||||
// would have stopped matching). In case we're in the process of
|
||||
// considering it, we must avoid infinite recursion.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// There are some pathological cases where returning true here is
|
||||
// incorrect, for example `type R struct { F []R }`, but these are
|
||||
// acceptable false negatives.
|
||||
if inProgress[typ] {
|
||||
// We're already looking at this type. The call that started it will take care of it.
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.seen[typ] = true
|
||||
inProgress[typ] = true
|
||||
|
||||
switch typ := typ.(type) {
|
||||
case *types.Signature:
|
||||
return m.t == argPointer
|
||||
return t == argPointer
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Map:
|
||||
if m.t == argPointer {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Recur: map[int]int matches %d.
|
||||
return m.match(typ.Key(), false) && m.match(typ.Elem(), false)
|
||||
return t == argPointer ||
|
||||
// Recur: map[int]int matches %d.
|
||||
(matchArgTypeInternal(pass, t, typ.Key(), arg, inProgress) && matchArgTypeInternal(pass, t, typ.Elem(), arg, inProgress))
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Chan:
|
||||
return m.t&argPointer != 0
|
||||
return t&argPointer != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Array:
|
||||
// Same as slice.
|
||||
if types.Identical(typ.Elem().Underlying(), types.Typ[types.Byte]) && m.t&argString != 0 {
|
||||
if types.Identical(typ.Elem().Underlying(), types.Typ[types.Byte]) && t&argString != 0 {
|
||||
return true // %s matches []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Recur: []int matches %d.
|
||||
return m.match(typ.Elem(), false)
|
||||
return matchArgTypeInternal(pass, t, typ.Elem(), arg, inProgress)
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Slice:
|
||||
// Same as array.
|
||||
if types.Identical(typ.Elem().Underlying(), types.Typ[types.Byte]) && m.t&argString != 0 {
|
||||
if types.Identical(typ.Elem().Underlying(), types.Typ[types.Byte]) && t&argString != 0 {
|
||||
return true // %s matches []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
if m.t == argPointer {
|
||||
if t == argPointer {
|
||||
return true // %p prints a slice's 0th element
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Recur: []int matches %d. But watch out for
|
||||
// type T []T
|
||||
// If the element is a pointer type (type T[]*T), it's handled fine by the Pointer case below.
|
||||
return m.match(typ.Elem(), false)
|
||||
return matchArgTypeInternal(pass, t, typ.Elem(), arg, inProgress)
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Pointer:
|
||||
// Ugly, but dealing with an edge case: a known pointer to an invalid type,
|
||||
// probably something from a failed import.
|
||||
if typ.Elem() == types.Typ[types.Invalid] {
|
||||
if typ.Elem().String() == "invalid type" {
|
||||
if false {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(arg.Pos(), "printf argument %v is pointer to invalid or unknown type", analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, arg))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true // special case
|
||||
}
|
||||
// If it's actually a pointer with %p, it prints as one.
|
||||
if m.t == argPointer {
|
||||
if t == argPointer {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typeparams.IsTypeParam(typ.Elem()) {
|
||||
return true // We don't know whether the logic below applies. Give up.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
under := typ.Elem().Underlying()
|
||||
switch under.(type) {
|
||||
case *types.Struct: // see below
|
||||
|
|
@ -190,31 +118,19 @@ func (m *argMatcher) match(typ types.Type, topLevel bool) bool {
|
|||
case *types.Map: // see below
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// Check whether the rest can print pointers.
|
||||
return m.t&argPointer != 0
|
||||
return t&argPointer != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
// If it's a top-level pointer to a struct, array, slice, type param, or
|
||||
// If it's a top-level pointer to a struct, array, slice, or
|
||||
// map, that's equivalent in our analysis to whether we can
|
||||
// print the type being pointed to. Pointers in nested levels
|
||||
// are not supported to minimize fmt running into loops.
|
||||
if !topLevel {
|
||||
if len(inProgress) > 1 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m.match(under, false)
|
||||
return matchArgTypeInternal(pass, t, under, arg, inProgress)
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Struct:
|
||||
// report whether all the elements of the struct match the expected type. For
|
||||
// instance, with "%d" all the elements must be printable with the "%d" format.
|
||||
for i := 0; i < typ.NumFields(); i++ {
|
||||
typf := typ.Field(i)
|
||||
if !m.match(typf.Type(), false) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if m.t&argString != 0 && !typf.Exported() && isConvertibleToString(typf.Type()) {
|
||||
// Issue #17798: unexported Stringer or error cannot be properly formatted.
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
return matchStructArgType(pass, t, typ, arg, inProgress)
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Interface:
|
||||
// There's little we can do.
|
||||
|
|
@ -226,7 +142,7 @@ func (m *argMatcher) match(typ types.Type, topLevel bool) bool {
|
|||
switch typ.Kind() {
|
||||
case types.UntypedBool,
|
||||
types.Bool:
|
||||
return m.t&argBool != 0
|
||||
return t&argBool != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case types.UntypedInt,
|
||||
types.Int,
|
||||
|
|
@ -240,32 +156,35 @@ func (m *argMatcher) match(typ types.Type, topLevel bool) bool {
|
|||
types.Uint32,
|
||||
types.Uint64,
|
||||
types.Uintptr:
|
||||
return m.t&argInt != 0
|
||||
return t&argInt != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case types.UntypedFloat,
|
||||
types.Float32,
|
||||
types.Float64:
|
||||
return m.t&argFloat != 0
|
||||
return t&argFloat != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case types.UntypedComplex,
|
||||
types.Complex64,
|
||||
types.Complex128:
|
||||
return m.t&argComplex != 0
|
||||
return t&argComplex != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case types.UntypedString,
|
||||
types.String:
|
||||
return m.t&argString != 0
|
||||
return t&argString != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case types.UnsafePointer:
|
||||
return m.t&(argPointer|argInt) != 0
|
||||
return t&(argPointer|argInt) != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case types.UntypedRune:
|
||||
return m.t&(argInt|argRune) != 0
|
||||
return t&(argInt|argRune) != 0
|
||||
|
||||
case types.UntypedNil:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
|
||||
case types.Invalid:
|
||||
if false {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(arg.Pos(), "printf argument %v has invalid or unknown type", analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, arg))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true // Probably a type check problem.
|
||||
}
|
||||
panic("unreachable")
|
||||
|
|
@ -274,7 +193,7 @@ func (m *argMatcher) match(typ types.Type, topLevel bool) bool {
|
|||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func isConvertibleToString(typ types.Type) bool {
|
||||
func isConvertibleToString(pass *analysis.Pass, typ types.Type) bool {
|
||||
if bt, ok := typ.(*types.Basic); ok && bt.Kind() == types.UntypedNil {
|
||||
// We explicitly don't want untyped nil, which is
|
||||
// convertible to both of the interfaces below, as it
|
||||
|
|
@ -309,3 +228,19 @@ func hasBasicType(pass *analysis.Pass, x ast.Expr, kind types.BasicKind) bool {
|
|||
b, ok := t.(*types.Basic)
|
||||
return ok && b.Kind() == kind
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// matchStructArgType reports whether all the elements of the struct match the expected
|
||||
// type. For instance, with "%d" all the elements must be printable with the "%d" format.
|
||||
func matchStructArgType(pass *analysis.Pass, t printfArgType, typ *types.Struct, arg ast.Expr, inProgress map[types.Type]bool) bool {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < typ.NumFields(); i++ {
|
||||
typf := typ.Field(i)
|
||||
if !matchArgTypeInternal(pass, t, typf.Type(), arg, inProgress) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t&argString != 0 && !typf.Exported() && isConvertibleToString(pass, typf.Type()) {
|
||||
// Issue #17798: unexported Stringer or error cannot be properly formatted.
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,14 +14,11 @@ import (
|
|||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/constant"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/internal/analysisutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = "check for shifts that equal or exceed the width of the integer"
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,36 +93,9 @@ func checkLongShift(pass *analysis.Pass, node ast.Node, x, y ast.Expr) {
|
|||
if t == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var structuralTypes []types.Type
|
||||
switch t := t.(type) {
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.StructuralTerms(t)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return // invalid type
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, term := range terms {
|
||||
structuralTypes = append(structuralTypes, term.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
structuralTypes = append(structuralTypes, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
sizes := make(map[int64]struct{})
|
||||
for _, t := range structuralTypes {
|
||||
size := 8 * pass.TypesSizes.Sizeof(t)
|
||||
sizes[size] = struct{}{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
minSize := int64(math.MaxInt64)
|
||||
for size := range sizes {
|
||||
if size < minSize {
|
||||
minSize = size
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if amt >= minSize {
|
||||
size := 8 * pass.TypesSizes.Sizeof(t)
|
||||
if amt >= size {
|
||||
ident := analysisutil.Format(pass.Fset, x)
|
||||
qualifier := ""
|
||||
if len(sizes) > 1 {
|
||||
qualifier = "may be "
|
||||
}
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(node, "%s (%s%d bits) too small for shift of %d", ident, qualifier, minSize, amt)
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(node, "%s (%d bits) too small for shift of %d", ident, size, amt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -45,8 +45,7 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fnName := fn.FullName()
|
||||
if fnName != "sort.Slice" && fnName != "sort.SliceStable" && fnName != "sort.SliceIsSorted" {
|
||||
if fn.FullName() != "sort.Slice" {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,7 +115,7 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
pass.Report(analysis.Diagnostic{
|
||||
Pos: call.Pos(),
|
||||
End: call.End(),
|
||||
Message: fmt.Sprintf("%s's argument must be a slice; is called with %s", fnName, typ.String()),
|
||||
Message: fmt.Sprintf("sort.Slice's argument must be a slice; is called with %s", typ.String()),
|
||||
SuggestedFixes: fixes,
|
||||
})
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ var Analyzer = &analysis.Analyzer{
|
|||
// we let it go. But if it does have a fmt.ScanState, then the
|
||||
// rest has to match.
|
||||
var canonicalMethods = map[string]struct{ args, results []string }{
|
||||
"As": {[]string{"any"}, []string{"bool"}}, // errors.As
|
||||
"As": {[]string{"interface{}"}, []string{"bool"}}, // errors.As
|
||||
// "Flush": {{}, {"error"}}, // http.Flusher and jpeg.writer conflict
|
||||
"Format": {[]string{"=fmt.State", "rune"}, []string{}}, // fmt.Formatter
|
||||
"GobDecode": {[]string{"[]byte"}, []string{"error"}}, // gob.GobDecoder
|
||||
|
|
@ -194,9 +194,7 @@ func matchParams(pass *analysis.Pass, expect []string, actual *types.Tuple, pref
|
|||
func matchParamType(expect string, actual types.Type) bool {
|
||||
expect = strings.TrimPrefix(expect, "=")
|
||||
// Overkill but easy.
|
||||
t := typeString(actual)
|
||||
return t == expect ||
|
||||
(t == "any" || t == "interface{}") && (expect == "any" || expect == "interface{}")
|
||||
return typeString(actual) == expect
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var errorType = types.Universe.Lookup("error").Type().Underlying().(*types.Interface)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,12 +10,10 @@ import (
|
|||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = `check for string(int) conversions
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,35 +36,6 @@ var Analyzer = &analysis.Analyzer{
|
|||
Run: run,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// describe returns a string describing the type typ contained within the type
|
||||
// set of inType. If non-empty, inName is used as the name of inType (this is
|
||||
// necessary so that we can use alias type names that may not be reachable from
|
||||
// inType itself).
|
||||
func describe(typ, inType types.Type, inName string) string {
|
||||
name := inName
|
||||
if typ != inType {
|
||||
name = typeName(typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name == "" {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var parentheticals []string
|
||||
if underName := typeName(typ.Underlying()); underName != "" && underName != name {
|
||||
parentheticals = append(parentheticals, underName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typ != inType && inName != "" && inName != name {
|
||||
parentheticals = append(parentheticals, "in "+inName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(parentheticals) > 0 {
|
||||
name += " (" + strings.Join(parentheticals, ", ") + ")"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func typeName(typ types.Type) string {
|
||||
if v, _ := typ.(interface{ Name() string }); v != nil {
|
||||
return v.Name()
|
||||
|
|
@ -85,11 +54,6 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
inspect.Preorder(nodeFilter, func(n ast.Node) {
|
||||
call := n.(*ast.CallExpr)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(call.Args) != 1 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
arg := call.Args[0]
|
||||
|
||||
// Retrieve target type name.
|
||||
var tname *types.TypeName
|
||||
switch fun := call.Fun.(type) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -101,119 +65,62 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
if tname == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
target := tname.Name()
|
||||
|
||||
// In the conversion T(v) of a value v of type V to a target type T, we
|
||||
// look for types T0 in the type set of T and V0 in the type set of V, such
|
||||
// that V0->T0 is a problematic conversion. If T and V are not type
|
||||
// parameters, this amounts to just checking if V->T is a problematic
|
||||
// conversion.
|
||||
|
||||
// First, find a type T0 in T that has an underlying type of string.
|
||||
T := tname.Type()
|
||||
ttypes, err := structuralTypes(T)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return // invalid type
|
||||
// Check that target type T in T(v) has an underlying type of string.
|
||||
T, _ := tname.Type().Underlying().(*types.Basic)
|
||||
if T == nil || T.Kind() != types.String {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s := T.Name(); target != s {
|
||||
target += " (" + s + ")"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var T0 types.Type // string type in the type set of T
|
||||
|
||||
for _, tt := range ttypes {
|
||||
u, _ := tt.Underlying().(*types.Basic)
|
||||
if u != nil && u.Kind() == types.String {
|
||||
T0 = tt
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Check that type V of v has an underlying integral type that is not byte or rune.
|
||||
if len(call.Args) != 1 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if T0 == nil {
|
||||
// No target types have an underlying type of string.
|
||||
v := call.Args[0]
|
||||
vtyp := pass.TypesInfo.TypeOf(v)
|
||||
V, _ := vtyp.Underlying().(*types.Basic)
|
||||
if V == nil || V.Info()&types.IsInteger == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch V.Kind() {
|
||||
case types.Byte, types.Rune, types.UntypedRune:
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Next, find a type V0 in V that has an underlying integral type that is
|
||||
// not byte or rune.
|
||||
V := pass.TypesInfo.TypeOf(arg)
|
||||
vtypes, err := structuralTypes(V)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return // invalid type
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var V0 types.Type // integral type in the type set of V
|
||||
|
||||
for _, vt := range vtypes {
|
||||
u, _ := vt.Underlying().(*types.Basic)
|
||||
if u != nil && u.Info()&types.IsInteger != 0 {
|
||||
switch u.Kind() {
|
||||
case types.Byte, types.Rune, types.UntypedRune:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
V0 = vt
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if V0 == nil {
|
||||
// No source types are non-byte or rune integer types.
|
||||
// Retrieve source type name.
|
||||
source := typeName(vtyp)
|
||||
if source == "" {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
convertibleToRune := true // if true, we can suggest a fix
|
||||
for _, t := range vtypes {
|
||||
if !types.ConvertibleTo(t, types.Typ[types.Rune]) {
|
||||
convertibleToRune = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s := V.Name(); source != s {
|
||||
source += " (" + s + ")"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
target := describe(T0, T, tname.Name())
|
||||
source := describe(V0, V, typeName(V))
|
||||
|
||||
if target == "" || source == "" {
|
||||
return // something went wrong
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
diag := analysis.Diagnostic{
|
||||
Pos: n.Pos(),
|
||||
Message: fmt.Sprintf("conversion from %s to %s yields a string of one rune, not a string of digits (did you mean fmt.Sprint(x)?)", source, target),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if convertibleToRune {
|
||||
diag.SuggestedFixes = []analysis.SuggestedFix{
|
||||
SuggestedFixes: []analysis.SuggestedFix{
|
||||
{
|
||||
Message: "Did you mean to convert a rune to a string?",
|
||||
TextEdits: []analysis.TextEdit{
|
||||
{
|
||||
Pos: arg.Pos(),
|
||||
End: arg.Pos(),
|
||||
Pos: v.Pos(),
|
||||
End: v.Pos(),
|
||||
NewText: []byte("rune("),
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
Pos: arg.End(),
|
||||
End: arg.End(),
|
||||
Pos: v.End(),
|
||||
End: v.End(),
|
||||
NewText: []byte(")"),
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
pass.Report(diag)
|
||||
})
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func structuralTypes(t types.Type) ([]types.Type, error) {
|
||||
var structuralTypes []types.Type
|
||||
switch t := t.(type) {
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.StructuralTerms(t)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, term := range terms {
|
||||
structuralTypes = append(structuralTypes, term.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
structuralTypes = append(structuralTypes, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return structuralTypes, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
42
vendor/golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/testinggoroutine/testinggoroutine.go
generated
vendored
42
vendor/golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/testinggoroutine/testinggoroutine.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/internal/analysisutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = `report calls to (*testing.T).Fatal from goroutines started by a test.
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,44 +119,11 @@ func typeIsTestingDotTOrB(expr ast.Expr) (string, bool) {
|
|||
return varTypeName, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// goStmtFunc returns the ast.Node of a call expression
|
||||
// that was invoked as a go statement. Currently, only
|
||||
// function literals declared in the same function, and
|
||||
// static calls within the same package are supported.
|
||||
func goStmtFun(goStmt *ast.GoStmt) ast.Node {
|
||||
switch fun := goStmt.Call.Fun.(type) {
|
||||
case *ast.IndexExpr, *typeparams.IndexListExpr:
|
||||
x, _, _, _ := typeparams.UnpackIndexExpr(fun)
|
||||
id, _ := x.(*ast.Ident)
|
||||
if id == nil {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if id.Obj == nil {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if funDecl, ok := id.Obj.Decl.(ast.Node); ok {
|
||||
return funDecl
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *ast.Ident:
|
||||
// TODO(cuonglm): improve this once golang/go#48141 resolved.
|
||||
if fun.Obj == nil {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if funDecl, ok := fun.Obj.Decl.(ast.Node); ok {
|
||||
return funDecl
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *ast.FuncLit:
|
||||
return goStmt.Call.Fun
|
||||
}
|
||||
return goStmt.Call
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// checkGoStmt traverses the goroutine and checks for the
|
||||
// use of the forbidden *testing.(B, T) methods.
|
||||
func checkGoStmt(pass *analysis.Pass, goStmt *ast.GoStmt) {
|
||||
fn := goStmtFun(goStmt)
|
||||
// Otherwise examine the goroutine to check for the forbidden methods.
|
||||
ast.Inspect(fn, func(n ast.Node) bool {
|
||||
ast.Inspect(goStmt, func(n ast.Node) bool {
|
||||
selExpr, ok := n.(*ast.SelectorExpr)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,11 +147,7 @@ func checkGoStmt(pass *analysis.Pass, goStmt *ast.GoStmt) {
|
|||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
if typeName, ok := typeIsTestingDotTOrB(field.Type); ok {
|
||||
var fnRange analysis.Range = goStmt
|
||||
if _, ok := fn.(*ast.FuncLit); ok {
|
||||
fnRange = selExpr
|
||||
}
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(fnRange, "call to (*%s).%s from a non-test goroutine", typeName, selExpr.Sel)
|
||||
pass.ReportRangef(selExpr, "call to (*%s).%s from a non-test goroutine", typeName, selExpr.Sel)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,15 +8,12 @@ package tests
|
|||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"regexp"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = `check for common mistaken usages of tests and examples
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,10 +42,10 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
// Ignore non-functions or functions with receivers.
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(fn.Name.Name, "Example"):
|
||||
checkExampleName(pass, fn)
|
||||
checkExampleOutput(pass, fn, f.Comments)
|
||||
checkExample(pass, fn)
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(fn.Name.Name, "Test"):
|
||||
checkTest(pass, fn, "Test")
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(fn.Name.Name, "Benchmark"):
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,59 +108,7 @@ func lookup(pkg *types.Package, name string) []types.Object {
|
|||
return ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// This pattern is taken from /go/src/go/doc/example.go
|
||||
var outputRe = regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)^[[:space:]]*(unordered )?output:`)
|
||||
|
||||
type commentMetadata struct {
|
||||
isOutput bool
|
||||
pos token.Pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkExampleOutput(pass *analysis.Pass, fn *ast.FuncDecl, fileComments []*ast.CommentGroup) {
|
||||
commentsInExample := []commentMetadata{}
|
||||
numOutputs := 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the comment blocks that are in the example. These comments are
|
||||
// guaranteed to be in order of appearance.
|
||||
for _, cg := range fileComments {
|
||||
if cg.Pos() < fn.Pos() {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
} else if cg.End() > fn.End() {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
isOutput := outputRe.MatchString(cg.Text())
|
||||
if isOutput {
|
||||
numOutputs++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
commentsInExample = append(commentsInExample, commentMetadata{
|
||||
isOutput: isOutput,
|
||||
pos: cg.Pos(),
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Change message based on whether there are multiple output comment blocks.
|
||||
msg := "output comment block must be the last comment block"
|
||||
if numOutputs > 1 {
|
||||
msg = "there can only be one output comment block per example"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i, cg := range commentsInExample {
|
||||
// Check for output comments that are not the last comment in the example.
|
||||
isLast := (i == len(commentsInExample)-1)
|
||||
if cg.isOutput && !isLast {
|
||||
pass.Report(
|
||||
analysis.Diagnostic{
|
||||
Pos: cg.pos,
|
||||
Message: msg,
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkExampleName(pass *analysis.Pass, fn *ast.FuncDecl) {
|
||||
func checkExample(pass *analysis.Pass, fn *ast.FuncDecl) {
|
||||
fnName := fn.Name.Name
|
||||
if params := fn.Type.Params; len(params.List) != 0 {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(fn.Pos(), "%s should be niladic", fnName)
|
||||
|
|
@ -171,9 +116,6 @@ func checkExampleName(pass *analysis.Pass, fn *ast.FuncDecl) {
|
|||
if results := fn.Type.Results; results != nil && len(results.List) != 0 {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(fn.Pos(), "%s should return nothing", fnName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tparams := typeparams.ForFuncType(fn.Type); tparams != nil && len(tparams.List) > 0 {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(fn.Pos(), "%s should not have type params", fnName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if fnName == "Example" {
|
||||
// Nothing more to do.
|
||||
|
|
@ -240,12 +182,6 @@ func checkTest(pass *analysis.Pass, fn *ast.FuncDecl, prefix string) {
|
|||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if tparams := typeparams.ForFuncType(fn.Type); tparams != nil && len(tparams.List) > 0 {
|
||||
// Note: cmd/go/internal/load also errors about TestXXX and BenchmarkXXX functions with type parameters.
|
||||
// We have currently decided to also warn before compilation/package loading. This can help users in IDEs.
|
||||
pass.Reportf(fn.Pos(), "%s has type parameters: it will not be run by go test as a %sXXX function", fn.Name.Name, prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !isTestSuffix(fn.Name.Name[len(prefix):]) {
|
||||
pass.Reportf(fn.Pos(), "%s has malformed name: first letter after '%s' must not be lowercase", fn.Name.Name, prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/types/typeutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const Doc = `report passing non-pointer or non-interface values to unmarshal
|
||||
|
|
@ -86,7 +85,7 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
|
||||
t := pass.TypesInfo.Types[call.Args[argidx]].Type
|
||||
switch t.Underlying().(type) {
|
||||
case *types.Pointer, *types.Interface, *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
case *types.Pointer, *types.Interface:
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/inspect"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis/passes/internal/analysisutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/inspector"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(adonovan): make this analysis modular: export a mustUseResult
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,11 +70,6 @@ func run(pass *analysis.Pass) (interface{}, error) {
|
|||
return // a conversion, not a call
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
x, _, _, _ := typeparams.UnpackIndexExpr(fun)
|
||||
if x != nil {
|
||||
fun = x // If this is generic function or method call, skip the instantiation arguments
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
selector, ok := fun.(*ast.SelectorExpr)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return // neither a method call nor a qualified ident
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,8 +11,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// PathEnclosingInterval returns the node that encloses the source
|
||||
|
|
@ -296,8 +294,8 @@ func childrenOf(n ast.Node) []ast.Node {
|
|||
|
||||
case *ast.FieldList:
|
||||
children = append(children,
|
||||
tok(n.Opening, len("(")), // or len("[")
|
||||
tok(n.Closing, len(")"))) // or len("]")
|
||||
tok(n.Opening, len("(")),
|
||||
tok(n.Closing, len(")")))
|
||||
|
||||
case *ast.File:
|
||||
// TODO test: Doc
|
||||
|
|
@ -324,9 +322,6 @@ func childrenOf(n ast.Node) []ast.Node {
|
|||
children = append(children, n.Recv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
children = append(children, n.Name)
|
||||
if tparams := typeparams.ForFuncType(n.Type); tparams != nil {
|
||||
children = append(children, tparams)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n.Type.Params != nil {
|
||||
children = append(children, n.Type.Params)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -376,13 +371,8 @@ func childrenOf(n ast.Node) []ast.Node {
|
|||
|
||||
case *ast.IndexExpr:
|
||||
children = append(children,
|
||||
tok(n.Lbrack, len("[")),
|
||||
tok(n.Rbrack, len("]")))
|
||||
|
||||
case *typeparams.IndexListExpr:
|
||||
children = append(children,
|
||||
tok(n.Lbrack, len("[")),
|
||||
tok(n.Rbrack, len("]")))
|
||||
tok(n.Lbrack, len("{")),
|
||||
tok(n.Rbrack, len("}")))
|
||||
|
||||
case *ast.InterfaceType:
|
||||
children = append(children,
|
||||
|
|
@ -591,8 +581,6 @@ func NodeDescription(n ast.Node) string {
|
|||
return "decrement statement"
|
||||
case *ast.IndexExpr:
|
||||
return "index expression"
|
||||
case *typeparams.IndexListExpr:
|
||||
return "index list expression"
|
||||
case *ast.InterfaceType:
|
||||
return "interface type"
|
||||
case *ast.KeyValueExpr:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -253,10 +253,6 @@ func (a *application) apply(parent ast.Node, name string, iter *iterator, n ast.
|
|||
a.apply(n, "X", nil, n.X)
|
||||
a.apply(n, "Index", nil, n.Index)
|
||||
|
||||
case *typeparams.IndexListExpr:
|
||||
a.apply(n, "X", nil, n.X)
|
||||
a.applyList(n, "Indices")
|
||||
|
||||
case *ast.SliceExpr:
|
||||
a.apply(n, "X", nil, n.X)
|
||||
a.apply(n, "Low", nil, n.Low)
|
||||
|
|
@ -443,7 +439,11 @@ func (a *application) apply(parent ast.Node, name string, iter *iterator, n ast.
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(fmt.Sprintf("Apply: unexpected node type %T", n))
|
||||
if typeparams.IsListExpr(n) {
|
||||
a.applyList(n, "ElemList")
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Sprintf("Apply: unexpected node type %T", n))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if a.post != nil && !a.post(&a.cursor) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,11 +9,7 @@ package inspector
|
|||
// The initial map-based implementation was too slow;
|
||||
// see https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/tools/+/135655/1/go/ast/inspector/inspector.go#196
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
import "go/ast"
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
nArrayType = iota
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,7 +47,6 @@ const (
|
|||
nImportSpec
|
||||
nIncDecStmt
|
||||
nIndexExpr
|
||||
nIndexListExpr
|
||||
nInterfaceType
|
||||
nKeyValueExpr
|
||||
nLabeledStmt
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,8 +164,6 @@ func typeOf(n ast.Node) uint64 {
|
|||
return 1 << nIncDecStmt
|
||||
case *ast.IndexExpr:
|
||||
return 1 << nIndexExpr
|
||||
case *typeparams.IndexListExpr:
|
||||
return 1 << nIndexListExpr
|
||||
case *ast.InterfaceType:
|
||||
return 1 << nInterfaceType
|
||||
case *ast.KeyValueExpr:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -50,24 +50,11 @@ func Find(importPath, srcDir string) (filename, path string) {
|
|||
// additional trailing data beyond the end of the export data.
|
||||
func NewReader(r io.Reader) (io.Reader, error) {
|
||||
buf := bufio.NewReader(r)
|
||||
_, size, err := gcimporter.FindExportData(buf)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if size >= 0 {
|
||||
// We were given an archive and found the __.PKGDEF in it.
|
||||
// This tells us the size of the export data, and we don't
|
||||
// need to return the entire file.
|
||||
return &io.LimitedReader{
|
||||
R: buf,
|
||||
N: size,
|
||||
}, nil
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// We were given an object file. As such, we don't know how large
|
||||
// the export data is and must return the entire file.
|
||||
return buf, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, err := gcimporter.FindExportData(buf)
|
||||
// If we ever switch to a zip-like archive format with the ToC
|
||||
// at the end, we can return the correct portion of export data,
|
||||
// but for now we must return the entire rest of the file.
|
||||
return buf, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read reads export data from in, decodes it, and returns type
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -34,6 +34,9 @@ import (
|
|||
// (suspected) format errors, and whenever a change is made to the format.
|
||||
const debugFormat = false // default: false
|
||||
|
||||
// If trace is set, debugging output is printed to std out.
|
||||
const trace = false // default: false
|
||||
|
||||
// Current export format version. Increase with each format change.
|
||||
// Note: The latest binary (non-indexed) export format is at version 6.
|
||||
// This exporter is still at level 4, but it doesn't matter since
|
||||
|
|
@ -89,18 +92,16 @@ func internalErrorf(format string, args ...interface{}) error {
|
|||
// BExportData returns binary export data for pkg.
|
||||
// If no file set is provided, position info will be missing.
|
||||
func BExportData(fset *token.FileSet, pkg *types.Package) (b []byte, err error) {
|
||||
if !debug {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if e := recover(); e != nil {
|
||||
if ierr, ok := e.(internalError); ok {
|
||||
err = ierr
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Not an internal error; panic again.
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if e := recover(); e != nil {
|
||||
if ierr, ok := e.(internalError); ok {
|
||||
err = ierr
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Not an internal error; panic again.
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
p := exporter{
|
||||
fset: fset,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -74,10 +74,9 @@ func BImportData(fset *token.FileSet, imports map[string]*types.Package, data []
|
|||
pathList: []string{""}, // empty string is mapped to 0
|
||||
fake: fakeFileSet{
|
||||
fset: fset,
|
||||
files: make(map[string]*fileInfo),
|
||||
files: make(map[string]*token.File),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer p.fake.setLines() // set lines for files in fset
|
||||
|
||||
// read version info
|
||||
var versionstr string
|
||||
|
|
@ -339,49 +338,37 @@ func (p *importer) pos() token.Pos {
|
|||
// Synthesize a token.Pos
|
||||
type fakeFileSet struct {
|
||||
fset *token.FileSet
|
||||
files map[string]*fileInfo
|
||||
files map[string]*token.File
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type fileInfo struct {
|
||||
file *token.File
|
||||
lastline int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const maxlines = 64 * 1024
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *fakeFileSet) pos(file string, line, column int) token.Pos {
|
||||
// TODO(mdempsky): Make use of column.
|
||||
|
||||
// Since we don't know the set of needed file positions, we reserve maxlines
|
||||
// positions per file. We delay calling token.File.SetLines until all
|
||||
// positions have been calculated (by way of fakeFileSet.setLines), so that
|
||||
// we can avoid setting unnecessary lines. See also golang/go#46586.
|
||||
// Since we don't know the set of needed file positions, we
|
||||
// reserve maxlines positions per file.
|
||||
const maxlines = 64 * 1024
|
||||
f := s.files[file]
|
||||
if f == nil {
|
||||
f = &fileInfo{file: s.fset.AddFile(file, -1, maxlines)}
|
||||
f = s.fset.AddFile(file, -1, maxlines)
|
||||
s.files[file] = f
|
||||
// Allocate the fake linebreak indices on first use.
|
||||
// TODO(adonovan): opt: save ~512KB using a more complex scheme?
|
||||
fakeLinesOnce.Do(func() {
|
||||
fakeLines = make([]int, maxlines)
|
||||
for i := range fakeLines {
|
||||
fakeLines[i] = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
f.SetLines(fakeLines)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if line > maxlines {
|
||||
line = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if line > f.lastline {
|
||||
f.lastline = line
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Return a fake position assuming that f.file consists only of newlines.
|
||||
return token.Pos(f.file.Base() + line - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *fakeFileSet) setLines() {
|
||||
fakeLinesOnce.Do(func() {
|
||||
fakeLines = make([]int, maxlines)
|
||||
for i := range fakeLines {
|
||||
fakeLines[i] = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
for _, f := range s.files {
|
||||
f.file.SetLines(fakeLines[:f.lastline])
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Treat the file as if it contained only newlines
|
||||
// and column=1: use the line number as the offset.
|
||||
return f.Pos(line - 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
|
|
@ -1042,7 +1029,6 @@ func predeclared() []types.Type {
|
|||
// used internally by gc; never used by this package or in .a files
|
||||
anyType{},
|
||||
}
|
||||
predecl = append(predecl, additionalPredeclared()...)
|
||||
})
|
||||
return predecl
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ import (
|
|||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func readGopackHeader(r *bufio.Reader) (name string, size int64, err error) {
|
||||
func readGopackHeader(r *bufio.Reader) (name string, size int, err error) {
|
||||
// See $GOROOT/include/ar.h.
|
||||
hdr := make([]byte, 16+12+6+6+8+10+2)
|
||||
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, hdr)
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,8 +28,7 @@ func readGopackHeader(r *bufio.Reader) (name string, size int64, err error) {
|
|||
fmt.Printf("header: %s", hdr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s := strings.TrimSpace(string(hdr[16+12+6+6+8:][:10]))
|
||||
length, err := strconv.Atoi(s)
|
||||
size = int64(length)
|
||||
size, err = strconv.Atoi(s)
|
||||
if err != nil || hdr[len(hdr)-2] != '`' || hdr[len(hdr)-1] != '\n' {
|
||||
err = fmt.Errorf("invalid archive header")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
|
@ -43,8 +42,8 @@ func readGopackHeader(r *bufio.Reader) (name string, size int64, err error) {
|
|||
// file by reading from it. The reader must be positioned at the
|
||||
// start of the file before calling this function. The hdr result
|
||||
// is the string before the export data, either "$$" or "$$B".
|
||||
// The size result is the length of the export data in bytes, or -1 if not known.
|
||||
func FindExportData(r *bufio.Reader) (hdr string, size int64, err error) {
|
||||
//
|
||||
func FindExportData(r *bufio.Reader) (hdr string, err error) {
|
||||
// Read first line to make sure this is an object file.
|
||||
line, err := r.ReadSlice('\n')
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,7 +54,7 @@ func FindExportData(r *bufio.Reader) (hdr string, size int64, err error) {
|
|||
if string(line) == "!<arch>\n" {
|
||||
// Archive file. Scan to __.PKGDEF.
|
||||
var name string
|
||||
if name, size, err = readGopackHeader(r); err != nil {
|
||||
if name, _, err = readGopackHeader(r); err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -71,7 +70,6 @@ func FindExportData(r *bufio.Reader) (hdr string, size int64, err error) {
|
|||
err = fmt.Errorf("can't find export data (%v)", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
size -= int64(len(line))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Now at __.PKGDEF in archive or still at beginning of file.
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,12 +86,8 @@ func FindExportData(r *bufio.Reader) (hdr string, size int64, err error) {
|
|||
err = fmt.Errorf("can't find export data (%v)", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
size -= int64(len(line))
|
||||
}
|
||||
hdr = string(line)
|
||||
if size < 0 {
|
||||
size = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -29,14 +29,8 @@ import (
|
|||
"text/scanner"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// Enable debug during development: it adds some additional checks, and
|
||||
// prevents errors from being recovered.
|
||||
debug = false
|
||||
|
||||
// If trace is set, debugging output is printed to std out.
|
||||
trace = false
|
||||
)
|
||||
// debugging/development support
|
||||
const debug = false
|
||||
|
||||
var pkgExts = [...]string{".a", ".o"}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -185,7 +179,7 @@ func Import(packages map[string]*types.Package, path, srcDir string, lookup func
|
|||
|
||||
var hdr string
|
||||
buf := bufio.NewReader(rc)
|
||||
if hdr, _, err = FindExportData(buf); err != nil {
|
||||
if hdr, err = FindExportData(buf); err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,6 @@ package gcimporter
|
|||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding/binary"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/constant"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,12 +19,12 @@ import (
|
|||
"math/big"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Current indexed export format version. Increase with each format change.
|
||||
// 0: Go1.11 encoding
|
||||
const iexportVersion = 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Current bundled export format version. Increase with each format change.
|
||||
// 0: initial implementation
|
||||
const bundleVersion = 0
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,35 +35,31 @@ const bundleVersion = 0
|
|||
// The package path of the top-level package will not be recorded,
|
||||
// so that calls to IImportData can override with a provided package path.
|
||||
func IExportData(out io.Writer, fset *token.FileSet, pkg *types.Package) error {
|
||||
return iexportCommon(out, fset, false, iexportVersion, []*types.Package{pkg})
|
||||
return iexportCommon(out, fset, false, []*types.Package{pkg})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IExportBundle writes an indexed export bundle for pkgs to out.
|
||||
func IExportBundle(out io.Writer, fset *token.FileSet, pkgs []*types.Package) error {
|
||||
return iexportCommon(out, fset, true, iexportVersion, pkgs)
|
||||
return iexportCommon(out, fset, true, pkgs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func iexportCommon(out io.Writer, fset *token.FileSet, bundle bool, version int, pkgs []*types.Package) (err error) {
|
||||
if !debug {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if e := recover(); e != nil {
|
||||
if ierr, ok := e.(internalError); ok {
|
||||
err = ierr
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Not an internal error; panic again.
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
func iexportCommon(out io.Writer, fset *token.FileSet, bundle bool, pkgs []*types.Package) (err error) {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if e := recover(); e != nil {
|
||||
if ierr, ok := e.(internalError); ok {
|
||||
err = ierr
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Not an internal error; panic again.
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
p := iexporter{
|
||||
fset: fset,
|
||||
version: version,
|
||||
allPkgs: map[*types.Package]bool{},
|
||||
stringIndex: map[string]uint64{},
|
||||
declIndex: map[types.Object]uint64{},
|
||||
tparamNames: map[types.Object]string{},
|
||||
typIndex: map[types.Type]uint64{},
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !bundle {
|
||||
|
|
@ -124,7 +119,7 @@ func iexportCommon(out io.Writer, fset *token.FileSet, bundle bool, version int,
|
|||
if bundle {
|
||||
hdr.uint64(bundleVersion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
hdr.uint64(uint64(p.version))
|
||||
hdr.uint64(iexportVersion)
|
||||
hdr.uint64(uint64(p.strings.Len()))
|
||||
hdr.uint64(dataLen)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -141,12 +136,8 @@ func iexportCommon(out io.Writer, fset *token.FileSet, bundle bool, version int,
|
|||
// non-compiler tools and includes a complete package description
|
||||
// (i.e., name and height).
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) writeIndex(index map[types.Object]uint64) {
|
||||
type pkgObj struct {
|
||||
obj types.Object
|
||||
name string // qualified name; differs from obj.Name for type params
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Build a map from packages to objects from that package.
|
||||
pkgObjs := map[*types.Package][]pkgObj{}
|
||||
pkgObjs := map[*types.Package][]types.Object{}
|
||||
|
||||
// For the main index, make sure to include every package that
|
||||
// we reference, even if we're not exporting (or reexporting)
|
||||
|
|
@ -159,8 +150,7 @@ func (w *exportWriter) writeIndex(index map[types.Object]uint64) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for obj := range index {
|
||||
name := w.p.exportName(obj)
|
||||
pkgObjs[obj.Pkg()] = append(pkgObjs[obj.Pkg()], pkgObj{obj, name})
|
||||
pkgObjs[obj.Pkg()] = append(pkgObjs[obj.Pkg()], obj)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var pkgs []*types.Package
|
||||
|
|
@ -168,7 +158,7 @@ func (w *exportWriter) writeIndex(index map[types.Object]uint64) {
|
|||
pkgs = append(pkgs, pkg)
|
||||
|
||||
sort.Slice(objs, func(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return objs[i].name < objs[j].name
|
||||
return objs[i].Name() < objs[j].Name()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -185,25 +175,15 @@ func (w *exportWriter) writeIndex(index map[types.Object]uint64) {
|
|||
objs := pkgObjs[pkg]
|
||||
w.uint64(uint64(len(objs)))
|
||||
for _, obj := range objs {
|
||||
w.string(obj.name)
|
||||
w.uint64(index[obj.obj])
|
||||
w.string(obj.Name())
|
||||
w.uint64(index[obj])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// exportName returns the 'exported' name of an object. It differs from
|
||||
// obj.Name() only for type parameters (see tparamExportName for details).
|
||||
func (p *iexporter) exportName(obj types.Object) (res string) {
|
||||
if name := p.tparamNames[obj]; name != "" {
|
||||
return name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return obj.Name()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type iexporter struct {
|
||||
fset *token.FileSet
|
||||
out *bytes.Buffer
|
||||
version int
|
||||
fset *token.FileSet
|
||||
out *bytes.Buffer
|
||||
|
||||
localpkg *types.Package
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -217,21 +197,9 @@ type iexporter struct {
|
|||
strings intWriter
|
||||
stringIndex map[string]uint64
|
||||
|
||||
data0 intWriter
|
||||
declIndex map[types.Object]uint64
|
||||
tparamNames map[types.Object]string // typeparam->exported name
|
||||
typIndex map[types.Type]uint64
|
||||
|
||||
indent int // for tracing support
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *iexporter) trace(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
if !trace {
|
||||
// Call sites should also be guarded, but having this check here allows
|
||||
// easily enabling/disabling debug trace statements.
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Printf(strings.Repeat("..", p.indent)+format+"\n", args...)
|
||||
data0 intWriter
|
||||
declIndex map[types.Object]uint64
|
||||
typIndex map[types.Type]uint64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// stringOff returns the offset of s within the string section.
|
||||
|
|
@ -257,7 +225,7 @@ func (p *iexporter) pushDecl(obj types.Object) {
|
|||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.declIndex[obj] = ^uint64(0) // mark obj present in work queue
|
||||
p.declIndex[obj] = ^uint64(0) // mark n present in work queue
|
||||
p.declTodo.pushTail(obj)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -265,11 +233,10 @@ func (p *iexporter) pushDecl(obj types.Object) {
|
|||
type exportWriter struct {
|
||||
p *iexporter
|
||||
|
||||
data intWriter
|
||||
currPkg *types.Package
|
||||
prevFile string
|
||||
prevLine int64
|
||||
prevColumn int64
|
||||
data intWriter
|
||||
currPkg *types.Package
|
||||
prevFile string
|
||||
prevLine int64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) exportPath(pkg *types.Package) string {
|
||||
|
|
@ -280,14 +247,6 @@ func (w *exportWriter) exportPath(pkg *types.Package) string {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *iexporter) doDecl(obj types.Object) {
|
||||
if trace {
|
||||
p.trace("exporting decl %v (%T)", obj, obj)
|
||||
p.indent++
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
p.indent--
|
||||
p.trace("=> %s", obj)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
w := p.newWriter()
|
||||
w.setPkg(obj.Pkg(), false)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -302,24 +261,8 @@ func (p *iexporter) doDecl(obj types.Object) {
|
|||
if sig.Recv() != nil {
|
||||
panic(internalErrorf("unexpected method: %v", sig))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Function.
|
||||
if typeparams.ForSignature(sig).Len() == 0 {
|
||||
w.tag('F')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
w.tag('G')
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.tag('F')
|
||||
w.pos(obj.Pos())
|
||||
// The tparam list of the function type is the declaration of the type
|
||||
// params. So, write out the type params right now. Then those type params
|
||||
// will be referenced via their type offset (via typOff) in all other
|
||||
// places in the signature and function where they are used.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// While importing the type parameters, tparamList computes and records
|
||||
// their export name, so that it can be later used when writing the index.
|
||||
if tparams := typeparams.ForSignature(sig); tparams.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
w.tparamList(obj.Name(), tparams, obj.Pkg())
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.signature(sig)
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Const:
|
||||
|
|
@ -328,56 +271,30 @@ func (p *iexporter) doDecl(obj types.Object) {
|
|||
w.value(obj.Type(), obj.Val())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.TypeName:
|
||||
t := obj.Type()
|
||||
|
||||
if tparam, ok := t.(*typeparams.TypeParam); ok {
|
||||
w.tag('P')
|
||||
w.pos(obj.Pos())
|
||||
constraint := tparam.Constraint()
|
||||
if p.version >= iexportVersionGo1_18 {
|
||||
implicit := false
|
||||
if iface, _ := constraint.(*types.Interface); iface != nil {
|
||||
implicit = typeparams.IsImplicit(iface)
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.bool(implicit)
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.typ(constraint, obj.Pkg())
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if obj.IsAlias() {
|
||||
w.tag('A')
|
||||
w.pos(obj.Pos())
|
||||
w.typ(t, obj.Pkg())
|
||||
w.typ(obj.Type(), obj.Pkg())
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Defined type.
|
||||
named, ok := t.(*types.Named)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
panic(internalErrorf("%s is not a defined type", t))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typeparams.ForNamed(named).Len() == 0 {
|
||||
w.tag('T')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
w.tag('U')
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.tag('T')
|
||||
w.pos(obj.Pos())
|
||||
|
||||
if typeparams.ForNamed(named).Len() > 0 {
|
||||
// While importing the type parameters, tparamList computes and records
|
||||
// their export name, so that it can be later used when writing the index.
|
||||
w.tparamList(obj.Name(), typeparams.ForNamed(named), obj.Pkg())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
underlying := obj.Type().Underlying()
|
||||
w.typ(underlying, obj.Pkg())
|
||||
|
||||
t := obj.Type()
|
||||
if types.IsInterface(t) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
named, ok := t.(*types.Named)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
panic(internalErrorf("%s is not a defined type", t))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n := named.NumMethods()
|
||||
w.uint64(uint64(n))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
|
|
@ -385,17 +302,6 @@ func (p *iexporter) doDecl(obj types.Object) {
|
|||
w.pos(m.Pos())
|
||||
w.string(m.Name())
|
||||
sig, _ := m.Type().(*types.Signature)
|
||||
|
||||
// Receiver type parameters are type arguments of the receiver type, so
|
||||
// their name must be qualified before exporting recv.
|
||||
if rparams := typeparams.RecvTypeParams(sig); rparams.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
prefix := obj.Name() + "." + m.Name()
|
||||
for i := 0; i < rparams.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
rparam := rparams.At(i)
|
||||
name := tparamExportName(prefix, rparam)
|
||||
w.p.tparamNames[rparam.Obj()] = name
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.param(sig.Recv())
|
||||
w.signature(sig)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -412,48 +318,6 @@ func (w *exportWriter) tag(tag byte) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) pos(pos token.Pos) {
|
||||
if w.p.version >= iexportVersionPosCol {
|
||||
w.posV1(pos)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
w.posV0(pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) posV1(pos token.Pos) {
|
||||
if w.p.fset == nil {
|
||||
w.int64(0)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p := w.p.fset.Position(pos)
|
||||
file := p.Filename
|
||||
line := int64(p.Line)
|
||||
column := int64(p.Column)
|
||||
|
||||
deltaColumn := (column - w.prevColumn) << 1
|
||||
deltaLine := (line - w.prevLine) << 1
|
||||
|
||||
if file != w.prevFile {
|
||||
deltaLine |= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if deltaLine != 0 {
|
||||
deltaColumn |= 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
w.int64(deltaColumn)
|
||||
if deltaColumn&1 != 0 {
|
||||
w.int64(deltaLine)
|
||||
if deltaLine&1 != 0 {
|
||||
w.string(file)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
w.prevFile = file
|
||||
w.prevLine = line
|
||||
w.prevColumn = column
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) posV0(pos token.Pos) {
|
||||
if w.p.fset == nil {
|
||||
w.int64(0)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
|
@ -495,11 +359,10 @@ func (w *exportWriter) pkg(pkg *types.Package) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) qualifiedIdent(obj types.Object) {
|
||||
name := w.p.exportName(obj)
|
||||
|
||||
// Ensure any referenced declarations are written out too.
|
||||
w.p.pushDecl(obj)
|
||||
w.string(name)
|
||||
|
||||
w.string(obj.Name())
|
||||
w.pkg(obj.Pkg())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -533,32 +396,11 @@ func (w *exportWriter) startType(k itag) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) doTyp(t types.Type, pkg *types.Package) {
|
||||
if trace {
|
||||
w.p.trace("exporting type %s (%T)", t, t)
|
||||
w.p.indent++
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
w.p.indent--
|
||||
w.p.trace("=> %s", t)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch t := t.(type) {
|
||||
case *types.Named:
|
||||
if targs := typeparams.NamedTypeArgs(t); targs.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
w.startType(instanceType)
|
||||
// TODO(rfindley): investigate if this position is correct, and if it
|
||||
// matters.
|
||||
w.pos(t.Obj().Pos())
|
||||
w.typeList(targs, pkg)
|
||||
w.typ(typeparams.NamedTypeOrigin(t), pkg)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.startType(definedType)
|
||||
w.qualifiedIdent(t.Obj())
|
||||
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
w.startType(typeParamType)
|
||||
w.qualifiedIdent(t.Obj())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Pointer:
|
||||
w.startType(pointerType)
|
||||
w.typ(t.Elem(), pkg)
|
||||
|
|
@ -619,14 +461,9 @@ func (w *exportWriter) doTyp(t types.Type, pkg *types.Package) {
|
|||
n := t.NumEmbeddeds()
|
||||
w.uint64(uint64(n))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
ft := t.EmbeddedType(i)
|
||||
tPkg := pkg
|
||||
if named, _ := ft.(*types.Named); named != nil {
|
||||
w.pos(named.Obj().Pos())
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
w.pos(token.NoPos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.typ(ft, tPkg)
|
||||
f := t.Embedded(i)
|
||||
w.pos(f.Obj().Pos())
|
||||
w.typ(f.Obj().Type(), f.Obj().Pkg())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n = t.NumExplicitMethods()
|
||||
|
|
@ -639,16 +476,6 @@ func (w *exportWriter) doTyp(t types.Type, pkg *types.Package) {
|
|||
w.signature(sig)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case *typeparams.Union:
|
||||
w.startType(unionType)
|
||||
nt := t.Len()
|
||||
w.uint64(uint64(nt))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < nt; i++ {
|
||||
term := t.Term(i)
|
||||
w.bool(term.Tilde())
|
||||
w.typ(term.Type(), pkg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(internalErrorf("unexpected type: %v, %v", t, reflect.TypeOf(t)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -670,56 +497,6 @@ func (w *exportWriter) signature(sig *types.Signature) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) typeList(ts *typeparams.TypeList, pkg *types.Package) {
|
||||
w.uint64(uint64(ts.Len()))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < ts.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
w.typ(ts.At(i), pkg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) tparamList(prefix string, list *typeparams.TypeParamList, pkg *types.Package) {
|
||||
ll := uint64(list.Len())
|
||||
w.uint64(ll)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < list.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
tparam := list.At(i)
|
||||
// Set the type parameter exportName before exporting its type.
|
||||
exportName := tparamExportName(prefix, tparam)
|
||||
w.p.tparamNames[tparam.Obj()] = exportName
|
||||
w.typ(list.At(i), pkg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const blankMarker = "$"
|
||||
|
||||
// tparamExportName returns the 'exported' name of a type parameter, which
|
||||
// differs from its actual object name: it is prefixed with a qualifier, and
|
||||
// blank type parameter names are disambiguated by their index in the type
|
||||
// parameter list.
|
||||
func tparamExportName(prefix string, tparam *typeparams.TypeParam) string {
|
||||
assert(prefix != "")
|
||||
name := tparam.Obj().Name()
|
||||
if name == "_" {
|
||||
name = blankMarker + strconv.Itoa(tparam.Index())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return prefix + "." + name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// tparamName returns the real name of a type parameter, after stripping its
|
||||
// qualifying prefix and reverting blank-name encoding. See tparamExportName
|
||||
// for details.
|
||||
func tparamName(exportName string) string {
|
||||
// Remove the "path" from the type param name that makes it unique.
|
||||
ix := strings.LastIndex(exportName, ".")
|
||||
if ix < 0 {
|
||||
errorf("malformed type parameter export name %s: missing prefix", exportName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
name := exportName[ix+1:]
|
||||
if strings.HasPrefix(name, blankMarker) {
|
||||
return "_"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) paramList(tup *types.Tuple) {
|
||||
n := tup.Len()
|
||||
w.uint64(uint64(n))
|
||||
|
|
@ -736,9 +513,6 @@ func (w *exportWriter) param(obj types.Object) {
|
|||
|
||||
func (w *exportWriter) value(typ types.Type, v constant.Value) {
|
||||
w.typ(typ, nil)
|
||||
if w.p.version >= iexportVersionGo1_18 {
|
||||
w.int64(int64(v.Kind()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch b := typ.Underlying().(*types.Basic); b.Info() & types.IsConstType {
|
||||
case types.IsBoolean:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,9 +18,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"go/types"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type intReader struct {
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,19 +41,6 @@ func (r *intReader) uint64() uint64 {
|
|||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Keep this in sync with constants in iexport.go.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
iexportVersionGo1_11 = 0
|
||||
iexportVersionPosCol = 1
|
||||
iexportVersionGo1_18 = 2
|
||||
iexportVersionGenerics = 2
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type ident struct {
|
||||
pkg string
|
||||
name string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const predeclReserved = 32
|
||||
|
||||
type itag uint64
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,9 +56,6 @@ const (
|
|||
signatureType
|
||||
structType
|
||||
interfaceType
|
||||
typeParamType
|
||||
instanceType
|
||||
unionType
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// IImportData imports a package from the serialized package data
|
||||
|
|
@ -97,17 +78,15 @@ func IImportBundle(fset *token.FileSet, imports map[string]*types.Package, data
|
|||
func iimportCommon(fset *token.FileSet, imports map[string]*types.Package, data []byte, bundle bool, path string) (pkgs []*types.Package, err error) {
|
||||
const currentVersion = 1
|
||||
version := int64(-1)
|
||||
if !debug {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if e := recover(); e != nil {
|
||||
if version > currentVersion {
|
||||
err = fmt.Errorf("cannot import %q (%v), export data is newer version - update tool", path, e)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = fmt.Errorf("cannot import %q (%v), possibly version skew - reinstall package", path, e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if e := recover(); e != nil {
|
||||
if version > currentVersion {
|
||||
err = fmt.Errorf("cannot import %q (%v), export data is newer version - update tool", path, e)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = fmt.Errorf("cannot import %q (%v), possibly version skew - reinstall package", path, e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
r := &intReader{bytes.NewReader(data), path}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -122,13 +101,9 @@ func iimportCommon(fset *token.FileSet, imports map[string]*types.Package, data
|
|||
|
||||
version = int64(r.uint64())
|
||||
switch version {
|
||||
case iexportVersionGo1_18, iexportVersionPosCol, iexportVersionGo1_11:
|
||||
case currentVersion, 0:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if version > iexportVersionGo1_18 {
|
||||
errorf("unstable iexport format version %d, just rebuild compiler and std library", version)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
errorf("unknown iexport format version %d", version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
errorf("unknown iexport format version %d", version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sLen := int64(r.uint64())
|
||||
|
|
@ -140,8 +115,8 @@ func iimportCommon(fset *token.FileSet, imports map[string]*types.Package, data
|
|||
r.Seek(sLen+dLen, io.SeekCurrent)
|
||||
|
||||
p := iimporter{
|
||||
version: int(version),
|
||||
ipath: path,
|
||||
version: int(version),
|
||||
|
||||
stringData: stringData,
|
||||
stringCache: make(map[uint64]string),
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,16 +125,12 @@ func iimportCommon(fset *token.FileSet, imports map[string]*types.Package, data
|
|||
declData: declData,
|
||||
pkgIndex: make(map[*types.Package]map[string]uint64),
|
||||
typCache: make(map[uint64]types.Type),
|
||||
// Separate map for typeparams, keyed by their package and unique
|
||||
// name.
|
||||
tparamIndex: make(map[ident]types.Type),
|
||||
|
||||
fake: fakeFileSet{
|
||||
fset: fset,
|
||||
files: make(map[string]*fileInfo),
|
||||
files: make(map[string]*token.File),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer p.fake.setLines() // set lines for files in fset
|
||||
|
||||
for i, pt := range predeclared() {
|
||||
p.typCache[uint64(i)] = pt
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,42 +216,22 @@ func iimportCommon(fset *token.FileSet, imports map[string]*types.Package, data
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type iimporter struct {
|
||||
version int
|
||||
ipath string
|
||||
version int
|
||||
|
||||
stringData []byte
|
||||
stringCache map[uint64]string
|
||||
pkgCache map[uint64]*types.Package
|
||||
|
||||
declData []byte
|
||||
pkgIndex map[*types.Package]map[string]uint64
|
||||
typCache map[uint64]types.Type
|
||||
tparamIndex map[ident]types.Type
|
||||
declData []byte
|
||||
pkgIndex map[*types.Package]map[string]uint64
|
||||
typCache map[uint64]types.Type
|
||||
|
||||
fake fakeFileSet
|
||||
interfaceList []*types.Interface
|
||||
|
||||
indent int // for tracing support
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *iimporter) trace(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
if !trace {
|
||||
// Call sites should also be guarded, but having this check here allows
|
||||
// easily enabling/disabling debug trace statements.
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Printf(strings.Repeat("..", p.indent)+format+"\n", args...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *iimporter) doDecl(pkg *types.Package, name string) {
|
||||
if debug {
|
||||
p.trace("import decl %s", name)
|
||||
p.indent++
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
p.indent--
|
||||
p.trace("=> %s", name)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
// See if we've already imported this declaration.
|
||||
if obj := pkg.Scope().Lookup(name); obj != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
|
@ -322,7 +273,7 @@ func (p *iimporter) pkgAt(off uint64) *types.Package {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *iimporter) typAt(off uint64, base *types.Named) types.Type {
|
||||
if t, ok := p.typCache[off]; ok && canReuse(base, t) {
|
||||
if t, ok := p.typCache[off]; ok && (base == nil || !isInterface(t)) {
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -334,30 +285,12 @@ func (p *iimporter) typAt(off uint64, base *types.Named) types.Type {
|
|||
r.declReader.Reset(p.declData[off-predeclReserved:])
|
||||
t := r.doType(base)
|
||||
|
||||
if canReuse(base, t) {
|
||||
if base == nil || !isInterface(t) {
|
||||
p.typCache[off] = t
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// canReuse reports whether the type rhs on the RHS of the declaration for def
|
||||
// may be re-used.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Specifically, if def is non-nil and rhs is an interface type with methods, it
|
||||
// may not be re-used because we have a convention of setting the receiver type
|
||||
// for interface methods to def.
|
||||
func canReuse(def *types.Named, rhs types.Type) bool {
|
||||
if def == nil {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
iface, _ := rhs.(*types.Interface)
|
||||
if iface == nil {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Don't use iface.Empty() here as iface may not be complete.
|
||||
return iface.NumEmbeddeds() == 0 && iface.NumExplicitMethods() == 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type importReader struct {
|
||||
p *iimporter
|
||||
declReader bytes.Reader
|
||||
|
|
@ -382,26 +315,17 @@ func (r *importReader) obj(name string) {
|
|||
|
||||
r.declare(types.NewConst(pos, r.currPkg, name, typ, val))
|
||||
|
||||
case 'F', 'G':
|
||||
var tparams []*typeparams.TypeParam
|
||||
if tag == 'G' {
|
||||
tparams = r.tparamList()
|
||||
}
|
||||
sig := r.signature(nil, nil, tparams)
|
||||
case 'F':
|
||||
sig := r.signature(nil)
|
||||
|
||||
r.declare(types.NewFunc(pos, r.currPkg, name, sig))
|
||||
|
||||
case 'T', 'U':
|
||||
case 'T':
|
||||
// Types can be recursive. We need to setup a stub
|
||||
// declaration before recursing.
|
||||
obj := types.NewTypeName(pos, r.currPkg, name, nil)
|
||||
named := types.NewNamed(obj, nil, nil)
|
||||
// Declare obj before calling r.tparamList, so the new type name is recognized
|
||||
// if used in the constraint of one of its own typeparams (see #48280).
|
||||
r.declare(obj)
|
||||
if tag == 'U' {
|
||||
tparams := r.tparamList()
|
||||
typeparams.SetForNamed(named, tparams)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
underlying := r.p.typAt(r.uint64(), named).Underlying()
|
||||
named.SetUnderlying(underlying)
|
||||
|
|
@ -411,55 +335,12 @@ func (r *importReader) obj(name string) {
|
|||
mpos := r.pos()
|
||||
mname := r.ident()
|
||||
recv := r.param()
|
||||
|
||||
// If the receiver has any targs, set those as the
|
||||
// rparams of the method (since those are the
|
||||
// typeparams being used in the method sig/body).
|
||||
base := baseType(recv.Type())
|
||||
assert(base != nil)
|
||||
targs := typeparams.NamedTypeArgs(base)
|
||||
var rparams []*typeparams.TypeParam
|
||||
if targs.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
rparams = make([]*typeparams.TypeParam, targs.Len())
|
||||
for i := range rparams {
|
||||
rparams[i] = targs.At(i).(*typeparams.TypeParam)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
msig := r.signature(recv, rparams, nil)
|
||||
msig := r.signature(recv)
|
||||
|
||||
named.AddMethod(types.NewFunc(mpos, r.currPkg, mname, msig))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case 'P':
|
||||
// We need to "declare" a typeparam in order to have a name that
|
||||
// can be referenced recursively (if needed) in the type param's
|
||||
// bound.
|
||||
if r.p.version < iexportVersionGenerics {
|
||||
errorf("unexpected type param type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
name0 := tparamName(name)
|
||||
tn := types.NewTypeName(pos, r.currPkg, name0, nil)
|
||||
t := typeparams.NewTypeParam(tn, nil)
|
||||
|
||||
// To handle recursive references to the typeparam within its
|
||||
// bound, save the partial type in tparamIndex before reading the bounds.
|
||||
id := ident{r.currPkg.Name(), name}
|
||||
r.p.tparamIndex[id] = t
|
||||
var implicit bool
|
||||
if r.p.version >= iexportVersionGo1_18 {
|
||||
implicit = r.bool()
|
||||
}
|
||||
constraint := r.typ()
|
||||
if implicit {
|
||||
iface, _ := constraint.(*types.Interface)
|
||||
if iface == nil {
|
||||
errorf("non-interface constraint marked implicit")
|
||||
}
|
||||
typeparams.MarkImplicit(iface)
|
||||
}
|
||||
typeparams.SetTypeParamConstraint(t, constraint)
|
||||
|
||||
case 'V':
|
||||
typ := r.typ()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -476,10 +357,6 @@ func (r *importReader) declare(obj types.Object) {
|
|||
|
||||
func (r *importReader) value() (typ types.Type, val constant.Value) {
|
||||
typ = r.typ()
|
||||
if r.p.version >= iexportVersionGo1_18 {
|
||||
// TODO: add support for using the kind.
|
||||
_ = constant.Kind(r.int64())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch b := typ.Underlying().(*types.Basic); b.Info() & types.IsConstType {
|
||||
case types.IsBoolean:
|
||||
|
|
@ -622,7 +499,7 @@ func (r *importReader) qualifiedIdent() (*types.Package, string) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *importReader) pos() token.Pos {
|
||||
if r.p.version >= iexportVersionPosCol {
|
||||
if r.p.version >= 1 {
|
||||
r.posv1()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.posv0()
|
||||
|
|
@ -670,17 +547,8 @@ func isInterface(t types.Type) bool {
|
|||
func (r *importReader) pkg() *types.Package { return r.p.pkgAt(r.uint64()) }
|
||||
func (r *importReader) string() string { return r.p.stringAt(r.uint64()) }
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *importReader) doType(base *types.Named) (res types.Type) {
|
||||
k := r.kind()
|
||||
if debug {
|
||||
r.p.trace("importing type %d (base: %s)", k, base)
|
||||
r.p.indent++
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
r.p.indent--
|
||||
r.p.trace("=> %s", res)
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch k {
|
||||
func (r *importReader) doType(base *types.Named) types.Type {
|
||||
switch k := r.kind(); k {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
errorf("unexpected kind tag in %q: %v", r.p.ipath, k)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
|
|
@ -703,7 +571,7 @@ func (r *importReader) doType(base *types.Named) (res types.Type) {
|
|||
return types.NewMap(r.typ(), r.typ())
|
||||
case signatureType:
|
||||
r.currPkg = r.pkg()
|
||||
return r.signature(nil, nil, nil)
|
||||
return r.signature(nil)
|
||||
|
||||
case structType:
|
||||
r.currPkg = r.pkg()
|
||||
|
|
@ -743,56 +611,13 @@ func (r *importReader) doType(base *types.Named) (res types.Type) {
|
|||
recv = types.NewVar(token.NoPos, r.currPkg, "", base)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
msig := r.signature(recv, nil, nil)
|
||||
msig := r.signature(recv)
|
||||
methods[i] = types.NewFunc(mpos, r.currPkg, mname, msig)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
typ := newInterface(methods, embeddeds)
|
||||
r.p.interfaceList = append(r.p.interfaceList, typ)
|
||||
return typ
|
||||
|
||||
case typeParamType:
|
||||
if r.p.version < iexportVersionGenerics {
|
||||
errorf("unexpected type param type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
pkg, name := r.qualifiedIdent()
|
||||
id := ident{pkg.Name(), name}
|
||||
if t, ok := r.p.tparamIndex[id]; ok {
|
||||
// We're already in the process of importing this typeparam.
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Otherwise, import the definition of the typeparam now.
|
||||
r.p.doDecl(pkg, name)
|
||||
return r.p.tparamIndex[id]
|
||||
|
||||
case instanceType:
|
||||
if r.p.version < iexportVersionGenerics {
|
||||
errorf("unexpected instantiation type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// pos does not matter for instances: they are positioned on the original
|
||||
// type.
|
||||
_ = r.pos()
|
||||
len := r.uint64()
|
||||
targs := make([]types.Type, len)
|
||||
for i := range targs {
|
||||
targs[i] = r.typ()
|
||||
}
|
||||
baseType := r.typ()
|
||||
// The imported instantiated type doesn't include any methods, so
|
||||
// we must always use the methods of the base (orig) type.
|
||||
// TODO provide a non-nil *Environment
|
||||
t, _ := typeparams.Instantiate(nil, baseType, targs, false)
|
||||
return t
|
||||
|
||||
case unionType:
|
||||
if r.p.version < iexportVersionGenerics {
|
||||
errorf("unexpected instantiation type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
terms := make([]*typeparams.Term, r.uint64())
|
||||
for i := range terms {
|
||||
terms[i] = typeparams.NewTerm(r.bool(), r.typ())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return typeparams.NewUnion(terms)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -800,25 +625,11 @@ func (r *importReader) kind() itag {
|
|||
return itag(r.uint64())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *importReader) signature(recv *types.Var, rparams []*typeparams.TypeParam, tparams []*typeparams.TypeParam) *types.Signature {
|
||||
func (r *importReader) signature(recv *types.Var) *types.Signature {
|
||||
params := r.paramList()
|
||||
results := r.paramList()
|
||||
variadic := params.Len() > 0 && r.bool()
|
||||
return typeparams.NewSignatureType(recv, rparams, tparams, params, results, variadic)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *importReader) tparamList() []*typeparams.TypeParam {
|
||||
n := r.uint64()
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
xs := make([]*typeparams.TypeParam, n)
|
||||
for i := range xs {
|
||||
// Note: the standard library importer is tolerant of nil types here,
|
||||
// though would panic in SetTypeParams.
|
||||
xs[i] = r.typ().(*typeparams.TypeParam)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return xs
|
||||
return types.NewSignature(recv, params, results, variadic)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *importReader) paramList() *types.Tuple {
|
||||
|
|
@ -863,13 +674,3 @@ func (r *importReader) byte() byte {
|
|||
}
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func baseType(typ types.Type) *types.Named {
|
||||
// pointer receivers are never types.Named types
|
||||
if p, _ := typ.(*types.Pointer); p != nil {
|
||||
typ = p.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
// receiver base types are always (possibly generic) types.Named types
|
||||
n, _ := typ.(*types.Named)
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build !go1.18
|
||||
// +build !go1.18
|
||||
|
||||
package gcimporter
|
||||
|
||||
import "go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
const iexportVersion = iexportVersionGo1_11
|
||||
|
||||
func additionalPredeclared() []types.Type {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build go1.18
|
||||
// +build go1.18
|
||||
|
||||
package gcimporter
|
||||
|
||||
import "go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
const iexportVersion = iexportVersionGenerics
|
||||
|
||||
// additionalPredeclared returns additional predeclared types in go.1.18.
|
||||
func additionalPredeclared() []types.Type {
|
||||
return []types.Type{
|
||||
// comparable
|
||||
types.Universe.Lookup("comparable").Type(),
|
||||
|
||||
// any
|
||||
types.Universe.Lookup("any").Type(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/gcexportdata"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/gocommand"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/packagesinternal"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typesinternal"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -328,9 +327,6 @@ type Package struct {
|
|||
// The NeedSyntax LoadMode bit populates this field for packages matching the patterns.
|
||||
// If NeedDeps and NeedImports are also set, this field will also be populated
|
||||
// for dependencies.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Syntax is kept in the same order as CompiledGoFiles, with the caveat that nils are
|
||||
// removed. If parsing returned nil, Syntax may be shorter than CompiledGoFiles.
|
||||
Syntax []*ast.File
|
||||
|
||||
// TypesInfo provides type information about the package's syntax trees.
|
||||
|
|
@ -914,7 +910,6 @@ func (ld *loader) loadPackage(lpkg *loaderPackage) {
|
|||
Scopes: make(map[ast.Node]*types.Scope),
|
||||
Selections: make(map[*ast.SelectorExpr]*types.Selection),
|
||||
}
|
||||
typeparams.InitInstanceInfo(lpkg.TypesInfo)
|
||||
lpkg.TypesSizes = ld.sizes
|
||||
|
||||
importer := importerFunc(func(path string) (*types.Package, error) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,8 +25,8 @@
|
|||
//
|
||||
// The simplest way to create the SSA representation of a package is
|
||||
// to load typed syntax trees using golang.org/x/tools/go/packages, then
|
||||
// invoke the ssautil.Packages helper function. See Example_loadPackages
|
||||
// and Example_loadWholeProgram for examples.
|
||||
// invoke the ssautil.Packages helper function. See ExampleLoadPackages
|
||||
// and ExampleWholeProgram for examples.
|
||||
// The resulting ssa.Program contains all the packages and their
|
||||
// members, but SSA code is not created for function bodies until a
|
||||
// subsequent call to (*Package).Build or (*Program).Build.
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,6 +59,7 @@
|
|||
// *ChangeType ✔ ✔
|
||||
// *Const ✔
|
||||
// *Convert ✔ ✔
|
||||
// *SliceToArrayPointer ✔ ✔
|
||||
// *DebugRef ✔
|
||||
// *Defer ✔
|
||||
// *Extract ✔ ✔
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,7 +91,6 @@
|
|||
// *Select ✔ ✔
|
||||
// *Send ✔
|
||||
// *Slice ✔ ✔
|
||||
// *SliceToArrayPointer ✔ ✔
|
||||
// *Store ✔
|
||||
// *Type ✔ (type)
|
||||
// *TypeAssert ✔ ✔
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ func emitConv(f *Function, val Value, typ types.Type) Value {
|
|||
// Conversion from slice to array pointer?
|
||||
if slice, ok := ut_src.(*types.Slice); ok {
|
||||
if ptr, ok := ut_dst.(*types.Pointer); ok {
|
||||
if arr, ok := ptr.Elem().Underlying().(*types.Array); ok && types.Identical(slice.Elem(), arr.Elem()) {
|
||||
if arr, ok := ptr.Elem().(*types.Array); ok && types.Identical(slice.Elem(), arr.Elem()) {
|
||||
c := &SliceToArrayPointer{X: val}
|
||||
c.setType(ut_dst)
|
||||
return f.emit(c)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"io"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/types/typeutil"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,16 +38,8 @@ func relName(v Value, i Instruction) string {
|
|||
return v.Name()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// normalizeAnyFortesting controls whether we replace occurrences of
|
||||
// interface{} with any. It is only used for normalizing test output.
|
||||
var normalizeAnyForTesting bool
|
||||
|
||||
func relType(t types.Type, from *types.Package) string {
|
||||
s := types.TypeString(t, types.RelativeTo(from))
|
||||
if normalizeAnyForTesting {
|
||||
s = strings.ReplaceAll(s, "interface{}", "any")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
return types.TypeString(t, types.RelativeTo(from))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func relString(m Member, from *types.Package) string {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ func doPackages(initial []*packages.Package, mode ssa.BuilderMode, deps bool) (*
|
|||
// The mode parameter controls diagnostics and checking during SSA construction.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use golang.org/x/tools/go/packages and the Packages
|
||||
// function instead; see ssa.Example_loadPackages.
|
||||
// function instead; see ssa.ExampleLoadPackages.
|
||||
//
|
||||
func CreateProgram(lprog *loader.Program, mode ssa.BuilderMode) *ssa.Program {
|
||||
prog := ssa.NewProgram(lprog.Fset, mode)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,274 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2013 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package ssa
|
||||
|
||||
// CreateTestMainPackage synthesizes a main package that runs all the
|
||||
// tests of the supplied packages.
|
||||
// It is closely coupled to $GOROOT/src/cmd/go/test.go and $GOROOT/src/testing.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TODO(adonovan): throws this all away now that x/tools/go/packages
|
||||
// provides access to the actual synthetic test main files.
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/parser"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"text/template"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// FindTests returns the Test, Benchmark, and Example functions
|
||||
// (as defined by "go test") defined in the specified package,
|
||||
// and its TestMain function, if any.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use golang.org/x/tools/go/packages to access synthetic
|
||||
// testmain packages.
|
||||
func FindTests(pkg *Package) (tests, benchmarks, examples []*Function, main *Function) {
|
||||
prog := pkg.Prog
|
||||
|
||||
// The first two of these may be nil: if the program doesn't import "testing",
|
||||
// it can't contain any tests, but it may yet contain Examples.
|
||||
var testSig *types.Signature // func(*testing.T)
|
||||
var benchmarkSig *types.Signature // func(*testing.B)
|
||||
var exampleSig = types.NewSignature(nil, nil, nil, false) // func()
|
||||
|
||||
// Obtain the types from the parameters of testing.MainStart.
|
||||
if testingPkg := prog.ImportedPackage("testing"); testingPkg != nil {
|
||||
mainStart := testingPkg.Func("MainStart")
|
||||
params := mainStart.Signature.Params()
|
||||
testSig = funcField(params.At(1).Type())
|
||||
benchmarkSig = funcField(params.At(2).Type())
|
||||
|
||||
// Does the package define this function?
|
||||
// func TestMain(*testing.M)
|
||||
if f := pkg.Func("TestMain"); f != nil {
|
||||
sig := f.Type().(*types.Signature)
|
||||
starM := mainStart.Signature.Results().At(0).Type() // *testing.M
|
||||
if sig.Results().Len() == 0 &&
|
||||
sig.Params().Len() == 1 &&
|
||||
types.Identical(sig.Params().At(0).Type(), starM) {
|
||||
main = f
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(adonovan): use a stable order, e.g. lexical.
|
||||
for _, mem := range pkg.Members {
|
||||
if f, ok := mem.(*Function); ok &&
|
||||
ast.IsExported(f.Name()) &&
|
||||
strings.HasSuffix(prog.Fset.Position(f.Pos()).Filename, "_test.go") {
|
||||
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case testSig != nil && isTestSig(f, "Test", testSig):
|
||||
tests = append(tests, f)
|
||||
case benchmarkSig != nil && isTestSig(f, "Benchmark", benchmarkSig):
|
||||
benchmarks = append(benchmarks, f)
|
||||
case isTestSig(f, "Example", exampleSig):
|
||||
examples = append(examples, f)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Like isTest, but checks the signature too.
|
||||
func isTestSig(f *Function, prefix string, sig *types.Signature) bool {
|
||||
return isTest(f.Name(), prefix) && types.Identical(f.Signature, sig)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Given the type of one of the three slice parameters of testing.Main,
|
||||
// returns the function type.
|
||||
func funcField(slice types.Type) *types.Signature {
|
||||
return slice.(*types.Slice).Elem().Underlying().(*types.Struct).Field(1).Type().(*types.Signature)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isTest tells whether name looks like a test (or benchmark, according to prefix).
|
||||
// It is a Test (say) if there is a character after Test that is not a lower-case letter.
|
||||
// We don't want TesticularCancer.
|
||||
// Plundered from $GOROOT/src/cmd/go/test.go
|
||||
func isTest(name, prefix string) bool {
|
||||
if !strings.HasPrefix(name, prefix) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(name) == len(prefix) { // "Test" is ok
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ast.IsExported(name[len(prefix):])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CreateTestMainPackage creates and returns a synthetic "testmain"
|
||||
// package for the specified package if it defines tests, benchmarks or
|
||||
// executable examples, or nil otherwise. The new package is named
|
||||
// "main" and provides a function named "main" that runs the tests,
|
||||
// similar to the one that would be created by the 'go test' tool.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Subsequent calls to prog.AllPackages include the new package.
|
||||
// The package pkg must belong to the program prog.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Use golang.org/x/tools/go/packages to access synthetic
|
||||
// testmain packages.
|
||||
func (prog *Program) CreateTestMainPackage(pkg *Package) *Package {
|
||||
if pkg.Prog != prog {
|
||||
log.Fatal("Package does not belong to Program")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Template data
|
||||
var data struct {
|
||||
Pkg *Package
|
||||
Tests, Benchmarks, Examples []*Function
|
||||
Main *Function
|
||||
Go18 bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
data.Pkg = pkg
|
||||
|
||||
// Enumerate tests.
|
||||
data.Tests, data.Benchmarks, data.Examples, data.Main = FindTests(pkg)
|
||||
if data.Main == nil &&
|
||||
data.Tests == nil && data.Benchmarks == nil && data.Examples == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Synthesize source for testmain package.
|
||||
path := pkg.Pkg.Path() + "$testmain"
|
||||
tmpl := testmainTmpl
|
||||
if testingPkg := prog.ImportedPackage("testing"); testingPkg != nil {
|
||||
// In Go 1.8, testing.MainStart's first argument is an interface, not a func.
|
||||
data.Go18 = types.IsInterface(testingPkg.Func("MainStart").Signature.Params().At(0).Type())
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// The program does not import "testing", but FindTests
|
||||
// returned non-nil, which must mean there were Examples
|
||||
// but no Test, Benchmark, or TestMain functions.
|
||||
|
||||
// We'll simply call them from testmain.main; this will
|
||||
// ensure they don't panic, but will not check any
|
||||
// "Output:" comments.
|
||||
// (We should not execute an Example that has no
|
||||
// "Output:" comment, but it's impossible to tell here.)
|
||||
tmpl = examplesOnlyTmpl
|
||||
}
|
||||
var buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
if err := tmpl.Execute(&buf, data); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatalf("internal error expanding template for %s: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if false { // debugging
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, buf.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse and type-check the testmain package.
|
||||
f, err := parser.ParseFile(prog.Fset, path+".go", &buf, parser.Mode(0))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatalf("internal error parsing %s: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
conf := types.Config{
|
||||
DisableUnusedImportCheck: true,
|
||||
Importer: importer{pkg},
|
||||
}
|
||||
files := []*ast.File{f}
|
||||
info := &types.Info{
|
||||
Types: make(map[ast.Expr]types.TypeAndValue),
|
||||
Defs: make(map[*ast.Ident]types.Object),
|
||||
Uses: make(map[*ast.Ident]types.Object),
|
||||
Implicits: make(map[ast.Node]types.Object),
|
||||
Scopes: make(map[ast.Node]*types.Scope),
|
||||
Selections: make(map[*ast.SelectorExpr]*types.Selection),
|
||||
}
|
||||
testmainPkg, err := conf.Check(path, prog.Fset, files, info)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatalf("internal error type-checking %s: %v", path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Create and build SSA code.
|
||||
testmain := prog.CreatePackage(testmainPkg, files, info, false)
|
||||
testmain.SetDebugMode(false)
|
||||
testmain.Build()
|
||||
testmain.Func("main").Synthetic = "test main function"
|
||||
testmain.Func("init").Synthetic = "package initializer"
|
||||
return testmain
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An implementation of types.Importer for an already loaded SSA program.
|
||||
type importer struct {
|
||||
pkg *Package // package under test; may be non-importable
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (imp importer) Import(path string) (*types.Package, error) {
|
||||
if p := imp.pkg.Prog.ImportedPackage(path); p != nil {
|
||||
return p.Pkg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if path == imp.pkg.Pkg.Path() {
|
||||
return imp.pkg.Pkg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("not found") // can't happen
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var testmainTmpl = template.Must(template.New("testmain").Parse(`
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "io"
|
||||
import "os"
|
||||
import "testing"
|
||||
import p {{printf "%q" .Pkg.Pkg.Path}}
|
||||
|
||||
{{if .Go18}}
|
||||
type deps struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (deps) ImportPath() string { return "" }
|
||||
func (deps) MatchString(pat, str string) (bool, error) { return true, nil }
|
||||
func (deps) SetPanicOnExit0(bool) {}
|
||||
func (deps) StartCPUProfile(io.Writer) error { return nil }
|
||||
func (deps) StartTestLog(io.Writer) {}
|
||||
func (deps) StopCPUProfile() {}
|
||||
func (deps) StopTestLog() error { return nil }
|
||||
func (deps) WriteHeapProfile(io.Writer) error { return nil }
|
||||
func (deps) WriteProfileTo(string, io.Writer, int) error { return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
var match deps
|
||||
{{else}}
|
||||
func match(_, _ string) (bool, error) { return true, nil }
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
tests := []testing.InternalTest{
|
||||
{{range .Tests}}
|
||||
{ {{printf "%q" .Name}}, p.{{.Name}} },
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
benchmarks := []testing.InternalBenchmark{
|
||||
{{range .Benchmarks}}
|
||||
{ {{printf "%q" .Name}}, p.{{.Name}} },
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
examples := []testing.InternalExample{
|
||||
{{range .Examples}}
|
||||
{Name: {{printf "%q" .Name}}, F: p.{{.Name}}},
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
m := testing.MainStart(match, tests, benchmarks, examples)
|
||||
{{with .Main}}
|
||||
p.{{.Name}}(m)
|
||||
{{else}}
|
||||
os.Exit(m.Run())
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
`))
|
||||
|
||||
var examplesOnlyTmpl = template.Must(template.New("examples").Parse(`
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import p {{printf "%q" .Pkg.Pkg.Path}}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
{{range .Examples}}
|
||||
p.{{.Name}}()
|
||||
{{end}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
`))
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,12 +23,10 @@ package objectpath
|
|||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A Path is an opaque name that identifies a types.Object
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,16 +57,12 @@ type Path string
|
|||
// - The only PO operator is Package.Scope.Lookup, which requires an identifier.
|
||||
// - The only OT operator is Object.Type,
|
||||
// which we encode as '.' because dot cannot appear in an identifier.
|
||||
// - The TT operators are encoded as [EKPRUTC];
|
||||
// one of these (TypeParam) requires an integer operand,
|
||||
// which is encoded as a string of decimal digits.
|
||||
// - The TO operators are encoded as [AFMO];
|
||||
// - The TT operators are encoded as [EKPRU].
|
||||
// - The OT operators are encoded as [AFMO];
|
||||
// three of these (At,Field,Method) require an integer operand,
|
||||
// which is encoded as a string of decimal digits.
|
||||
// These indices are stable across different representations
|
||||
// of the same package, even source and export data.
|
||||
// The indices used are implementation specific and may not correspond to
|
||||
// the argument to the go/types function.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In the example below,
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
|
@ -95,19 +89,17 @@ const (
|
|||
opType = '.' // .Type() (Object)
|
||||
|
||||
// type->type operators
|
||||
opElem = 'E' // .Elem() (Pointer, Slice, Array, Chan, Map)
|
||||
opKey = 'K' // .Key() (Map)
|
||||
opParams = 'P' // .Params() (Signature)
|
||||
opResults = 'R' // .Results() (Signature)
|
||||
opUnderlying = 'U' // .Underlying() (Named)
|
||||
opTypeParam = 'T' // .TypeParams.At(i) (Named, Signature)
|
||||
opConstraint = 'C' // .Constraint() (TypeParam)
|
||||
opElem = 'E' // .Elem() (Pointer, Slice, Array, Chan, Map)
|
||||
opKey = 'K' // .Key() (Map)
|
||||
opParams = 'P' // .Params() (Signature)
|
||||
opResults = 'R' // .Results() (Signature)
|
||||
opUnderlying = 'U' // .Underlying() (Named)
|
||||
|
||||
// type->object operators
|
||||
opAt = 'A' // .At(i) (Tuple)
|
||||
opField = 'F' // .Field(i) (Struct)
|
||||
opMethod = 'M' // .Method(i) (Named or Interface; not Struct: "promoted" names are ignored)
|
||||
opObj = 'O' // .Obj() (Named, TypeParam)
|
||||
opAt = 'A' // .At(i) (Tuple)
|
||||
opField = 'F' // .Field(i) (Struct)
|
||||
opMethod = 'M' // .Method(i) (Named or Interface; not Struct: "promoted" names are ignored)
|
||||
opObj = 'O' // .Obj() (Named)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// The For function returns the path to an object relative to its package,
|
||||
|
|
@ -198,15 +190,10 @@ func For(obj types.Object) (Path, error) {
|
|||
// 3. Not a package-level object.
|
||||
// Reject obviously non-viable cases.
|
||||
switch obj := obj.(type) {
|
||||
case *types.TypeName:
|
||||
if _, ok := obj.Type().(*typeparams.TypeParam); !ok {
|
||||
// With the exception of type parameters, only package-level type names
|
||||
// have a path.
|
||||
return "", fmt.Errorf("no path for %v", obj)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *types.Const, // Only package-level constants have a path.
|
||||
*types.Label, // Labels are function-local.
|
||||
*types.PkgName: // PkgNames are file-local.
|
||||
*types.TypeName, // Only package-level types have a path.
|
||||
*types.Label, // Labels are function-local.
|
||||
*types.PkgName: // PkgNames are file-local.
|
||||
return "", fmt.Errorf("no path for %v", obj)
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Var:
|
||||
|
|
@ -258,12 +245,6 @@ func For(obj types.Object) (Path, error) {
|
|||
return Path(r), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if named, _ := T.(*types.Named); named != nil {
|
||||
if r := findTypeParam(obj, typeparams.ForNamed(named), path); r != nil {
|
||||
// generic named type
|
||||
return Path(r), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// defined (named) type
|
||||
if r := find(obj, T.Underlying(), append(path, opUnderlying)); r != nil {
|
||||
return Path(r), nil
|
||||
|
|
@ -289,12 +270,8 @@ func For(obj types.Object) (Path, error) {
|
|||
// Inspect declared methods of defined types.
|
||||
if T, ok := o.Type().(*types.Named); ok {
|
||||
path = append(path, opType)
|
||||
// Note that method index here is always with respect
|
||||
// to canonical ordering of methods, regardless of how
|
||||
// they appear in the underlying type.
|
||||
canonical := canonicalize(T)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(canonical); i++ {
|
||||
m := canonical[i]
|
||||
for i := 0; i < T.NumMethods(); i++ {
|
||||
m := T.Method(i)
|
||||
path2 := appendOpArg(path, opMethod, i)
|
||||
if m == obj {
|
||||
return Path(path2), nil // found declared method
|
||||
|
|
@ -336,9 +313,6 @@ func find(obj types.Object, T types.Type, path []byte) []byte {
|
|||
}
|
||||
return find(obj, T.Elem(), append(path, opElem))
|
||||
case *types.Signature:
|
||||
if r := findTypeParam(obj, typeparams.ForSignature(T), path); r != nil {
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r := find(obj, T.Params(), append(path, opParams)); r != nil {
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -379,30 +353,10 @@ func find(obj types.Object, T types.Type, path []byte) []byte {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
name := T.Obj()
|
||||
if name == obj {
|
||||
return append(path, opObj)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r := find(obj, T.Constraint(), append(path, opConstraint)); r != nil {
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
panic(T)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findTypeParam(obj types.Object, list *typeparams.TypeParamList, path []byte) []byte {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < list.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
tparam := list.At(i)
|
||||
path2 := appendOpArg(path, opTypeParam, i)
|
||||
if r := find(obj, tparam, path2); r != nil {
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Object returns the object denoted by path p within the package pkg.
|
||||
func Object(pkg *types.Package, p Path) (types.Object, error) {
|
||||
if p == "" {
|
||||
|
|
@ -427,13 +381,10 @@ func Object(pkg *types.Package, p Path) (types.Object, error) {
|
|||
type hasElem interface {
|
||||
Elem() types.Type
|
||||
}
|
||||
// abstraction of *types.{Named,Signature}
|
||||
type hasTypeParams interface {
|
||||
TypeParams() *typeparams.TypeParamList
|
||||
}
|
||||
// abstraction of *types.{Named,TypeParam}
|
||||
type hasObj interface {
|
||||
Obj() *types.TypeName
|
||||
// abstraction of *types.{Interface,Named}
|
||||
type hasMethods interface {
|
||||
Method(int) *types.Func
|
||||
NumMethods() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The loop state is the pair (t, obj),
|
||||
|
|
@ -450,7 +401,7 @@ func Object(pkg *types.Package, p Path) (types.Object, error) {
|
|||
// Codes [AFM] have an integer operand.
|
||||
var index int
|
||||
switch code {
|
||||
case opAt, opField, opMethod, opTypeParam:
|
||||
case opAt, opField, opMethod:
|
||||
rest := strings.TrimLeft(suffix, "0123456789")
|
||||
numerals := suffix[:len(suffix)-len(rest)]
|
||||
suffix = rest
|
||||
|
|
@ -515,32 +466,14 @@ func Object(pkg *types.Package, p Path) (types.Object, error) {
|
|||
case opUnderlying:
|
||||
named, ok := t.(*types.Named)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %T, want named)", code, t, t)
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %s, want named)", code, t, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t = named.Underlying()
|
||||
|
||||
case opTypeParam:
|
||||
hasTypeParams, ok := t.(hasTypeParams) // Named, Signature
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %T, want named or signature)", code, t, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
tparams := hasTypeParams.TypeParams()
|
||||
if n := tparams.Len(); index >= n {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("tuple index %d out of range [0-%d)", index, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t = tparams.At(index)
|
||||
|
||||
case opConstraint:
|
||||
tparam, ok := t.(*typeparams.TypeParam)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %T, want type parameter)", code, t, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t = tparam.Constraint()
|
||||
|
||||
case opAt:
|
||||
tuple, ok := t.(*types.Tuple)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %T, want tuple)", code, t, t)
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %s, want tuple)", code, t, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n := tuple.Len(); index >= n {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("tuple index %d out of range [0-%d)", index, n)
|
||||
|
|
@ -562,21 +495,20 @@ func Object(pkg *types.Package, p Path) (types.Object, error) {
|
|||
case opMethod:
|
||||
hasMethods, ok := t.(hasMethods) // Interface or Named
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %T, want interface or named)", code, t, t)
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %s, want interface or named)", code, t, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
canonical := canonicalize(hasMethods)
|
||||
if n := len(canonical); index >= n {
|
||||
if n := hasMethods.NumMethods(); index >= n {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("method index %d out of range [0-%d)", index, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
obj = canonical[index]
|
||||
obj = hasMethods.Method(index)
|
||||
t = nil
|
||||
|
||||
case opObj:
|
||||
hasObj, ok := t.(hasObj)
|
||||
named, ok := t.(*types.Named)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %T, want named or type param)", code, t, t)
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot apply %q to %s (got %s, want named)", code, t, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
obj = hasObj.Obj()
|
||||
obj = named.Obj()
|
||||
t = nil
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
|
|
@ -590,28 +522,3 @@ func Object(pkg *types.Package, p Path) (types.Object, error) {
|
|||
|
||||
return obj, nil // success
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hasMethods is an abstraction of *types.{Interface,Named}. This is pulled up
|
||||
// because it is used by methodOrdering, which is in turn used by both encoding
|
||||
// and decoding.
|
||||
type hasMethods interface {
|
||||
Method(int) *types.Func
|
||||
NumMethods() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// canonicalize returns a canonical order for the methods in a hasMethod.
|
||||
func canonicalize(hm hasMethods) []*types.Func {
|
||||
count := hm.NumMethods()
|
||||
if count <= 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
canon := make([]*types.Func, count)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < count; i++ {
|
||||
canon[i] = hm.Method(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
less := func(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return canon[i].Id() < canon[j].Id()
|
||||
}
|
||||
sort.Slice(canon, less)
|
||||
return canon
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,29 +9,13 @@ import (
|
|||
"go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/astutil"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Callee returns the named target of a function call, if any:
|
||||
// a function, method, builtin, or variable.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Functions and methods may potentially have type parameters.
|
||||
func Callee(info *types.Info, call *ast.CallExpr) types.Object {
|
||||
fun := astutil.Unparen(call.Fun)
|
||||
|
||||
// Look through type instantiation if necessary.
|
||||
isInstance := false
|
||||
switch fun.(type) {
|
||||
case *ast.IndexExpr, *typeparams.IndexListExpr:
|
||||
// When extracting the callee from an *IndexExpr, we need to check that
|
||||
// it is a *types.Func and not a *types.Var.
|
||||
// Example: Don't match a slice m within the expression `m[0]()`.
|
||||
isInstance = true
|
||||
fun, _, _, _ = typeparams.UnpackIndexExpr(fun)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var obj types.Object
|
||||
switch fun := fun.(type) {
|
||||
switch fun := astutil.Unparen(call.Fun).(type) {
|
||||
case *ast.Ident:
|
||||
obj = info.Uses[fun] // type, var, builtin, or declared func
|
||||
case *ast.SelectorExpr:
|
||||
|
|
@ -44,18 +28,11 @@ func Callee(info *types.Info, call *ast.CallExpr) types.Object {
|
|||
if _, ok := obj.(*types.TypeName); ok {
|
||||
return nil // T(x) is a conversion, not a call
|
||||
}
|
||||
// A Func is required to match instantiations.
|
||||
if _, ok := obj.(*types.Func); isInstance && !ok {
|
||||
return nil // Was not a Func.
|
||||
}
|
||||
return obj
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StaticCallee returns the target (function or method) of a static function
|
||||
// call, if any. It returns nil for calls to builtins.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: for calls of instantiated functions and methods, StaticCallee returns
|
||||
// the corresponding generic function or method on the generic type.
|
||||
// StaticCallee returns the target (function or method) of a static
|
||||
// function call, if any. It returns nil for calls to builtins.
|
||||
func StaticCallee(info *types.Info, call *ast.CallExpr) *types.Func {
|
||||
if f, ok := Callee(info, call).(*types.Func); ok && !interfaceMethod(f) {
|
||||
return f
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,8 +11,6 @@ import (
|
|||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/internal/typeparams"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Map is a hash-table-based mapping from types (types.Type) to
|
||||
|
|
@ -213,29 +211,11 @@ func (m *Map) KeysString() string {
|
|||
// Call MakeHasher to create a Hasher.
|
||||
type Hasher struct {
|
||||
memo map[types.Type]uint32
|
||||
|
||||
// ptrMap records pointer identity.
|
||||
ptrMap map[interface{}]uint32
|
||||
|
||||
// sigTParams holds type parameters from the signature being hashed.
|
||||
// Signatures are considered identical modulo renaming of type parameters, so
|
||||
// within the scope of a signature type the identity of the signature's type
|
||||
// parameters is just their index.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Since the language does not currently support referring to uninstantiated
|
||||
// generic types or functions, and instantiated signatures do not have type
|
||||
// parameter lists, we should never encounter a second non-empty type
|
||||
// parameter list when hashing a generic signature.
|
||||
sigTParams *typeparams.TypeParamList
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MakeHasher returns a new Hasher instance.
|
||||
func MakeHasher() Hasher {
|
||||
return Hasher{
|
||||
memo: make(map[types.Type]uint32),
|
||||
ptrMap: make(map[interface{}]uint32),
|
||||
sigTParams: nil,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Hasher{make(map[types.Type]uint32)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Hash computes a hash value for the given type t such that
|
||||
|
|
@ -293,62 +273,17 @@ func (h Hasher) hashFor(t types.Type) uint32 {
|
|||
if t.Variadic() {
|
||||
hash *= 8863
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Use a separate hasher for types inside of the signature, where type
|
||||
// parameter identity is modified to be (index, constraint). We must use a
|
||||
// new memo for this hasher as type identity may be affected by this
|
||||
// masking. For example, in func[T any](*T), the identity of *T depends on
|
||||
// whether we are mapping the argument in isolation, or recursively as part
|
||||
// of hashing the signature.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We should never encounter a generic signature while hashing another
|
||||
// generic signature, but defensively set sigTParams only if h.mask is
|
||||
// unset.
|
||||
tparams := typeparams.ForSignature(t)
|
||||
if h.sigTParams == nil && tparams.Len() != 0 {
|
||||
h = Hasher{
|
||||
// There may be something more efficient than discarding the existing
|
||||
// memo, but it would require detecting whether types are 'tainted' by
|
||||
// references to type parameters.
|
||||
memo: make(map[types.Type]uint32),
|
||||
// Re-using ptrMap ensures that pointer identity is preserved in this
|
||||
// hasher.
|
||||
ptrMap: h.ptrMap,
|
||||
sigTParams: tparams,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < tparams.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
tparam := tparams.At(i)
|
||||
hash += 7 * h.Hash(tparam.Constraint())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hash + 3*h.hashTuple(t.Params()) + 5*h.hashTuple(t.Results())
|
||||
|
||||
case *typeparams.Union:
|
||||
return h.hashUnion(t)
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Interface:
|
||||
// Interfaces are identical if they have the same set of methods, with
|
||||
// identical names and types, and they have the same set of type
|
||||
// restrictions. See go/types.identical for more details.
|
||||
var hash uint32 = 9103
|
||||
|
||||
// Hash methods.
|
||||
for i, n := 0, t.NumMethods(); i < n; i++ {
|
||||
// See go/types.identicalMethods for rationale.
|
||||
// Method order is not significant.
|
||||
// Ignore m.Pkg().
|
||||
m := t.Method(i)
|
||||
hash += 3*hashString(m.Name()) + 5*h.Hash(m.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Hash type restrictions.
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.InterfaceTermSet(t)
|
||||
// if err != nil t has invalid type restrictions.
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
hash += h.hashTermSet(terms)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return hash
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Map:
|
||||
|
|
@ -358,22 +293,13 @@ func (h Hasher) hashFor(t types.Type) uint32 {
|
|||
return 9127 + 2*uint32(t.Dir()) + 3*h.Hash(t.Elem())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Named:
|
||||
hash := h.hashPtr(t.Obj())
|
||||
targs := typeparams.NamedTypeArgs(t)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < targs.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
targ := targs.At(i)
|
||||
hash += 2 * h.Hash(targ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return hash
|
||||
|
||||
case *typeparams.TypeParam:
|
||||
return h.hashTypeParam(t)
|
||||
// Not safe with a copying GC; objects may move.
|
||||
return uint32(reflect.ValueOf(t.Obj()).Pointer())
|
||||
|
||||
case *types.Tuple:
|
||||
return h.hashTuple(t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
panic(fmt.Sprintf("%T: %v", t, t))
|
||||
panic(t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h Hasher) hashTuple(tuple *types.Tuple) uint32 {
|
||||
|
|
@ -385,57 +311,3 @@ func (h Hasher) hashTuple(tuple *types.Tuple) uint32 {
|
|||
}
|
||||
return hash
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h Hasher) hashUnion(t *typeparams.Union) uint32 {
|
||||
// Hash type restrictions.
|
||||
terms, err := typeparams.UnionTermSet(t)
|
||||
// if err != nil t has invalid type restrictions. Fall back on a non-zero
|
||||
// hash.
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 9151
|
||||
}
|
||||
return h.hashTermSet(terms)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h Hasher) hashTermSet(terms []*typeparams.Term) uint32 {
|
||||
var hash uint32 = 9157 + 2*uint32(len(terms))
|
||||
for _, term := range terms {
|
||||
// term order is not significant.
|
||||
termHash := h.Hash(term.Type())
|
||||
if term.Tilde() {
|
||||
termHash *= 9161
|
||||
}
|
||||
hash += 3 * termHash
|
||||
}
|
||||
return hash
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hashTypeParam returns a hash of the type parameter t, with a hash value
|
||||
// depending on whether t is contained in h.sigTParams.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If h.sigTParams is set and contains t, then we are in the process of hashing
|
||||
// a signature, and the hash value of t must depend only on t's index and
|
||||
// constraint: signatures are considered identical modulo type parameter
|
||||
// renaming.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Otherwise the hash of t depends only on t's pointer identity.
|
||||
func (h Hasher) hashTypeParam(t *typeparams.TypeParam) uint32 {
|
||||
if h.sigTParams != nil {
|
||||
i := t.Index()
|
||||
if i >= 0 && i < h.sigTParams.Len() && t == h.sigTParams.At(i) {
|
||||
return 9173 + 2*h.Hash(t.Constraint()) + 3*uint32(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return h.hashPtr(t.Obj())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hashPtr hashes the pointer identity of ptr. It uses h.ptrMap to ensure that
|
||||
// pointers values are not dependent on the GC.
|
||||
func (h Hasher) hashPtr(ptr interface{}) uint32 {
|
||||
if hash, ok := h.ptrMap[ptr]; ok {
|
||||
return hash
|
||||
}
|
||||
hash := uint32(reflect.ValueOf(ptr).Pointer())
|
||||
h.ptrMap[ptr] = hash
|
||||
return hash
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -9,7 +9,6 @@ package imports
|
|||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,7 +60,6 @@ func sortImports(localPrefix string, fset *token.FileSet, f *ast.File) {
|
|||
|
||||
// mergeImports merges all the import declarations into the first one.
|
||||
// Taken from golang.org/x/tools/ast/astutil.
|
||||
// This does not adjust line numbers properly
|
||||
func mergeImports(fset *token.FileSet, f *ast.File) {
|
||||
if len(f.Decls) <= 1 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
|
@ -239,17 +237,8 @@ func sortSpecs(localPrefix string, fset *token.FileSet, f *ast.File, specs []ast
|
|||
p := s.Pos()
|
||||
line := fset.File(p).Line(p)
|
||||
for previousLine := line - 1; previousLine >= firstSpecLine; {
|
||||
// MergeLine can panic. Avoid the panic at the cost of not removing the blank line
|
||||
// golang/go#50329
|
||||
if previousLine > 0 && previousLine < fset.File(p).LineCount() {
|
||||
fset.File(p).MergeLine(previousLine)
|
||||
previousLine--
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// try to gather some data to diagnose how this could happen
|
||||
req := "Please report what the imports section of your go file looked like."
|
||||
log.Printf("panic avoided: first:%d line:%d previous:%d max:%d. %s",
|
||||
firstSpecLine, line, previousLine, fset.File(p).LineCount(), req)
|
||||
}
|
||||
fset.File(p).MergeLine(previousLine)
|
||||
previousLine--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return specs
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -180,8 +180,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"NewReader",
|
||||
"NewWriter",
|
||||
"Order",
|
||||
"Reader",
|
||||
"Writer",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"compress/zlib": []string{
|
||||
"BestCompression",
|
||||
|
|
@ -643,9 +641,7 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"Named",
|
||||
"NamedArg",
|
||||
"NullBool",
|
||||
"NullByte",
|
||||
"NullFloat64",
|
||||
"NullInt16",
|
||||
"NullInt32",
|
||||
"NullInt64",
|
||||
"NullString",
|
||||
|
|
@ -2252,7 +2248,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"SHT_LOOS",
|
||||
"SHT_LOPROC",
|
||||
"SHT_LOUSER",
|
||||
"SHT_MIPS_ABIFLAGS",
|
||||
"SHT_NOBITS",
|
||||
"SHT_NOTE",
|
||||
"SHT_NULL",
|
||||
|
|
@ -3066,7 +3061,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"ParseExpr",
|
||||
"ParseExprFrom",
|
||||
"ParseFile",
|
||||
"SkipObjectResolution",
|
||||
"SpuriousErrors",
|
||||
"Trace",
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
|
@ -3447,7 +3441,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"Pt",
|
||||
"RGBA",
|
||||
"RGBA64",
|
||||
"RGBA64Image",
|
||||
"Rect",
|
||||
"Rectangle",
|
||||
"RegisterFormat",
|
||||
|
|
@ -3514,7 +3507,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"Op",
|
||||
"Over",
|
||||
"Quantizer",
|
||||
"RGBA64Image",
|
||||
"Src",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"image/gif": []string{
|
||||
|
|
@ -3620,7 +3612,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"FS",
|
||||
"File",
|
||||
"FileInfo",
|
||||
"FileInfoToDirEntry",
|
||||
"FileMode",
|
||||
"Glob",
|
||||
"GlobFS",
|
||||
|
|
@ -3781,18 +3772,15 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"Max",
|
||||
"MaxFloat32",
|
||||
"MaxFloat64",
|
||||
"MaxInt",
|
||||
"MaxInt16",
|
||||
"MaxInt32",
|
||||
"MaxInt64",
|
||||
"MaxInt8",
|
||||
"MaxUint",
|
||||
"MaxUint16",
|
||||
"MaxUint32",
|
||||
"MaxUint64",
|
||||
"MaxUint8",
|
||||
"Min",
|
||||
"MinInt",
|
||||
"MinInt16",
|
||||
"MinInt32",
|
||||
"MinInt64",
|
||||
|
|
@ -4090,7 +4078,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"UnknownNetworkError",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"net/http": []string{
|
||||
"AllowQuerySemicolons",
|
||||
"CanonicalHeaderKey",
|
||||
"Client",
|
||||
"CloseNotifier",
|
||||
|
|
@ -4673,7 +4660,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"Value",
|
||||
"ValueError",
|
||||
"ValueOf",
|
||||
"VisibleFields",
|
||||
"Zero",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"regexp": []string{
|
||||
|
|
@ -4813,10 +4799,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"UnlockOSThread",
|
||||
"Version",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"runtime/cgo": []string{
|
||||
"Handle",
|
||||
"NewHandle",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"runtime/debug": []string{
|
||||
"BuildInfo",
|
||||
"FreeOSMemory",
|
||||
|
|
@ -4933,7 +4915,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"QuoteRuneToGraphic",
|
||||
"QuoteToASCII",
|
||||
"QuoteToGraphic",
|
||||
"QuotedPrefix",
|
||||
"Unquote",
|
||||
"UnquoteChar",
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
|
@ -10353,7 +10334,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"PipeNode",
|
||||
"Pos",
|
||||
"RangeNode",
|
||||
"SkipFuncCheck",
|
||||
"StringNode",
|
||||
"TemplateNode",
|
||||
"TextNode",
|
||||
|
|
@ -10378,7 +10358,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"July",
|
||||
"June",
|
||||
"Kitchen",
|
||||
"Layout",
|
||||
"LoadLocation",
|
||||
"LoadLocationFromTZData",
|
||||
"Local",
|
||||
|
|
@ -10427,8 +10406,6 @@ var stdlib = map[string][]string{
|
|||
"UTC",
|
||||
"Unix",
|
||||
"UnixDate",
|
||||
"UnixMicro",
|
||||
"UnixMilli",
|
||||
"Until",
|
||||
"Wednesday",
|
||||
"Weekday",
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,23 +27,23 @@ const (
|
|||
// RuneRoles detects the roles of each byte rune in an input string and stores it in the output
|
||||
// slice. The rune role depends on the input type. Stops when it parsed all the runes in the string
|
||||
// or when it filled the output. If output is nil, then it gets created.
|
||||
func RuneRoles(candidate []byte, reuse []RuneRole) []RuneRole {
|
||||
func RuneRoles(str string, reuse []RuneRole) []RuneRole {
|
||||
var output []RuneRole
|
||||
if cap(reuse) < len(candidate) {
|
||||
output = make([]RuneRole, 0, len(candidate))
|
||||
if cap(reuse) < len(str) {
|
||||
output = make([]RuneRole, 0, len(str))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
output = reuse[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
prev, prev2 := rtNone, rtNone
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(candidate); i++ {
|
||||
r := rune(candidate[i])
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(str); i++ {
|
||||
r := rune(str[i])
|
||||
|
||||
role := RNone
|
||||
|
||||
curr := rtLower
|
||||
if candidate[i] <= unicode.MaxASCII {
|
||||
curr = runeType(rt[candidate[i]] - '0')
|
||||
if str[i] <= unicode.MaxASCII {
|
||||
curr = runeType(rt[str[i]] - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if curr == rtLower {
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ func RuneRoles(candidate []byte, reuse []RuneRole) []RuneRole {
|
|||
if prev == rtUpper {
|
||||
// This and previous characters are both upper case.
|
||||
|
||||
if i+1 == len(candidate) {
|
||||
if i+1 == len(str) {
|
||||
// This is last character, previous was also uppercase -> this is UCTail
|
||||
// i.e., (current char is C): aBC / BC / ABC
|
||||
role = RUCTail
|
||||
|
|
@ -118,26 +118,11 @@ func LastSegment(input string, roles []RuneRole) string {
|
|||
return input[start+1 : end+1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fromChunks copies string chunks into the given buffer.
|
||||
func fromChunks(chunks []string, buffer []byte) []byte {
|
||||
ii := 0
|
||||
for _, chunk := range chunks {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(chunk); i++ {
|
||||
if ii >= cap(buffer) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
buffer[ii] = chunk[i]
|
||||
ii++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buffer[:ii]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// toLower transforms the input string to lower case, which is stored in the output byte slice.
|
||||
// ToLower transforms the input string to lower case, which is stored in the output byte slice.
|
||||
// The lower casing considers only ASCII values - non ASCII values are left unmodified.
|
||||
// Stops when parsed all input or when it filled the output slice. If output is nil, then it gets
|
||||
// created.
|
||||
func toLower(input []byte, reuse []byte) []byte {
|
||||
func ToLower(input string, reuse []byte) []byte {
|
||||
output := reuse
|
||||
if cap(reuse) < len(input) {
|
||||
output = make([]byte, len(input))
|
||||
|
|
@ -145,7 +130,7 @@ func toLower(input []byte, reuse []byte) []byte {
|
|||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(input); i++ {
|
||||
r := rune(input[i])
|
||||
if input[i] <= unicode.MaxASCII {
|
||||
if r <= unicode.MaxASCII {
|
||||
if 'A' <= r && r <= 'Z' {
|
||||
r += 'a' - 'A'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -51,12 +51,8 @@ type Matcher struct {
|
|||
lastCandidateLen int // in bytes
|
||||
lastCandidateMatched bool
|
||||
|
||||
// Reusable buffers to avoid allocating for every candidate.
|
||||
// - inputBuf stores the concatenated input chunks
|
||||
// - lowerBuf stores the last candidate in lower-case
|
||||
// - rolesBuf stores the calculated roles for each rune in the last
|
||||
// candidate.
|
||||
inputBuf [MaxInputSize]byte
|
||||
// Here we save the last candidate in lower-case. This is basically a byte slice we reuse for
|
||||
// performance reasons, so the slice is not reallocated for every candidate.
|
||||
lowerBuf [MaxInputSize]byte
|
||||
rolesBuf [MaxInputSize]RuneRole
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -76,7 +72,7 @@ func NewMatcher(pattern string) *Matcher {
|
|||
|
||||
m := &Matcher{
|
||||
pattern: pattern,
|
||||
patternLower: toLower([]byte(pattern), nil),
|
||||
patternLower: ToLower(pattern, nil),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i, c := range m.patternLower {
|
||||
|
|
@ -92,7 +88,7 @@ func NewMatcher(pattern string) *Matcher {
|
|||
m.patternShort = m.patternLower
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
m.patternRoles = RuneRoles([]byte(pattern), nil)
|
||||
m.patternRoles = RuneRoles(pattern, nil)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(pattern) > 0 {
|
||||
maxCharScore := 4
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,15 +102,10 @@ func NewMatcher(pattern string) *Matcher {
|
|||
// This is not designed for parallel use. Multiple candidates must be scored sequentially.
|
||||
// Returns a score between 0 and 1 (0 - no match, 1 - perfect match).
|
||||
func (m *Matcher) Score(candidate string) float32 {
|
||||
return m.ScoreChunks([]string{candidate})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Matcher) ScoreChunks(chunks []string) float32 {
|
||||
candidate := fromChunks(chunks, m.inputBuf[:])
|
||||
if len(candidate) > MaxInputSize {
|
||||
candidate = candidate[:MaxInputSize]
|
||||
}
|
||||
lower := toLower(candidate, m.lowerBuf[:])
|
||||
lower := ToLower(candidate, m.lowerBuf[:])
|
||||
m.lastCandidateLen = len(candidate)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(m.pattern) == 0 {
|
||||
|
|
@ -183,7 +174,7 @@ func (m *Matcher) MatchedRanges() []int {
|
|||
return ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Matcher) match(candidate []byte, candidateLower []byte) bool {
|
||||
func (m *Matcher) match(candidate string, candidateLower []byte) bool {
|
||||
i, j := 0, 0
|
||||
for ; i < len(candidateLower) && j < len(m.patternLower); i++ {
|
||||
if candidateLower[i] == m.patternLower[j] {
|
||||
|
|
@ -201,7 +192,7 @@ func (m *Matcher) match(candidate []byte, candidateLower []byte) bool {
|
|||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Matcher) computeScore(candidate []byte, candidateLower []byte) int {
|
||||
func (m *Matcher) computeScore(candidate string, candidateLower []byte) int {
|
||||
pattLen, candLen := len(m.pattern), len(candidate)
|
||||
|
||||
for j := 0; j <= len(m.pattern); j++ {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,236 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package fuzzy
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SymbolMatcher implements a fuzzy matching algorithm optimized for Go symbols
|
||||
// of the form:
|
||||
// example.com/path/to/package.object.field
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Knowing that we are matching symbols like this allows us to make the
|
||||
// following optimizations:
|
||||
// - We can incorporate right-to-left relevance directly into the score
|
||||
// calculation.
|
||||
// - We can match from right to left, discarding leading bytes if the input is
|
||||
// too long.
|
||||
// - We just take the right-most match without losing too much precision. This
|
||||
// allows us to use an O(n) algorithm.
|
||||
// - We can operate directly on chunked strings; in many cases we will
|
||||
// be storing the package path and/or package name separately from the
|
||||
// symbol or identifiers, so doing this avoids allocating strings.
|
||||
// - We can return the index of the right-most match, allowing us to trim
|
||||
// irrelevant qualification.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This implementation is experimental, serving as a reference fast algorithm
|
||||
// to compare to the fuzzy algorithm implemented by Matcher.
|
||||
type SymbolMatcher struct {
|
||||
// Using buffers of length 256 is both a reasonable size for most qualified
|
||||
// symbols, and makes it easy to avoid bounds checks by using uint8 indexes.
|
||||
pattern [256]rune
|
||||
patternLen uint8
|
||||
inputBuffer [256]rune // avoid allocating when considering chunks
|
||||
roles [256]uint32 // which roles does a rune play (word start, etc.)
|
||||
segments [256]uint8 // how many segments from the right is each rune
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
segmentStart uint32 = 1 << iota
|
||||
wordStart
|
||||
separator
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// NewSymbolMatcher creates a SymbolMatcher that may be used to match the given
|
||||
// search pattern.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Currently this matcher only accepts case-insensitive fuzzy patterns.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// An empty pattern matches no input.
|
||||
func NewSymbolMatcher(pattern string) *SymbolMatcher {
|
||||
m := &SymbolMatcher{}
|
||||
for _, p := range pattern {
|
||||
m.pattern[m.patternLen] = unicode.ToLower(p)
|
||||
m.patternLen++
|
||||
if m.patternLen == 255 || int(m.patternLen) == len(pattern) {
|
||||
// break at 255 so that we can represent patternLen with a uint8.
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Match looks for the right-most match of the search pattern within the symbol
|
||||
// represented by concatenating the given chunks, returning its offset and
|
||||
// score.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If a match is found, the first return value will hold the absolute byte
|
||||
// offset within all chunks for the start of the symbol. In other words, the
|
||||
// index of the match within strings.Join(chunks, ""). If no match is found,
|
||||
// the first return value will be -1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The second return value will be the score of the match, which is always
|
||||
// between 0 and 1, inclusive. A score of 0 indicates no match.
|
||||
func (m *SymbolMatcher) Match(chunks []string) (int, float64) {
|
||||
// Explicit behavior for an empty pattern.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// As a minor optimization, this also avoids nilness checks later on, since
|
||||
// the compiler can prove that m != nil.
|
||||
if m.patternLen == 0 {
|
||||
return -1, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// First phase: populate the input buffer with lower-cased runes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We could also check for a forward match here, but since we'd have to write
|
||||
// the entire input anyway this has negligible impact on performance.
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
inputLen = uint8(0)
|
||||
modifiers = wordStart | segmentStart
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
input:
|
||||
for _, chunk := range chunks {
|
||||
for _, r := range chunk {
|
||||
if r == '.' || r == '/' {
|
||||
modifiers |= separator
|
||||
}
|
||||
// optimization: avoid calls to unicode.ToLower, which can't be inlined.
|
||||
l := r
|
||||
if r <= unicode.MaxASCII {
|
||||
if 'A' <= r && r <= 'Z' {
|
||||
l = r + 'a' - 'A'
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
l = unicode.ToLower(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if l != r {
|
||||
modifiers |= wordStart
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.inputBuffer[inputLen] = l
|
||||
m.roles[inputLen] = modifiers
|
||||
inputLen++
|
||||
if m.roles[inputLen-1]&separator != 0 {
|
||||
modifiers = wordStart | segmentStart
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
modifiers = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO: we should prefer the right-most input if it overflows, rather
|
||||
// than the left-most as we're doing here.
|
||||
if inputLen == 255 {
|
||||
break input
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Second phase: find the right-most match, and count segments from the
|
||||
// right.
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
pi = uint8(m.patternLen - 1) // pattern index
|
||||
p = m.pattern[pi] // pattern rune
|
||||
start = -1 // start offset of match
|
||||
rseg = uint8(0)
|
||||
)
|
||||
const maxSeg = 3 // maximum number of segments from the right to count, for scoring purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
for ii := inputLen - 1; ; ii-- {
|
||||
r := m.inputBuffer[ii]
|
||||
if rseg < maxSeg && m.roles[ii]&separator != 0 {
|
||||
rseg++
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.segments[ii] = rseg
|
||||
if p == r {
|
||||
if pi == 0 {
|
||||
start = int(ii)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
pi--
|
||||
p = m.pattern[pi]
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Don't check ii >= 0 in the loop condition: ii is a uint8.
|
||||
if ii == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if start < 0 {
|
||||
// no match: skip scoring
|
||||
return -1, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Third phase: find the shortest match, and compute the score.
|
||||
|
||||
// Score is the average score for each character.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A character score is the multiple of:
|
||||
// 1. 1.0 if the character starts a segment, .8 if the character start a
|
||||
// mid-segment word, otherwise 0.6. This carries over to immediately
|
||||
// following characters.
|
||||
// 2. For the final character match, the multiplier from (1) is reduced to
|
||||
// .8 if the next character in the input is a mid-segment word, or 0.6 if
|
||||
// the next character in the input is not a word or segment start. This
|
||||
// ensures that we favor whole-word or whole-segment matches over prefix
|
||||
// matches.
|
||||
// 3. 1.0 if the character is part of the last segment, otherwise
|
||||
// 1.0-.2*<segments from the right>, with a max segment count of 3.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a very naive algorithm, but it is fast. There's lots of prior art
|
||||
// here, and we should leverage it. For example, we could explicitly consider
|
||||
// character distance, and exact matches of words or segments.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Also note that this might not actually find the highest scoring match, as
|
||||
// doing so could require a non-linear algorithm, depending on how the score
|
||||
// is calculated.
|
||||
|
||||
pi = 0
|
||||
p = m.pattern[pi]
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
segStreak = 1.0
|
||||
wordStreak = 0.8
|
||||
noStreak = 0.6
|
||||
perSegment = 0.2 // we count at most 3 segments above
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
streakBonus := noStreak
|
||||
totScore := 0.0
|
||||
for ii := uint8(start); ii < inputLen; ii++ {
|
||||
r := m.inputBuffer[ii]
|
||||
if r == p {
|
||||
pi++
|
||||
p = m.pattern[pi]
|
||||
// Note: this could be optimized with some bit operations.
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case m.roles[ii]&segmentStart != 0 && segStreak > streakBonus:
|
||||
streakBonus = segStreak
|
||||
case m.roles[ii]&wordStart != 0 && wordStreak > streakBonus:
|
||||
streakBonus = wordStreak
|
||||
}
|
||||
finalChar := pi >= m.patternLen
|
||||
// finalCost := 1.0
|
||||
if finalChar && streakBonus > noStreak {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case ii == inputLen-1 || m.roles[ii+1]&segmentStart != 0:
|
||||
// Full segment: no reduction
|
||||
case m.roles[ii+1]&wordStart != 0:
|
||||
streakBonus = wordStreak
|
||||
default:
|
||||
streakBonus = noStreak
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
totScore += streakBonus * (1.0 - float64(m.segments[ii])*perSegment)
|
||||
if finalChar {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
streakBonus = noStreak
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return start, totScore / float64(m.patternLen)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package typeparams contains common utilities for writing tools that interact
|
||||
// with generic Go code, as introduced with Go 1.18.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Many of the types and functions in this package are proxies for the new APIs
|
||||
// introduced in the standard library with Go 1.18. For example, the
|
||||
// typeparams.Union type is an alias for go/types.Union, and the ForTypeSpec
|
||||
// function returns the value of the go/ast.TypeSpec.TypeParams field. At Go
|
||||
// versions older than 1.18 these helpers are implemented as stubs, allowing
|
||||
// users of this package to write code that handles generic constructs inline,
|
||||
// even if the Go version being used to compile does not support generics.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Additionally, this package contains common utilities for working with the
|
||||
// new generic constructs, to supplement the standard library APIs. Notably,
|
||||
// the StructuralTerms API computes a minimal representation of the structural
|
||||
// restrictions on a type parameter. In the future, this API may be available
|
||||
// from go/types.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See the example/README.md for a more detailed guide on how to update tools
|
||||
// to support generics.
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// UnpackIndexExpr extracts data from AST nodes that represent index
|
||||
// expressions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For an ast.IndexExpr, the resulting indices slice will contain exactly one
|
||||
// index expression. For an ast.IndexListExpr (go1.18+), it may have a variable
|
||||
// number of index expressions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For nodes that don't represent index expressions, the first return value of
|
||||
// UnpackIndexExpr will be nil.
|
||||
func UnpackIndexExpr(n ast.Node) (x ast.Expr, lbrack token.Pos, indices []ast.Expr, rbrack token.Pos) {
|
||||
switch e := n.(type) {
|
||||
case *ast.IndexExpr:
|
||||
return e.X, e.Lbrack, []ast.Expr{e.Index}, e.Rbrack
|
||||
case *IndexListExpr:
|
||||
return e.X, e.Lbrack, e.Indices, e.Rbrack
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, token.NoPos, nil, token.NoPos
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PackIndexExpr returns an *ast.IndexExpr or *ast.IndexListExpr, depending on
|
||||
// the cardinality of indices. Calling PackIndexExpr with len(indices) == 0
|
||||
// will panic.
|
||||
func PackIndexExpr(x ast.Expr, lbrack token.Pos, indices []ast.Expr, rbrack token.Pos) ast.Expr {
|
||||
switch len(indices) {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
panic("empty indices")
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
return &ast.IndexExpr{
|
||||
X: x,
|
||||
Lbrack: lbrack,
|
||||
Index: indices[0],
|
||||
Rbrack: rbrack,
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return &IndexListExpr{
|
||||
X: x,
|
||||
Lbrack: lbrack,
|
||||
Indices: indices,
|
||||
Rbrack: rbrack,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsTypeParam reports whether t is a type parameter.
|
||||
func IsTypeParam(t types.Type) bool {
|
||||
_, ok := t.(*TypeParam)
|
||||
return ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package typeparams provides functions to work indirectly with type parameter
|
||||
// data stored in go/ast and go/types objects, while these API are guarded by a
|
||||
// build constraint.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This package exists to make it easier for tools to work with generic code,
|
||||
// while also compiling against older Go versions.
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build !go1.18
|
||||
// +build !go1.18
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
// Enabled reports whether type parameters are enabled in the current build
|
||||
// environment.
|
||||
const Enabled = false
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build go1.18
|
||||
// +build go1.18
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
// Note: this constant is in a separate file as this is the only acceptable
|
||||
// diff between the <1.18 API of this package and the 1.18 API.
|
||||
|
||||
// Enabled reports whether type parameters are enabled in the current build
|
||||
// environment.
|
||||
const Enabled = true
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,216 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
//go:generate go run copytermlist.go
|
||||
|
||||
const debug = false
|
||||
|
||||
var ErrEmptyTypeSet = errors.New("empty type set")
|
||||
|
||||
// StructuralTerms returns a slice of terms representing the normalized
|
||||
// structural type restrictions of a type parameter, if any.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Structural type restrictions of a type parameter are created via
|
||||
// non-interface types embedded in its constraint interface (directly, or via a
|
||||
// chain of interface embeddings). For example, in the declaration
|
||||
// type T[P interface{~int; m()}] int
|
||||
// the structural restriction of the type parameter P is ~int.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With interface embedding and unions, the specification of structural type
|
||||
// restrictions may be arbitrarily complex. For example, consider the
|
||||
// following:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type A interface{ ~string|~[]byte }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type B interface{ int|string }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type C interface { ~string|~int }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type T[P interface{ A|B; C }] int
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In this example, the structural type restriction of P is ~string|int: A|B
|
||||
// expands to ~string|~[]byte|int|string, which reduces to ~string|~[]byte|int,
|
||||
// which when intersected with C (~string|~int) yields ~string|int.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// StructuralTerms computes these expansions and reductions, producing a
|
||||
// "normalized" form of the embeddings. A structural restriction is normalized
|
||||
// if it is a single union containing no interface terms, and is minimal in the
|
||||
// sense that removing any term changes the set of types satisfying the
|
||||
// constraint. It is left as a proof for the reader that, modulo sorting, there
|
||||
// is exactly one such normalized form.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because the minimal representation always takes this form, StructuralTerms
|
||||
// returns a slice of tilde terms corresponding to the terms of the union in
|
||||
// the normalized structural restriction. An error is returned if the
|
||||
// constraint interface is invalid, exceeds complexity bounds, or has an empty
|
||||
// type set. In the latter case, StructuralTerms returns ErrEmptyTypeSet.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// StructuralTerms makes no guarantees about the order of terms, except that it
|
||||
// is deterministic.
|
||||
func StructuralTerms(tparam *TypeParam) ([]*Term, error) {
|
||||
constraint := tparam.Constraint()
|
||||
if constraint == nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s has nil constraint", tparam)
|
||||
}
|
||||
iface, _ := constraint.Underlying().(*types.Interface)
|
||||
if iface == nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("constraint is %T, not *types.Interface", constraint.Underlying())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return InterfaceTermSet(iface)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InterfaceTermSet computes the normalized terms for a constraint interface,
|
||||
// returning an error if the term set cannot be computed or is empty. In the
|
||||
// latter case, the error will be ErrEmptyTypeSet.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See the documentation of StructuralTerms for more information on
|
||||
// normalization.
|
||||
func InterfaceTermSet(iface *types.Interface) ([]*Term, error) {
|
||||
return computeTermSet(iface)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnionTermSet computes the normalized terms for a union, returning an error
|
||||
// if the term set cannot be computed or is empty. In the latter case, the
|
||||
// error will be ErrEmptyTypeSet.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See the documentation of StructuralTerms for more information on
|
||||
// normalization.
|
||||
func UnionTermSet(union *Union) ([]*Term, error) {
|
||||
return computeTermSet(union)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func computeTermSet(typ types.Type) ([]*Term, error) {
|
||||
tset, err := computeTermSetInternal(typ, make(map[types.Type]*termSet), 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tset.terms.isEmpty() {
|
||||
return nil, ErrEmptyTypeSet
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tset.terms.isAll() {
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
var terms []*Term
|
||||
for _, term := range tset.terms {
|
||||
terms = append(terms, NewTerm(term.tilde, term.typ))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return terms, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A termSet holds the normalized set of terms for a given type.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The name termSet is intentionally distinct from 'type set': a type set is
|
||||
// all types that implement a type (and includes method restrictions), whereas
|
||||
// a term set just represents the structural restrictions on a type.
|
||||
type termSet struct {
|
||||
complete bool
|
||||
terms termlist
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func indentf(depth int, format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, strings.Repeat(".", depth)+format+"\n", args...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func computeTermSetInternal(t types.Type, seen map[types.Type]*termSet, depth int) (res *termSet, err error) {
|
||||
if t == nil {
|
||||
panic("nil type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if debug {
|
||||
indentf(depth, "%s", t.String())
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
indentf(depth, "=> %s", err)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
indentf(depth, "=> %s", res.terms.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const maxTermCount = 100
|
||||
if tset, ok := seen[t]; ok {
|
||||
if !tset.complete {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cycle detected in the declaration of %s", t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return tset, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Mark the current type as seen to avoid infinite recursion.
|
||||
tset := new(termSet)
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
tset.complete = true
|
||||
}()
|
||||
seen[t] = tset
|
||||
|
||||
switch u := t.Underlying().(type) {
|
||||
case *types.Interface:
|
||||
// The term set of an interface is the intersection of the term sets of its
|
||||
// embedded types.
|
||||
tset.terms = allTermlist
|
||||
for i := 0; i < u.NumEmbeddeds(); i++ {
|
||||
embedded := u.EmbeddedType(i)
|
||||
if _, ok := embedded.Underlying().(*TypeParam); ok {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid embedded type %T", embedded)
|
||||
}
|
||||
tset2, err := computeTermSetInternal(embedded, seen, depth+1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
tset.terms = tset.terms.intersect(tset2.terms)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *Union:
|
||||
// The term set of a union is the union of term sets of its terms.
|
||||
tset.terms = nil
|
||||
for i := 0; i < u.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
t := u.Term(i)
|
||||
var terms termlist
|
||||
switch t.Type().Underlying().(type) {
|
||||
case *types.Interface:
|
||||
tset2, err := computeTermSetInternal(t.Type(), seen, depth+1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
terms = tset2.terms
|
||||
case *TypeParam, *Union:
|
||||
// A stand-alone type parameter or union is not permitted as union
|
||||
// term.
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid union term %T", t)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if t.Type() == types.Typ[types.Invalid] {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
terms = termlist{{t.Tilde(), t.Type()}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
tset.terms = tset.terms.union(terms)
|
||||
if len(tset.terms) > maxTermCount {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("exceeded max term count %d", maxTermCount)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *TypeParam:
|
||||
panic("unreachable")
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// For all other types, the term set is just a single non-tilde term
|
||||
// holding the type itself.
|
||||
if u != types.Typ[types.Invalid] {
|
||||
tset.terms = termlist{{false, t}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return tset, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// under is a facade for the go/types internal function of the same name. It is
|
||||
// used by typeterm.go.
|
||||
func under(t types.Type) types.Type {
|
||||
return t.Underlying()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build !typeparams || !go1.17
|
||||
// +build !typeparams !go1.17
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// NOTE: doc comments must be kept in sync with typeparams.go.
|
||||
|
||||
// Enabled reports whether type parameters are enabled in the current build
|
||||
// environment.
|
||||
const Enabled = false
|
||||
|
||||
// UnpackIndex extracts all index expressions from e. For non-generic code this
|
||||
// is always one expression: e.Index, but may be more than one expression for
|
||||
// generic type instantiation.
|
||||
func UnpackIndex(e *ast.IndexExpr) []ast.Expr {
|
||||
return []ast.Expr{e.Index}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsListExpr reports whether n is an *ast.ListExpr, which is a new node type
|
||||
// introduced to hold type arguments for generic type instantiation.
|
||||
func IsListExpr(n ast.Node) bool {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForTypeDecl extracts the (possibly nil) type parameter node list from n.
|
||||
func ForTypeDecl(*ast.TypeSpec) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForFuncDecl extracts the (possibly nil) type parameter node list from n.
|
||||
func ForFuncDecl(*ast.FuncDecl) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForSignature extracts the (possibly empty) type parameter object list from
|
||||
// sig.
|
||||
func ForSignature(*types.Signature) []*types.TypeName {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasTypeSet reports if iface has a type set.
|
||||
func HasTypeSet(*types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsComparable reports if iface is the comparable interface.
|
||||
func IsComparable(*types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsConstraint reports whether iface may only be used as a type parameter
|
||||
// constraint (i.e. has a type set or is the comparable interface).
|
||||
func IsConstraint(*types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForNamed extracts the (possibly empty) type parameter object list from
|
||||
// named.
|
||||
func ForNamed(*types.Named) []*types.TypeName {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NamedTArgs extracts the (possibly empty) type argument list from named.
|
||||
func NamedTArgs(*types.Named) []types.Type {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InitInferred initializes info to record inferred type information.
|
||||
func InitInferred(*types.Info) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetInferred extracts inferred type information from info for e.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The expression e may have an inferred type if it is an *ast.IndexExpr
|
||||
// representing partial instantiation of a generic function type for which type
|
||||
// arguments have been inferred using constraint type inference, or if it is an
|
||||
// *ast.CallExpr for which type type arguments have be inferred using both
|
||||
// constraint type inference and function argument inference.
|
||||
func GetInferred(*types.Info, ast.Expr) ([]types.Type, *types.Signature) {
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Code generated by copytermlist.go DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A termlist represents the type set represented by the union
|
||||
// t1 ∪ y2 ∪ ... tn of the type sets of the terms t1 to tn.
|
||||
// A termlist is in normal form if all terms are disjoint.
|
||||
// termlist operations don't require the operands to be in
|
||||
// normal form.
|
||||
type termlist []*term
|
||||
|
||||
// allTermlist represents the set of all types.
|
||||
// It is in normal form.
|
||||
var allTermlist = termlist{new(term)}
|
||||
|
||||
// String prints the termlist exactly (without normalization).
|
||||
func (xl termlist) String() string {
|
||||
if len(xl) == 0 {
|
||||
return "∅"
|
||||
}
|
||||
var buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
for i, x := range xl {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
buf.WriteString(" ∪ ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf.WriteString(x.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isEmpty reports whether the termlist xl represents the empty set of types.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) isEmpty() bool {
|
||||
// If there's a non-nil term, the entire list is not empty.
|
||||
// If the termlist is in normal form, this requires at most
|
||||
// one iteration.
|
||||
for _, x := range xl {
|
||||
if x != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isAll reports whether the termlist xl represents the set of all types.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) isAll() bool {
|
||||
// If there's a 𝓤 term, the entire list is 𝓤.
|
||||
// If the termlist is in normal form, this requires at most
|
||||
// one iteration.
|
||||
for _, x := range xl {
|
||||
if x != nil && x.typ == nil {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// norm returns the normal form of xl.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) norm() termlist {
|
||||
// Quadratic algorithm, but good enough for now.
|
||||
// TODO(gri) fix asymptotic performance
|
||||
used := make([]bool, len(xl))
|
||||
var rl termlist
|
||||
for i, xi := range xl {
|
||||
if xi == nil || used[i] {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j := i + 1; j < len(xl); j++ {
|
||||
xj := xl[j]
|
||||
if xj == nil || used[j] {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if u1, u2 := xi.union(xj); u2 == nil {
|
||||
// If we encounter a 𝓤 term, the entire list is 𝓤.
|
||||
// Exit early.
|
||||
// (Note that this is not just an optimization;
|
||||
// if we continue, we may end up with a 𝓤 term
|
||||
// and other terms and the result would not be
|
||||
// in normal form.)
|
||||
if u1.typ == nil {
|
||||
return allTermlist
|
||||
}
|
||||
xi = u1
|
||||
used[j] = true // xj is now unioned into xi - ignore it in future iterations
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
rl = append(rl, xi)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return rl
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If the type set represented by xl is specified by a single (non-𝓤) term,
|
||||
// structuralType returns that type. Otherwise it returns nil.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) structuralType() types.Type {
|
||||
if nl := xl.norm(); len(nl) == 1 {
|
||||
return nl[0].typ // if nl.isAll() then typ is nil, which is ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// union returns the union xl ∪ yl.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) union(yl termlist) termlist {
|
||||
return append(xl, yl...).norm()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// intersect returns the intersection xl ∩ yl.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) intersect(yl termlist) termlist {
|
||||
if xl.isEmpty() || yl.isEmpty() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Quadratic algorithm, but good enough for now.
|
||||
// TODO(gri) fix asymptotic performance
|
||||
var rl termlist
|
||||
for _, x := range xl {
|
||||
for _, y := range yl {
|
||||
if r := x.intersect(y); r != nil {
|
||||
rl = append(rl, r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return rl.norm()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// equal reports whether xl and yl represent the same type set.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) equal(yl termlist) bool {
|
||||
// TODO(gri) this should be more efficient
|
||||
return xl.subsetOf(yl) && yl.subsetOf(xl)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// includes reports whether t ∈ xl.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) includes(t types.Type) bool {
|
||||
for _, x := range xl {
|
||||
if x.includes(t) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// supersetOf reports whether y ⊆ xl.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) supersetOf(y *term) bool {
|
||||
for _, x := range xl {
|
||||
if y.subsetOf(x) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// subsetOf reports whether xl ⊆ yl.
|
||||
func (xl termlist) subsetOf(yl termlist) bool {
|
||||
if yl.isEmpty() {
|
||||
return xl.isEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// each term x of xl must be a subset of yl
|
||||
for _, x := range xl {
|
||||
if !yl.supersetOf(x) {
|
||||
return false // x is not a subset yl
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build typeparams && go1.17
|
||||
// +build typeparams,go1.17
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// NOTE: doc comments must be kept in sync with notypeparams.go.
|
||||
|
||||
// Enabled reports whether type parameters are enabled in the current build
|
||||
// environment.
|
||||
const Enabled = true
|
||||
|
||||
// UnpackIndex extracts all index expressions from e. For non-generic code this
|
||||
// is always one expression: e.Index, but may be more than one expression for
|
||||
// generic type instantiation.
|
||||
func UnpackIndex(e *ast.IndexExpr) []ast.Expr {
|
||||
if x, _ := e.Index.(*ast.ListExpr); x != nil {
|
||||
return x.ElemList
|
||||
}
|
||||
if e.Index != nil {
|
||||
return []ast.Expr{e.Index}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsListExpr reports whether n is an *ast.ListExpr, which is a new node type
|
||||
// introduced to hold type arguments for generic type instantiation.
|
||||
func IsListExpr(n ast.Node) bool {
|
||||
_, ok := n.(*ast.ListExpr)
|
||||
return ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForTypeDecl extracts the (possibly nil) type parameter node list from n.
|
||||
func ForTypeDecl(n *ast.TypeSpec) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
return n.TParams
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForFuncDecl extracts the (possibly nil) type parameter node list from n.
|
||||
func ForFuncDecl(n *ast.FuncDecl) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
if n.Type != nil {
|
||||
return n.Type.TParams
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForSignature extracts the (possibly empty) type parameter object list from
|
||||
// sig.
|
||||
func ForSignature(sig *types.Signature) []*types.TypeName {
|
||||
return sig.TParams()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasTypeSet reports if iface has a type set.
|
||||
func HasTypeSet(iface *types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return iface.HasTypeList()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsComparable reports if iface is the comparable interface.
|
||||
func IsComparable(iface *types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return iface.IsComparable()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsConstraint reports whether iface may only be used as a type parameter
|
||||
// constraint (i.e. has a type set or is the comparable interface).
|
||||
func IsConstraint(iface *types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return iface.IsConstraint()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForNamed extracts the (possibly empty) type parameter object list from
|
||||
// named.
|
||||
func ForNamed(named *types.Named) []*types.TypeName {
|
||||
return named.TParams()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NamedTArgs extracts the (possibly empty) type argument list from named.
|
||||
func NamedTArgs(named *types.Named) []types.Type {
|
||||
return named.TArgs()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InitInferred initializes info to record inferred type information.
|
||||
func InitInferred(info *types.Info) {
|
||||
info.Inferred = make(map[ast.Expr]types.Inferred)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetInferred extracts inferred type information from info for e.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The expression e may have an inferred type if it is an *ast.IndexExpr
|
||||
// representing partial instantiation of a generic function type for which type
|
||||
// arguments have been inferred using constraint type inference, or if it is an
|
||||
// *ast.CallExpr for which type type arguments have be inferred using both
|
||||
// constraint type inference and function argument inference.
|
||||
func GetInferred(info *types.Info, e ast.Expr) ([]types.Type, *types.Signature) {
|
||||
if info.Inferred == nil {
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
inf := info.Inferred[e]
|
||||
return inf.TArgs, inf.Sig
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,192 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build !go1.18
|
||||
// +build !go1.18
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func unsupported() {
|
||||
panic("type parameters are unsupported at this go version")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IndexListExpr is a placeholder type, as type parameters are not supported at
|
||||
// this Go version. Its methods panic on use.
|
||||
type IndexListExpr struct {
|
||||
ast.Expr
|
||||
X ast.Expr // expression
|
||||
Lbrack token.Pos // position of "["
|
||||
Indices []ast.Expr // index expressions
|
||||
Rbrack token.Pos // position of "]"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForTypeSpec returns an empty field list, as type parameters on not supported
|
||||
// at this Go version.
|
||||
func ForTypeSpec(*ast.TypeSpec) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForFuncType returns an empty field list, as type parameters are not
|
||||
// supported at this Go version.
|
||||
func ForFuncType(*ast.FuncType) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TypeParam is a placeholder type, as type parameters are not supported at
|
||||
// this Go version. Its methods panic on use.
|
||||
type TypeParam struct{ types.Type }
|
||||
|
||||
func (*TypeParam) Index() int { unsupported(); return 0 }
|
||||
func (*TypeParam) Constraint() types.Type { unsupported(); return nil }
|
||||
func (*TypeParam) Obj() *types.TypeName { unsupported(); return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
// TypeParamList is a placeholder for an empty type parameter list.
|
||||
type TypeParamList struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (*TypeParamList) Len() int { return 0 }
|
||||
func (*TypeParamList) At(int) *TypeParam { unsupported(); return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
// TypeList is a placeholder for an empty type list.
|
||||
type TypeList struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (*TypeList) Len() int { return 0 }
|
||||
func (*TypeList) At(int) types.Type { unsupported(); return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTypeParam is unsupported at this Go version, and panics.
|
||||
func NewTypeParam(name *types.TypeName, constraint types.Type) *TypeParam {
|
||||
unsupported()
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTypeParamConstraint is unsupported at this Go version, and panics.
|
||||
func SetTypeParamConstraint(tparam *TypeParam, constraint types.Type) {
|
||||
unsupported()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewSignatureType calls types.NewSignature, panicking if recvTypeParams or
|
||||
// typeParams is non-empty.
|
||||
func NewSignatureType(recv *types.Var, recvTypeParams, typeParams []*TypeParam, params, results *types.Tuple, variadic bool) *types.Signature {
|
||||
if len(recvTypeParams) != 0 || len(typeParams) != 0 {
|
||||
panic("signatures cannot have type parameters at this Go version")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return types.NewSignature(recv, params, results, variadic)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForSignature returns an empty slice.
|
||||
func ForSignature(*types.Signature) *TypeParamList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RecvTypeParams returns a nil slice.
|
||||
func RecvTypeParams(sig *types.Signature) *TypeParamList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsComparable returns false, as no interfaces are type-restricted at this Go
|
||||
// version.
|
||||
func IsComparable(*types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsMethodSet returns true, as no interfaces are type-restricted at this Go
|
||||
// version.
|
||||
func IsMethodSet(*types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsImplicit returns false, as no interfaces are implicit at this Go version.
|
||||
func IsImplicit(*types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarkImplicit does nothing, because this Go version does not have implicit
|
||||
// interfaces.
|
||||
func MarkImplicit(*types.Interface) {}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForNamed returns an empty type parameter list, as type parameters are not
|
||||
// supported at this Go version.
|
||||
func ForNamed(*types.Named) *TypeParamList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetForNamed panics if tparams is non-empty.
|
||||
func SetForNamed(_ *types.Named, tparams []*TypeParam) {
|
||||
if len(tparams) > 0 {
|
||||
unsupported()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NamedTypeArgs returns nil.
|
||||
func NamedTypeArgs(*types.Named) *TypeList {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NamedTypeOrigin is the identity method at this Go version.
|
||||
func NamedTypeOrigin(named *types.Named) types.Type {
|
||||
return named
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Term holds information about a structural type restriction.
|
||||
type Term struct {
|
||||
tilde bool
|
||||
typ types.Type
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Term) Tilde() bool { return m.tilde }
|
||||
func (m *Term) Type() types.Type { return m.typ }
|
||||
func (m *Term) String() string {
|
||||
pre := ""
|
||||
if m.tilde {
|
||||
pre = "~"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pre + m.typ.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTerm is unsupported at this Go version, and panics.
|
||||
func NewTerm(tilde bool, typ types.Type) *Term {
|
||||
return &Term{tilde, typ}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Union is a placeholder type, as type parameters are not supported at this Go
|
||||
// version. Its methods panic on use.
|
||||
type Union struct{ types.Type }
|
||||
|
||||
func (*Union) Len() int { return 0 }
|
||||
func (*Union) Term(i int) *Term { unsupported(); return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
// NewUnion is unsupported at this Go version, and panics.
|
||||
func NewUnion(terms []*Term) *Union {
|
||||
unsupported()
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InitInstanceInfo is a noop at this Go version.
|
||||
func InitInstanceInfo(*types.Info) {}
|
||||
|
||||
// Instance is a placeholder type, as type parameters are not supported at this
|
||||
// Go version.
|
||||
type Instance struct {
|
||||
TypeArgs *TypeList
|
||||
Type types.Type
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetInstances returns a nil map, as type parameters are not supported at this
|
||||
// Go version.
|
||||
func GetInstances(info *types.Info) map[*ast.Ident]Instance { return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
// Context is a placeholder type, as type parameters are not supported at
|
||||
// this Go version.
|
||||
type Context struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Instantiate is unsupported on this Go version, and panics.
|
||||
func Instantiate(ctxt *Context, typ types.Type, targs []types.Type, validate bool) (types.Type, error) {
|
||||
unsupported()
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,146 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
//go:build go1.18
|
||||
// +build go1.18
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"go/types"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// IndexListExpr is an alias for ast.IndexListExpr.
|
||||
type IndexListExpr = ast.IndexListExpr
|
||||
|
||||
// ForTypeSpec returns n.TypeParams.
|
||||
func ForTypeSpec(n *ast.TypeSpec) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n.TypeParams
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForFuncType returns n.TypeParams.
|
||||
func ForFuncType(n *ast.FuncType) *ast.FieldList {
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n.TypeParams
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TypeParam is an alias for types.TypeParam
|
||||
type TypeParam = types.TypeParam
|
||||
|
||||
// TypeParamList is an alias for types.TypeParamList
|
||||
type TypeParamList = types.TypeParamList
|
||||
|
||||
// TypeList is an alias for types.TypeList
|
||||
type TypeList = types.TypeList
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTypeParam calls types.NewTypeParam.
|
||||
func NewTypeParam(name *types.TypeName, constraint types.Type) *TypeParam {
|
||||
return types.NewTypeParam(name, constraint)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTypeParamConstraint calls tparam.SetConstraint(constraint).
|
||||
func SetTypeParamConstraint(tparam *TypeParam, constraint types.Type) {
|
||||
tparam.SetConstraint(constraint)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewSignatureType calls types.NewSignatureType.
|
||||
func NewSignatureType(recv *types.Var, recvTypeParams, typeParams []*TypeParam, params, results *types.Tuple, variadic bool) *types.Signature {
|
||||
return types.NewSignatureType(recv, recvTypeParams, typeParams, params, results, variadic)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForSignature returns sig.TypeParams()
|
||||
func ForSignature(sig *types.Signature) *TypeParamList {
|
||||
return sig.TypeParams()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RecvTypeParams returns sig.RecvTypeParams().
|
||||
func RecvTypeParams(sig *types.Signature) *TypeParamList {
|
||||
return sig.RecvTypeParams()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsComparable calls iface.IsComparable().
|
||||
func IsComparable(iface *types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return iface.IsComparable()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsMethodSet calls iface.IsMethodSet().
|
||||
func IsMethodSet(iface *types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return iface.IsMethodSet()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsImplicit calls iface.IsImplicit().
|
||||
func IsImplicit(iface *types.Interface) bool {
|
||||
return iface.IsImplicit()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarkImplicit calls iface.MarkImplicit().
|
||||
func MarkImplicit(iface *types.Interface) {
|
||||
iface.MarkImplicit()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForNamed extracts the (possibly empty) type parameter object list from
|
||||
// named.
|
||||
func ForNamed(named *types.Named) *TypeParamList {
|
||||
return named.TypeParams()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetForNamed sets the type params tparams on n. Each tparam must be of
|
||||
// dynamic type *types.TypeParam.
|
||||
func SetForNamed(n *types.Named, tparams []*TypeParam) {
|
||||
n.SetTypeParams(tparams)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NamedTypeArgs returns named.TypeArgs().
|
||||
func NamedTypeArgs(named *types.Named) *TypeList {
|
||||
return named.TypeArgs()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NamedTypeOrigin returns named.Orig().
|
||||
func NamedTypeOrigin(named *types.Named) types.Type {
|
||||
return named.Origin()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Term is an alias for types.Term.
|
||||
type Term = types.Term
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTerm calls types.NewTerm.
|
||||
func NewTerm(tilde bool, typ types.Type) *Term {
|
||||
return types.NewTerm(tilde, typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Union is an alias for types.Union
|
||||
type Union = types.Union
|
||||
|
||||
// NewUnion calls types.NewUnion.
|
||||
func NewUnion(terms []*Term) *Union {
|
||||
return types.NewUnion(terms)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InitInstanceInfo initializes info to record information about type and
|
||||
// function instances.
|
||||
func InitInstanceInfo(info *types.Info) {
|
||||
info.Instances = make(map[*ast.Ident]types.Instance)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Instance is an alias for types.Instance.
|
||||
type Instance = types.Instance
|
||||
|
||||
// GetInstances returns info.Instances.
|
||||
func GetInstances(info *types.Info) map[*ast.Ident]Instance {
|
||||
return info.Instances
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Context is an alias for types.Context.
|
||||
type Context = types.Context
|
||||
|
||||
// Instantiate calls types.Instantiate.
|
||||
func Instantiate(ctxt *Context, typ types.Type, targs []types.Type, validate bool) (types.Type, error) {
|
||||
return types.Instantiate(ctxt, typ, targs, validate)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,170 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2021 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Code generated by copytermlist.go DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
package typeparams
|
||||
|
||||
import "go/types"
|
||||
|
||||
// A term describes elementary type sets:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ∅: (*term)(nil) == ∅ // set of no types (empty set)
|
||||
// 𝓤: &term{} == 𝓤 // set of all types (𝓤niverse)
|
||||
// T: &term{false, T} == {T} // set of type T
|
||||
// ~t: &term{true, t} == {t' | under(t') == t} // set of types with underlying type t
|
||||
//
|
||||
type term struct {
|
||||
tilde bool // valid if typ != nil
|
||||
typ types.Type
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (x *term) String() string {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case x == nil:
|
||||
return "∅"
|
||||
case x.typ == nil:
|
||||
return "𝓤"
|
||||
case x.tilde:
|
||||
return "~" + x.typ.String()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return x.typ.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// equal reports whether x and y represent the same type set.
|
||||
func (x *term) equal(y *term) bool {
|
||||
// easy cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case x == nil || y == nil:
|
||||
return x == y
|
||||
case x.typ == nil || y.typ == nil:
|
||||
return x.typ == y.typ
|
||||
}
|
||||
// ∅ ⊂ x, y ⊂ 𝓤
|
||||
|
||||
return x.tilde == y.tilde && types.Identical(x.typ, y.typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// union returns the union x ∪ y: zero, one, or two non-nil terms.
|
||||
func (x *term) union(y *term) (_, _ *term) {
|
||||
// easy cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case x == nil && y == nil:
|
||||
return nil, nil // ∅ ∪ ∅ == ∅
|
||||
case x == nil:
|
||||
return y, nil // ∅ ∪ y == y
|
||||
case y == nil:
|
||||
return x, nil // x ∪ ∅ == x
|
||||
case x.typ == nil:
|
||||
return x, nil // 𝓤 ∪ y == 𝓤
|
||||
case y.typ == nil:
|
||||
return y, nil // x ∪ 𝓤 == 𝓤
|
||||
}
|
||||
// ∅ ⊂ x, y ⊂ 𝓤
|
||||
|
||||
if x.disjoint(y) {
|
||||
return x, y // x ∪ y == (x, y) if x ∩ y == ∅
|
||||
}
|
||||
// x.typ == y.typ
|
||||
|
||||
// ~t ∪ ~t == ~t
|
||||
// ~t ∪ T == ~t
|
||||
// T ∪ ~t == ~t
|
||||
// T ∪ T == T
|
||||
if x.tilde || !y.tilde {
|
||||
return x, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return y, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// intersect returns the intersection x ∩ y.
|
||||
func (x *term) intersect(y *term) *term {
|
||||
// easy cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case x == nil || y == nil:
|
||||
return nil // ∅ ∩ y == ∅ and ∩ ∅ == ∅
|
||||
case x.typ == nil:
|
||||
return y // 𝓤 ∩ y == y
|
||||
case y.typ == nil:
|
||||
return x // x ∩ 𝓤 == x
|
||||
}
|
||||
// ∅ ⊂ x, y ⊂ 𝓤
|
||||
|
||||
if x.disjoint(y) {
|
||||
return nil // x ∩ y == ∅ if x ∩ y == ∅
|
||||
}
|
||||
// x.typ == y.typ
|
||||
|
||||
// ~t ∩ ~t == ~t
|
||||
// ~t ∩ T == T
|
||||
// T ∩ ~t == T
|
||||
// T ∩ T == T
|
||||
if !x.tilde || y.tilde {
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
return y
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// includes reports whether t ∈ x.
|
||||
func (x *term) includes(t types.Type) bool {
|
||||
// easy cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case x == nil:
|
||||
return false // t ∈ ∅ == false
|
||||
case x.typ == nil:
|
||||
return true // t ∈ 𝓤 == true
|
||||
}
|
||||
// ∅ ⊂ x ⊂ 𝓤
|
||||
|
||||
u := t
|
||||
if x.tilde {
|
||||
u = under(u)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return types.Identical(x.typ, u)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// subsetOf reports whether x ⊆ y.
|
||||
func (x *term) subsetOf(y *term) bool {
|
||||
// easy cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case x == nil:
|
||||
return true // ∅ ⊆ y == true
|
||||
case y == nil:
|
||||
return false // x ⊆ ∅ == false since x != ∅
|
||||
case y.typ == nil:
|
||||
return true // x ⊆ 𝓤 == true
|
||||
case x.typ == nil:
|
||||
return false // 𝓤 ⊆ y == false since y != 𝓤
|
||||
}
|
||||
// ∅ ⊂ x, y ⊂ 𝓤
|
||||
|
||||
if x.disjoint(y) {
|
||||
return false // x ⊆ y == false if x ∩ y == ∅
|
||||
}
|
||||
// x.typ == y.typ
|
||||
|
||||
// ~t ⊆ ~t == true
|
||||
// ~t ⊆ T == false
|
||||
// T ⊆ ~t == true
|
||||
// T ⊆ T == true
|
||||
return !x.tilde || y.tilde
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// disjoint reports whether x ∩ y == ∅.
|
||||
// x.typ and y.typ must not be nil.
|
||||
func (x *term) disjoint(y *term) bool {
|
||||
if debug && (x.typ == nil || y.typ == nil) {
|
||||
panic("invalid argument(s)")
|
||||
}
|
||||
ux := x.typ
|
||||
if y.tilde {
|
||||
ux = under(ux)
|
||||
}
|
||||
uy := y.typ
|
||||
if x.tilde {
|
||||
uy = under(uy)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return !types.Identical(ux, uy)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,15 +30,10 @@ func SetUsesCgo(conf *types.Config) bool {
|
|||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadGo116ErrorData extracts additional information from types.Error values
|
||||
// generated by Go version 1.16 and later: the error code, start position, and
|
||||
// end position. If all positions are valid, start <= err.Pos <= end.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the data could not be read, the final result parameter will be false.
|
||||
func ReadGo116ErrorData(err types.Error) (code ErrorCode, start, end token.Pos, ok bool) {
|
||||
func ReadGo116ErrorData(terr types.Error) (ErrorCode, token.Pos, token.Pos, bool) {
|
||||
var data [3]int
|
||||
// By coincidence all of these fields are ints, which simplifies things.
|
||||
v := reflect.ValueOf(err)
|
||||
v := reflect.ValueOf(terr)
|
||||
for i, name := range []string{"go116code", "go116start", "go116end"} {
|
||||
f := v.FieldByName(name)
|
||||
if !f.IsValid() {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -248,9 +248,6 @@ github.com/inconshreveable/mousetrap
|
|||
# github.com/jedisct1/dlog v0.0.0-20210927135244-3381aa132e7f
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.17
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/dlog
|
||||
# github.com/jedisct1/ewma v1.2.1-0.20220220223311-a30af446ecb9
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.12
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/ewma
|
||||
# github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith v0.0.0-20210101121932-da382b963868
|
||||
## explicit
|
||||
github.com/jedisct1/go-clocksmith
|
||||
|
|
@ -306,6 +303,9 @@ github.com/ldez/gomoddirectives
|
|||
# github.com/ldez/tagliatelle v0.2.0
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.16
|
||||
github.com/ldez/tagliatelle
|
||||
# github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma v0.0.0-20210320054258-4f227d7eb8a2
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.16
|
||||
github.com/lifenjoiner/ewma
|
||||
# github.com/magiconair/properties v1.8.1
|
||||
## explicit
|
||||
github.com/magiconair/properties
|
||||
|
|
@ -539,8 +539,8 @@ golang.org/x/crypto/nacl/box
|
|||
golang.org/x/crypto/nacl/secretbox
|
||||
golang.org/x/crypto/poly1305
|
||||
golang.org/x/crypto/salsa20/salsa
|
||||
# golang.org/x/mod v0.5.1
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.17
|
||||
# golang.org/x/mod v0.4.2
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.12
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod/internal/lazyregexp
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod/modfile
|
||||
golang.org/x/mod/module
|
||||
|
|
@ -576,7 +576,7 @@ golang.org/x/text/transform
|
|||
golang.org/x/text/unicode/bidi
|
||||
golang.org/x/text/unicode/norm
|
||||
golang.org/x/text/width
|
||||
# golang.org/x/tools v0.1.9
|
||||
# golang.org/x/tools v0.1.6-0.20210726203631-07bc1bf47fb2
|
||||
## explicit; go 1.17
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/cover
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/analysis
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue